DNA and RNA Structure Study Guide
Introduction
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are nucleic acids that contain genetic information and are read by cells to produce the RNA and proteins that allow living organisms to operate. This genetic information is duplicated and passed on to the next generation thanks to the well-known structure of the DNA, which is a double helix. DNA and RNA nucleotide comprises three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups.
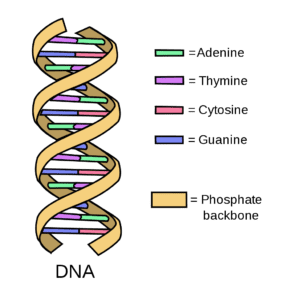
DNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid in cells that serves as the original template for protein creation. Deoxyribose, phosphates, and a unique sequence of nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) make up DNA (T).
DNA Structure
Brief insight into the structure and composition of DNA
- A living entity’s DNA molecules carry the instructions it needs to grow, develop, and reproduce. These instructions are found inside every cell and are passed down from parents to their children.
- It’s made up of nucleotides that have a nitrogenous group, a phosphate group, and a sugar group in them. In establishing the genetic code, the order of the nitrogenous bases thymine(T), guanine(G), cytosine(C), and adenine(A) is critical.
- The arrangement of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the formation of genes, which is important for protein synthesis. Another nucleic acid is RNA, which converts genetic information into proteins.
- The nucleotides are joined together to create two long strands that spiral to form a structure known as a double-helix, which resembles a ladder with the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the sides and the bases forming the rungs.
- As in guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with thymine, the bases on one strand couple up with the other.
- Because DNA molecules are incredibly lengthy, they cannot enter inside cells without the proper packaging. As a result, DNA forms chromosomes, which are tightly coiled structures.
- A single DNA molecule may be found on each chromosome. Within the nucleus of human cells, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes.
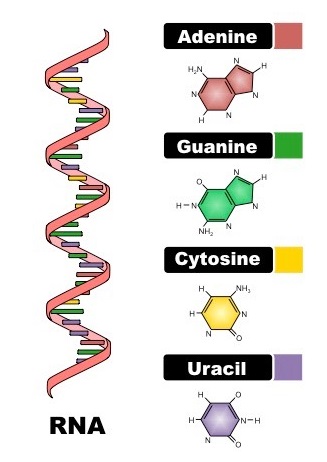
RNA
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a nucleic acid that has a direct role in protein production. Ribonucleic acid is an important nucleotide found in all living cells, with long nucleic acid strands. Its primary function is to act as a messenger, carrying DNA instructions for directing protein synthesis.
RNA Structure
The sugar ribose, phosphates, and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U) are all found in RNA (U). The nitrogenous bases A, G, and C are shared by DNA and RNA. Thymine and uracil are normally exclusively found in DNA and RNA, respectively.
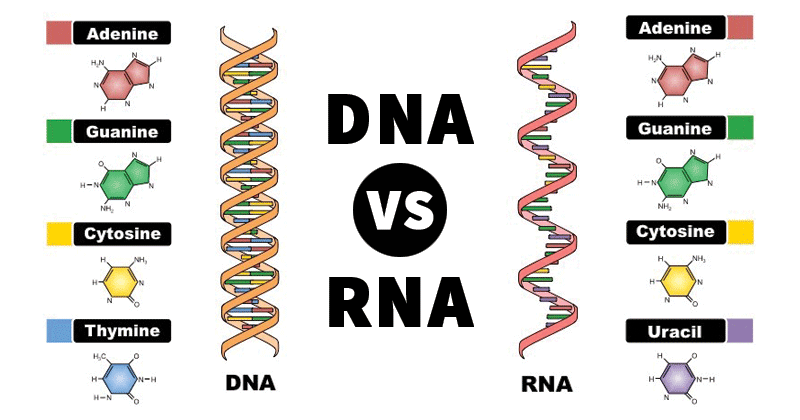
Differences Between DNA and RNA
Following are the important differences between DNA and RNA:
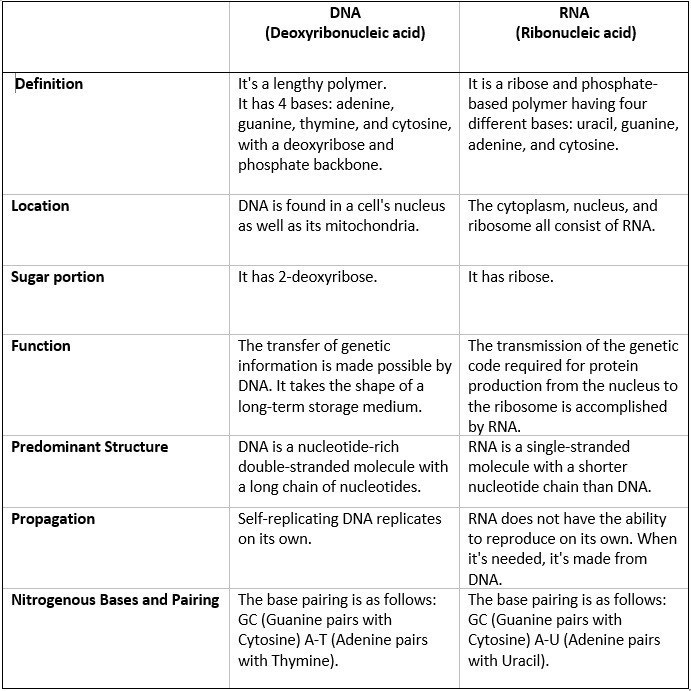
Conclusion:
- DNA and RNA are the two primary forms of nucleic acids.
- Nucleotides, which have a five-carbon sugar backbone, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base, are used to make DNA and RNA
- DNA encodes a cell’s operations, whereas RNA translates that code into proteins that carry out cellular tasks.
- An organism’s characteristics are formed by the sequence of nitrogen bases (A, T, C, G) in DNA.
- In nucleic acid molecules, the nitrogen bases A and T (or U in RNA) always go together, and C and G always go together, generating the 5′-3′ phosphodiester bond.
FAQs:
1. What are the 4 main differences between DNA and RNA?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thyamine are the four nitrogenous bases of DNA. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA.
2. What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA differ in two ways:
(a) RNA has the sugar ribose, whereas DNA has the slightly different sugar deoxyribose (a kind of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom)
(b) RNA has the nucleobase uracil, whereas DNA has thymine
3. What is the structure of RNA?
RNA is normally a single-stranded molecule, unlike DNA. In addition, RNA’s sugar is ribose rather than deoxyribose (ribose has one additional hydroxyl group on the second carbon), which explains the molecule’s name. Cytosine, Adenine, uracil, and guanine are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA.
4. How are RNA and DNA similar?
RNA vs. DNA are nucleic acids made up of nitrogen-containing bases linked by a sugar-phosphate backbone. Thymine is found in DNA, while Uracil is found in RNA. Instead of the deoxyribose found in DNA, RNA nucleotides contain sugar ribose.
5. Where is RNA found?
RNA begins its life in the nucleolus and subsequently goes to specialized cytoplasmic areas, depending on the RNA produced.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about DNA and RNA Structure! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- DNA and RNA. https://cm.jefferson.edu/learn/dna-and-rna/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- DNA vs. RNA – 5 Key Differences and Comparison. https://www.technologynetworks.com/genomics/lists/what-are-the-key-differences-between-dna-and-rna-296719. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- RNA. https://www.britannica.com/science/RNA. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- DNA and RNA. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introchem/chapter/dna-and-rna/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.