Mutations – Causes and Effects Study Guide
Introduction
Mutations are defined as permanent changes that take place in the DNA sequence of any living organism. Changes occur in the arrangement of the four base pairs, namely A, T, G, and C. Most cells can potentially recognize a mutation and repair it before it gets fixed.
Often mutations are harmless, unless they result in tumor formations and cell death.
Causes of Mutations
There are two basic causes of gene mutations.
- One is exposure to mutagens such as radiations like ultraviolet X-rays, certain viruses, or reactive chemicals and toxins.
- And the other are those which occur during DNA replication.
Types of Mutations
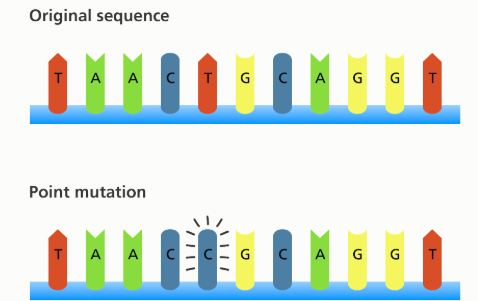
1. Point mutation:
- Point mutations are those genetic mutations in which changes occur in single base pairs.
- They are also called base-pair mutations.
- A majority of these result in a change in the functioning of a protein, and some give rise to a stop codon.
- When the stop codon is abruptly created in an abnormal position, it results in a non-functioning or truncated protein.
- Sometimes, single base pairs may be added or deleted. This causes a missed or frameshift reading of the triplet codons and may lead to the wrong amino acids.
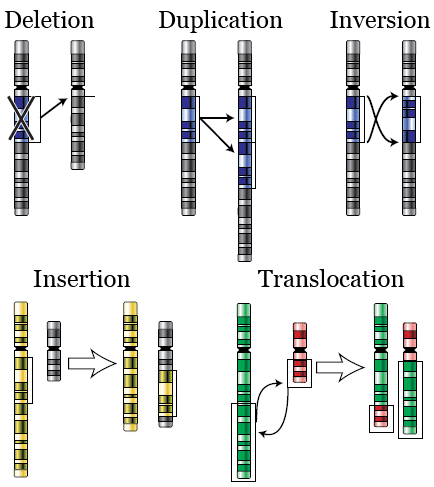
2. Chromosomal mutations:
- Chromosomal mutations are those mutations that involve more than a single gene.
- They may thus affect the function, structure, and subsequently, the inheritance of entire DNA molecules called chromosomes.
- These are often brought about by exposure to harmful radiation, which causes breaks in the genome like duplications, inversions, considerably big deletions, or translocations.
- This may result in serious abnormality issues.
- The wrong pairing of a translated or inverted chromosome can lead to gametes with deletions and duplicate numbers. This affects the subsequent progeny.
Aneuploidy is a condition in which entire chromosomes may be lost or gained, as seen in the Down syndrome disorder in human beings. Here the person is born with an extra chromosome 21 and thus has three duplicates of that chromosome instead of just the normal two.
Polyploidy is seen when there is a gain of either three, four, or more sets of chromosomes instead of only two.
3. Recombination mutations:
- In recombination mutations, the movement of DNA elements that change their location from one place to another may cause a mutation.
- The element may change at an important location, such as inside a gene or between pairs of mobile elements, that can cause change in genetic information.
Diseases caused by Mutations in DNA
1. Klinefelter syndrome:
- Klinefelter syndrome, also known as the XXY syndrome, is a result of a genetic mutation in which a male person has an extra X chromosome within his chromosome structure.
- In addition to the traditional male XY genotype, such a person has an extra X chromosome, resulting in additional female parts like breasts and cannot reproduce.
- This can happen even in other living organisms like whales, cats, and dogs.
In cats, an extra chromosome for the color of their fur on the X chromosome is carried, which results in more fur colors. This is usually seen in female cats since they inherit two X chromosomes, unlike male cats, who inherit only one X chromosome. This is typically seen in the female Calico cat, which has striking orange and black-colored fur. This is why they are known as Klinefelter’s Calicos.
