Variations in Population Study Guide
Introduction:
Mutation, recombination during gamete development, and environmental variables all cause variations. Genetic variation leads to differences in alleles, therefore, having different genotypes. To understand the process of variations within a population, let’s dive into this article.
Genotypic variance:
Changes in the chromosome or genes and different alleles of the same gene generate a genotypic variance. They are variations that can be passed down through the generations. Mutation, recombination, and other factors contribute to this.
Genotypic variation characteristics:
- Natural selection may use genetic diversity to raise or reduce the frequency of alleles already present in the population, a powerful factor in evolution.
- Mutation (which can produce whole new alleles in a population), random mating, random fertilization, and recombination between homologous chromosomes during meiosis (which reshuffles alleles within an organism’s progeny) can all contribute to genetic variation.
- Genetic variety is beneficial to a community because it allows certain individuals to adapt to their surroundings while still allowing the population to survive.
Adaptation to environment and evolution:
- Variation helps certain members of a population to adapt to changing conditions.
- Because natural selection mainly affects phenotypes, more genetic variation within a population typically leads to more phenotypic diversity.
- New alleles improve an organism’s capacity to live and reproduce, ensuring that the allele survives in the population.
- Other novel alleles, such as a defective oxygen-carrying protein, maybe instantly harmful, and animals containing these mutations die off.
Causes of genetic variation:
Genetic drift: Random sampling and random events that impact the survival and reproduction of those individuals cause genetic drift, which is the change in the frequency of an allele in a population.
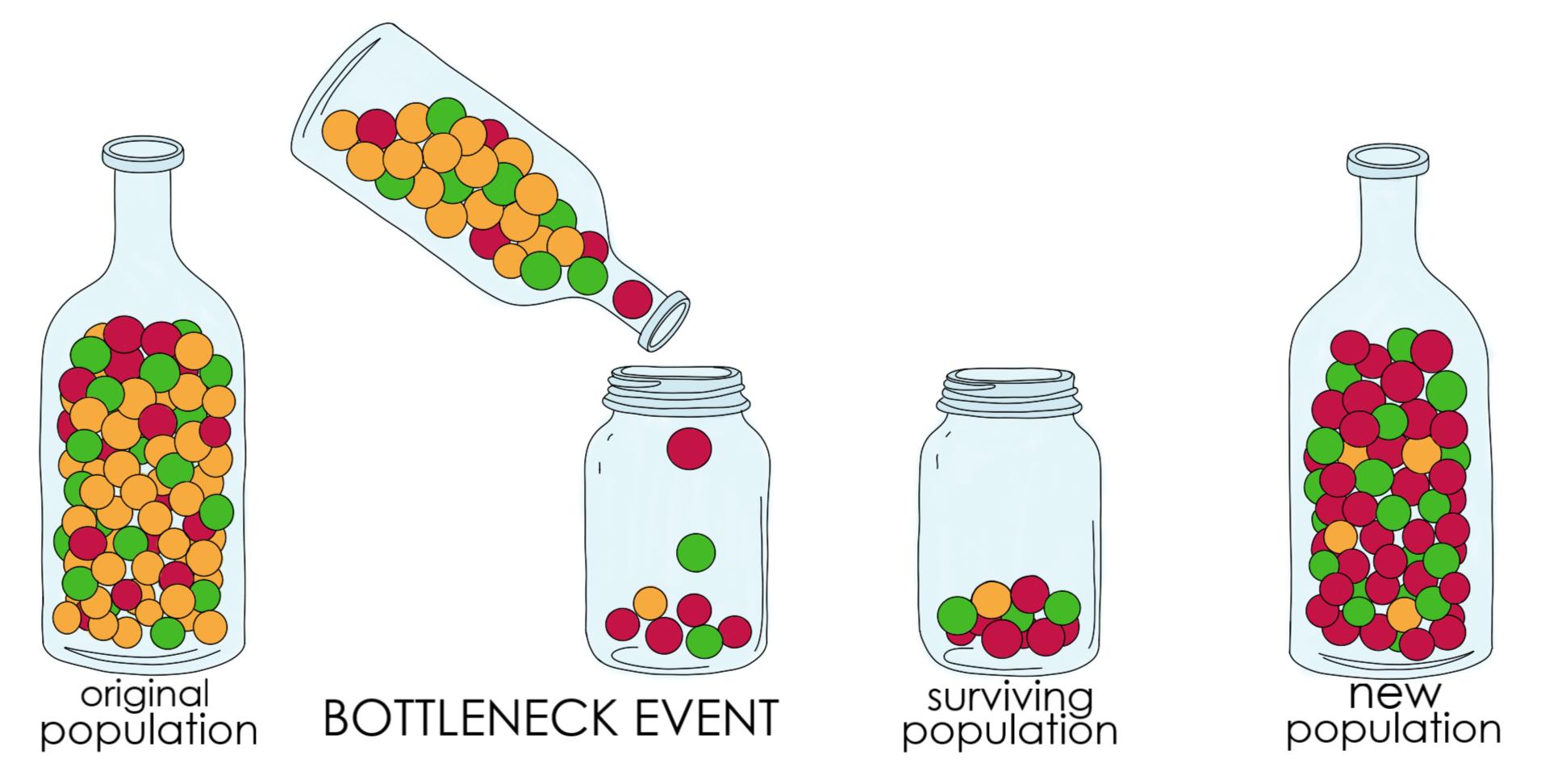
→ The bottleneck effect happens when a natural disaster or other comparable event kills a big section of the population at random, leaving survivors with allele frequencies that are very different from the prior population.
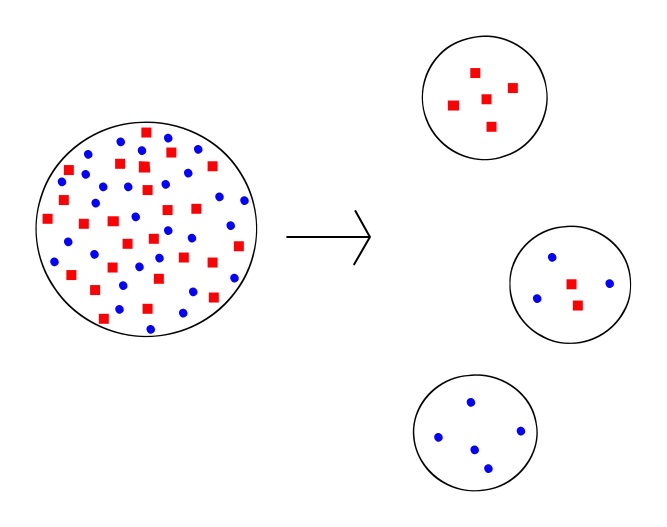
→ The founder effect happens when a subset of the population (known as “founders”) breaks away from the original population to form a new one with varying allele frequencies.
Small populations are more prone to genetic drift than big populations, which can buffer the population against random occurrences due to their higher numbers.
Mutation and gene flow: Individuals entering and leaving a group add new alleles and enhance genetic variation in that population.
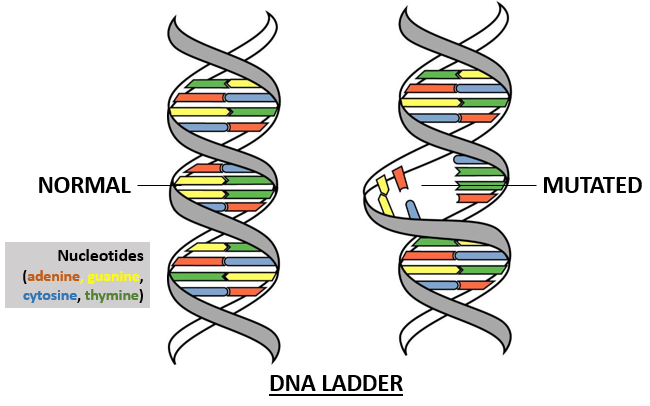
- Mutations are alterations to an organism’s DNA that introduce new alleles into a population, resulting in diversity.
