Origin of Life on Earth Study Guide
Introduction:
The earliest rocks having fossil evidence of life on earth are at least 3.5 billion years old. Therefore, we can understand that life originated at least 3.5 billion years ago. Let’s know more about the answer to when did life begin on earth in this article, along with other interesting facts.
Origin of the earth:
The Big Bang Theory tries to explain how the universe came to be. It mentions a massive explosion that is unfathomable in physical terms. As the universe became larger, the temperature dropped. Later on, hydrogen and helium were created.
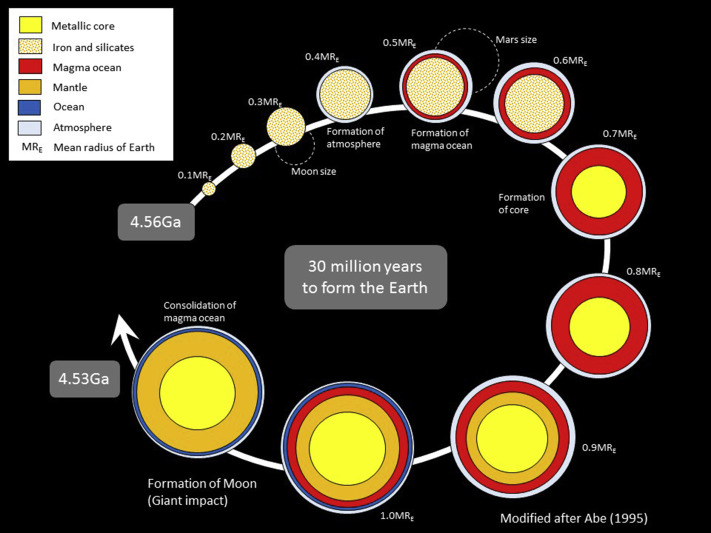
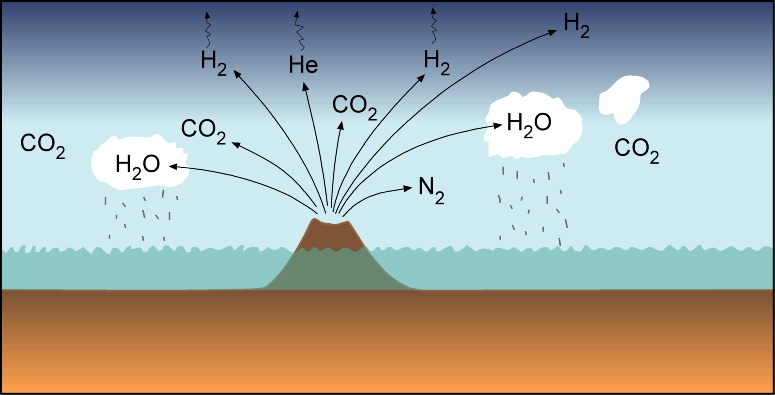
The gases concentrated due to gravity and produced the current universe’s galaxies. Earth was thought to have originated some 4.5 billion years ago in the Milky Way solar system. On the early earth, there was no atmosphere. The surface was blanketed with water vapor, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia emitted by the molten mass.
Modern or Chemosynthetic theory of the origin of life:
- Oparin, the Soviet biochemist, came up with this notion with the help of Haldane.
- According to this hypothesis, life arose in water on primeval earth from chemicals some 4.2 billion years ago, as a result of a sequence of chemical reactions, hence known as the biochemical theory of the origin of life.
- It’s also known as the contemporary synthetic hypothesis of life origins.
- This idea may be broken down into three stages: Chemogeny, biogenesis, and cognogeny.
Three stages of life origins:
1. Chemogeny:
Chemogeny describes the process of chemical evolution. This evolution was dependent on chemical reactions and the formation of substances. These substances include polysaccharides, lipids, polypeptides, nucleic acids, and other complex organic compounds.
Primitive atmosphere formation:
- The earth’s primordial atmosphere was made up of components like N, H, O, C, and others.
- Oxygen was present as oxides of aluminum, boron, hydrogen, and other elements, rather than in its free state.
Formation of inorganic compounds:
- When the temperature of the early earth dropped below, chemical evolution was encouraged.
- Hydrogen atoms were the most prevalent.
- They formed water by combining all available oxygen.
- They all formed ammonia and methane when mixed with nitrogen and carbon atoms, respectively.
Formation of simple organic compounds:
- As the earth cooled, it developed a solid crust, giving rise to depressions and elevations.
- Meanwhile, atmospheric water vapors gathered and finally fell as rain on the earth’s surface.
- The water that gathered in the depressions dissolved the minerals and eventually led to huge bodies of water known as oceans.
- When the earth’s surface cools to 50°C-60°C, inorganic molecules combine to generate simple organic chemicals like acetylene, ethylene, ethane, and methane in various forms.
Formation of complex organic compounds:
Through the processes of condensation, polymerization, and oxide reduction, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons mingled and recombined in various ways to generate complex organic molecules such as acetaldehyde, acetic acid, ethyl alcohol, amino acids.
2. Biogeny:
The genesis of primordial life is referred to as biogeny. It is the development of living organisms from other living organisms.