2. Sickle Cell Disease (SCD):
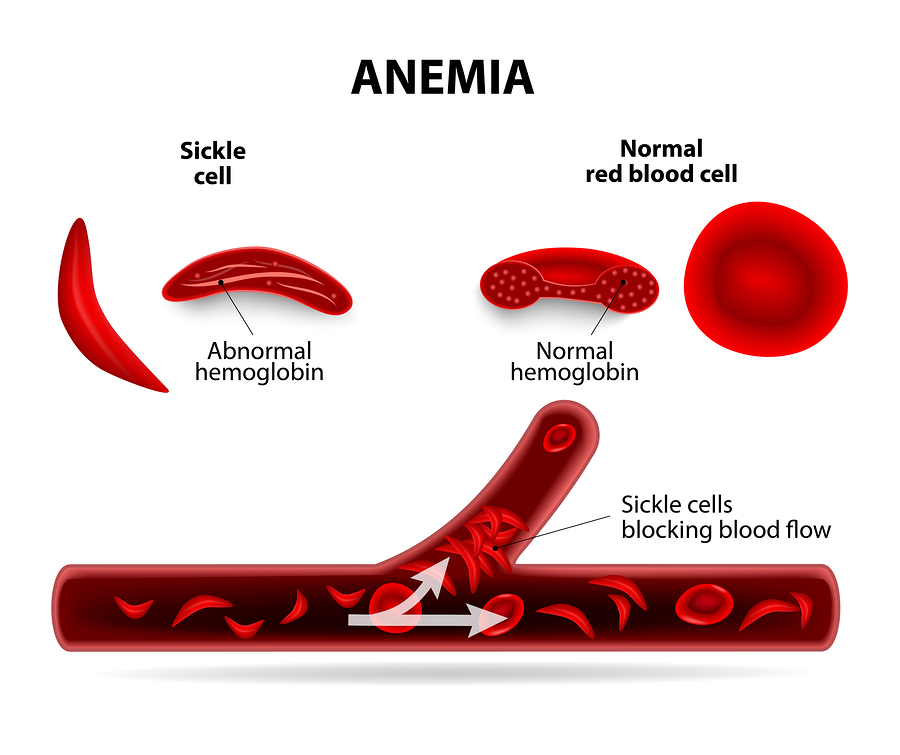
- SCD is named due to the sickling effect on the red blood cells.
- This happens due to mutation, which occurs on the eleventh chromosome and is characterized by the inheritance of a gene from both parents, which causes abnormal hemoglobin.
- It is usually manifested as the formation of blood clots, anemia, and episodes of severe pain called “sickle-cell crisis.”
- A majority of such are normally treated with medication, but this condition decreases the quality of life in such people.
- A positive effect is also seen in SCD patients as their chances of contracting malaria decrease, protecting the person from the effects of malaria and even death. This is predominantly seen in the African population.
Conclusion:
- Mutations in biology are typically manifested physically, and the effect of the mutation is largely dependant on its location.
- There may be beneficial, harmful, or silent mutations and they can lead to a change in the level of gene expression, gain or loss of a particular function, or in the worst cases, death.
FAQs:
1. What are the four types of mutations?
Germline, chromosomal, point, and frameshift mutations are the four types of mutations.
2. What are examples of mutations?
Colour blindness, cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, Haemophilia, Turner syndrome, etc., are some examples of mutations.
3. What is a mutation in science?
Mutation means a change in a genetic sequence of a living-organisms.
4. How do mutations occur?
Mutations can result from being exposed to certain viruses, ionizing radiations, chemicals, and also as a consequence of errors during cell division.
5. Are all mutations harmful?
Most mutations occurring in living organisms are not harmful, but some harmful ones may result in cancer or genetic disorders.
6. Where do mutations occur?
Germline mutations take place in sperms and eggs and may be passed on to the resulting offspring. Somatic mutations take place within the cells of the body and do not get passed on.
7. What is the role of mutations?
Mutations play a big role in evolution since new DNA sequences are created in a specific gene, resulting in new alleles. Also, mutations can bring about different traits in an organism.
8. What can change DNA?
Exposure to mutagens or conditions can cause changes in the genetic material or DNA of an organism.
9. What are the three main causes of mutation?
They are mutations occurring during DNA repair, mutations brought about due to mutagens, and mutations occurring during replication of DNA.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Mutations – Causes and Effects! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>