Evidence of Evolution Study Guide
Introduction:
Evolution is defined as a change in a species’ physical traits over many generations due to natural selection. Let’s take a closer look at each of these and identify the evidence of evolution.
Basis of evolution:
- Evolution is based on genetic diversity in a population, influencing an organism’s physical traits.
- Individuals with certain physical traits may have an advantage that can be passed on to their descendants.
- Evolutionary evidence is one of the most important pillars of current biological theory.
- It is the only way to prove all of the suggested evolution hypotheses.
- Fossils, comparative anatomy, and embryo development patterns are some of the evidence we have to support biological evolution.
Forms of evolution
According to biologists, there are two forms of evolution based on the scale:
-
Macroevolution is a term used to describe large-scale changes that occur over long periods, such as the emergence of new species and groupings.
-
Microevolution is a term used to describe small-scale changes in populations that affect just one or a few genes and occur over shorter durations.
Evidence of evolution
It describes how many creatures share an origin and how natural selection or genetic drift led to the evolution of many diverse organisms. There were two categories of comparative anatomy found: homologous organs and analogous organs.
Homologous features:
- If two or more species share a physical trait, such as a sophisticated bone structure or a body plan, it’s possible that they all received it from a common ancestor.
- Homologous physical traits are shared owing to evolutionary history (a common ancestor).
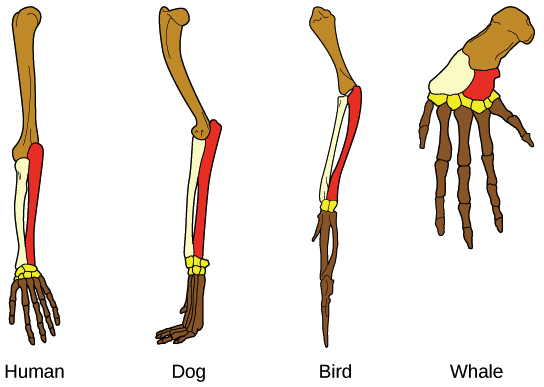
On the exterior, morphological features such as the forelimbs of whales, humans, birds, and dogs appear quite different. This is because they have evolved to function in various situations. However, if you examine the forelimb bone structure, you’ll notice that the arrangement of bones is extremely similar across species.
It’s more plausible that the fundamental architecture of bones was already present in a common ancestor of whales, humans, dogs, and birds than that such identical features arose independently in each species.
Vestigial structures:
- Structures homologous to significant structures in other creatures but have lost their primary ancestral role can sometimes be found in organisms.
- Vestigial structures have lost their function and are typically decreased in size. Human tailbones are an example of vestigial structures (a vestigial tail).
Analogous organs:
- The structure of these organs differs, but their functions are comparable. This demonstrates how various animals have developed and adapted to varied environments.
- Convergent evolution is the name given to this sort of evolution.
Consider the wings of certain birds and bats. Birds’ wings have feathers for flight, while bats’ wings are made of stretched skin with no feathers. Both serve the purpose of flying.