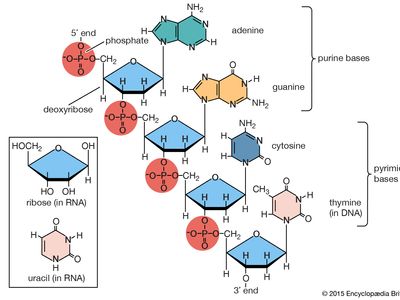
Formation of nucleic acids:
- In the primordial water, organic soup, organic components interacted and aggregated to form new molecules of greater size and complexity.
- During chemical reactions in primordial soil, nitrogen-bases interacted with sugar and phosphate to produce nucleotides at high temperatures.
- Nucleic acids are made up of many nucleotides linked together in various configurations to produce exceedingly complex molecules.
- Nucleic acids exhibited a propensity towards replication.
- The RNA World Hypothesis proposes that RNA could have been the earliest genetic material.
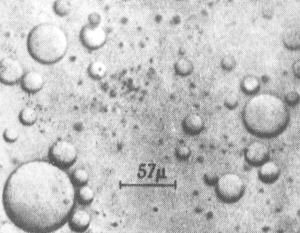
Formation of coacervates:
- Due to intermolecular interaction, the complex organic molecules of primordial soup are gathered into enormous colloidal cells termed coacervates of microspheres.
- Such coacervates were efficient and multiplied because they could grow and break.
Formation of primary organism:
- The first cellular creatures, known as eobionts, pre-cells, or protobionts, appeared about 3.8 billion years ago.
- Certain fatty acids with a high affinity for water formed the outer limiting membranes.
- Some eobiont proteins operate as enzymes for both positive and negative responses.
- Eobionts were shown to be identical to protovirus, a modern virus.
- Chemoheterotrophs were found in both anaerobic and prokaryotic environments.
3. Cognogeny:
Primary species diversification into multiple ways of life is involved in cognogeny. It caters to the diversification of protozoa into metazoa, metaphyta, and various other organisms.
Origin of autotrophs:
Chemoheterotrophs consumed organic nutrients as their numbers grew, contributing to a decline in the ocean’s natural food supply. As a result, primitive organisms created organic chemicals from inorganic molecules prevalent in the water. Due to the lack of chlorophyll, the anaerobic chemical breakdown has given the energy required for organic food production. During that time, bacterium chlorophyll underwent chemical changes to become real chlorophyll, resulting in the evolution of true photoautotrophs. These phototrophs made their food by photosynthesis, which used water as a raw source. Cyanobacteria were the first photoautotrophs to develop that were both oxygenic and aerobic.
Origin of eukaryotes:
- Prokaryotes that were formerly photosynthetic have switched to aerobic respiration.
- Then, like prokaryotes, cyanobacteria acquired a proper nucleus and evolved into eukaryotes.
- It was similar to the unicellular species of today.
- Through the colonization process, multicellular species have developed from unicellular creatures.
RNA World Hypothesis
Today we know that DNA is decoded into RNA which further forms proteins. The RNA world hypothesis suggests an RNA world existed on Earth before modern cells arose. RNA being a polynucleotide, has the potential to both store information and catalyze chemical reactions. This forms the basis of the RNA World hypothesis. An RNA molecule has the property to catalyze its own synthesis as it was discovered that RNA molecules themselves can act as catalysts. This would also suggest that RNA could have been the earliest genetic material present on Earth before DNA.
Conclusion:
- The Big Bang Theory tries to explain how the universe came to be.
- The genesis of primordial life is referred to as biogeny.
- Due to the lack of chlorophyll, the anaerobic chemical breakdown has given the energy required for organic food production.
- Through the colonization process, multicellular species have developed from unicellular creatures.
FAQs:
1. When was the first origin of life on Earth?
Because the earliest rocks having fossil evidence of life on Earth are at least 3.5 billion years old, we know that life originated there at least 3.5 billion years ago.
2. Where did human life begin on Earth?
Humans oinated in Africa, and most human evolution took place there. Early human fossils from 6 to 2 million years ago are only found in Africa.
3. What is meant by the origin of life?
The emergence of heritable and evolvable self-reproduction is the origin of life. Thus, life evolved from simple but already functioning molecules, with cooperation and natural selection driving its progressive growth toward increased complexity.
4. How did DNA originate?
In an RNA/protein universe, DNA and DNA replication processes developed late in early life history, and DNA evolved from RNA.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Origin of Life on Earth! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Origin of Life. https://www.lpi.usra.edu/science/kring/epo_web/impact_cratering/origin_of_life/index.html. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- Early Life on Earth – Animal Origins. https://naturalhistory.si.edu/education/teaching-resources/life-science/early-life-earth-animal-origins. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- 7 Theories on the Origin of Life. https://www.livescience.com/13363-7-theories-origin-life.html. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- The origin of life: The conditions that sparked life on Earth. https://researchoutreach.org/articles/origin-life-conditions-sparked-life-earth/. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- The origins of life on Earth. https://www.science.org.au/curious/space-time/origins-life-earth. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.