- Natural selection swiftly eliminates deleterious mutations from the population; damaging mutations prohibit organisms from reaching sexual maturity and reproducing.
- Other mutations are favorable and can help organisms attain sexual maturity and reproduce to spread in a community.
Phenotypic variation:
The variety in phenotypes that exists in a population is referred to as phenotypic variance. People exist in different forms and sizes. For example, height, weight, and body shape differ in all phenotypes.
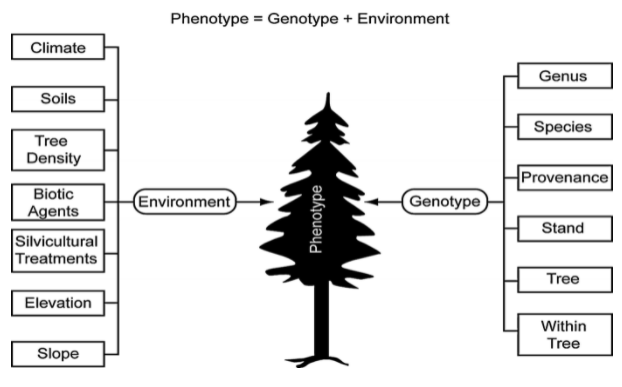
- Genes, environmental influences, or combined can cause phenotypes.
- Environmental variables are things in an organism’s environment or way of life that can have a variety of effects on it. Human body weight, for example, is controlled not just by heredity but also by nutrition. Diet is an example of an environmental component in this scenario.
- Some bacteria may carry a gene that codes for an enzyme that degrades an antibiotic into a non-harmful chemical. These bacteria will withstand antibiotic treatment: this trait is known as antibiotic resistance. Bacteria without the gene, on the other hand, will be vulnerable to antibiotics.
Importance of genetic diversity:
- Population ability to respond to changes in the environment is influenced by genetic diversity. Species and populations with little genetic diversity are at risk of decline or extinction.
- Genetically diverse populations are more resilient to environmental perturbation because they are more likely to contain individuals who can withstand environmental pressure.
Conclusion:
- Differences in the genetic composition or phenotypes of diverse species are known as variations.
- Mutation, recombination during gamete development, and environmental variables all cause variations.
- Changes in the chromosome or genes and different alleles of the same gene generate a genotypic variance. They are variations that can be passed down through the generations.
FAQs:
1. What are the 3 types of variation?
The many forms of genetic variants are as follows:
- SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) are single base-pair substitutions that can be transitional.
- Insertion or deletion of a single stretch of DNA sequence
- Genetic variation that occurs over a wider DNA sequence is structural variation.
2. Why do variations occur in the population?
Mutation (which can produce whole new alleles in a population), random mating, random fertilization, and recombination between homologous chromosomes during meiosis (which reshuffles alleles within an organism’s progeny) can all contribute to genetic variation.
3. What are examples of variations?
Humans and dogs have different-colored eyes and different-length tails respectively. This indicates that no two individuals in a species are alike. Variation refers to the differences between individuals within a species.
4. What is a variation in species?
Variation refers to the differences in traits between individuals of the same species. Some variation is handed down from parents to children during reproduction via genes. This is an example of inherited variation. Differences in the environment or what an individual does cause some variety.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Variations in Population! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Genetic Variation In A Population. https://www.encyclopedia.com/science/news-wires-white-papers-and-books/genetic-variation-population. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- Population Genetics. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-biology/chapter/population-genetics/. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- The Genetic Variation in a Population Is Caused by Multiple Factors. https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/the-genetic-variation-in-a-population-is-6526354/. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.
- Population-level genetic variation and climate change in a biodiversity hotspot. https://academic.oup.com/aob/article/119/2/215/2666348. Accessed 27 Dec, 2021.