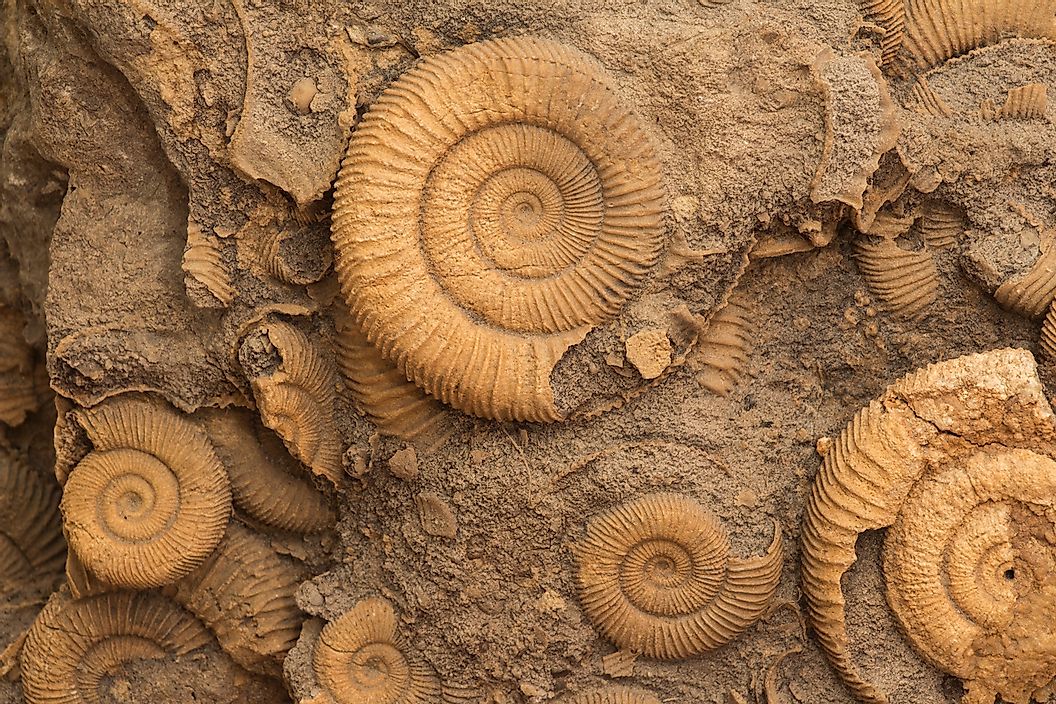
Fossils:
- Fossils are the preserved remnants or evidence of formerly existing species from the distant past.
- Unfortunately, the fossil record is neither full nor unbroken: most creatures do not fossilize, and humans seldom discover those that do.
- Nonetheless, human-collected fossils provide unique insights on evolution over extended timeframes.
- Fossils chronicle the existence of now-extinct species, demonstrating that various creatures lived on earth at various times throughout its history.
- They can also aid scientists in reconstructing current-day species’ evolutionary history.
- The horse lineage, for example, has produced some of the most well-studied fossils. Scientists created a huge, branching “family tree” for horses and their now-extinct cousins using these fossils. Changes in the lineage that led to today’s horses, such as the conversion of toed feet to hooves, might represent adaptability to environmental changes.
Homologous genes:
Biologists frequently compare the sequences of comparable genes present in various species (commonly referred to as homologous or orthologous genes) to determine how those species are connected evolutionarily. The underlying premise behind this method is that two species have the “same” gene since they share an ancestor. Because this gene was already present in their last common ancestor, humans, cows, chickens, and chimps all share genes that encode the hormone insulin.
Embryonic Development:
Until a certain stage of gestation, the embryos of many species have a similar structure. Human embryos, pig embryos, reptile embryos, and bird embryos, for example, have comparable embryonic development. As they grow older, they transform into the appropriate species. This demonstrates shared ancestry once again.
Conclusion:
- Homologous structures suggest comparable selected forces may create similar adaptations, whereas analogous structures show similar selective pressures can cause similar adaptations (beneficial features).
- Similarities and differences among biological molecules (for example, in the DNA sequence of genes) can be utilized to assess the relatedness of species.
- Although imperfect, the fossil record gives information on what animals existed at different points in earth’s history.
FAQs:
1. What are the four factors that show evidence of evolution?
Anatomy, molecular biology, fossils, and direct observation are all evidence for evolution.
2. What are the three main lines of evidence for evolution?
Darwin supported his idea of evolution by natural selection with several lines of evidence, including fossil data, biogeographical evidence, and anatomical evidence.
3. What is the oldest evidence of evolution?
Biogenic carbon fingerprints and stromatolite fossils found in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks from western Greenland are the earliest evidence of life. In Western Australia, suspected “remains of biotic life” were discovered in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in 2015.
4. What are the five pieces of evidence of evolution?
This section covers five sorts of evidence for evolution: ancient creature remnants, fossil layers, similarities among living animals, DNA similarities, and embryo similarities.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Evidence of Evolution! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Evolution of Life. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/1.8/primary/lesson/evolution-of-life-bio/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- Evidence for Evolution. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-wmopen-biology1/chapter/outcome-evidence-for-evolution/. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.
- What is the evidence for evolution?. https://biologos.org/common-questions/what-is-the-evidence-for-evolution. Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.