Cell Size Study Guide
Introduction:
In 1665, Robert Hooke discovered cells under a compound microscope. He examined a piece of cork and saw minute shapes like little rooms. As a result, he termed his findings “cells.” In biology, a cell is a basic membrane-bound unit that contains the essential components of life. A single cell, such as a bacterium or yeast, can also be a complete organism in and by itself. In multicellular organisms, cells develop specific roles as they grow, and these cells collaborate with other specialized cells to form tissues, organs, and organ systems.
The cell structure comprises distinct components that perform a specific role required to carry out life’s operations. Cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus are these components.
Cell size
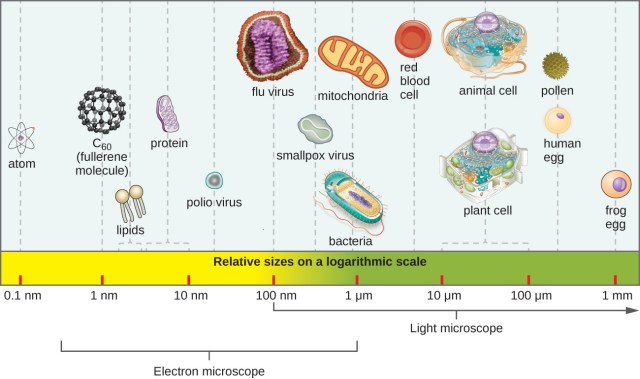
The cell size varies. Cells in living creatures can be as little as a millionth of a meter or as big as a few centimeters. Typically, all cells are tiny and cannot be seen with the human eye. As a result, they must be magnified using a microscope to be seen.
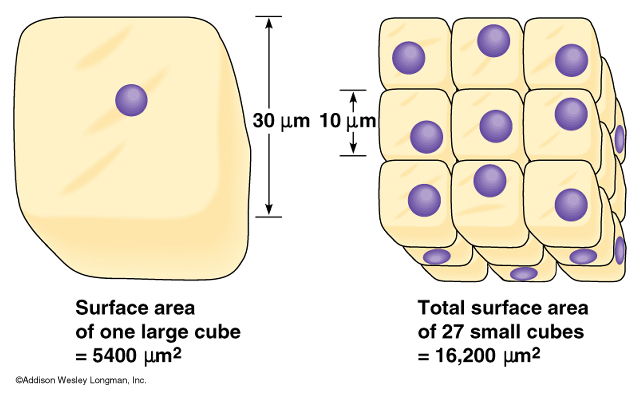
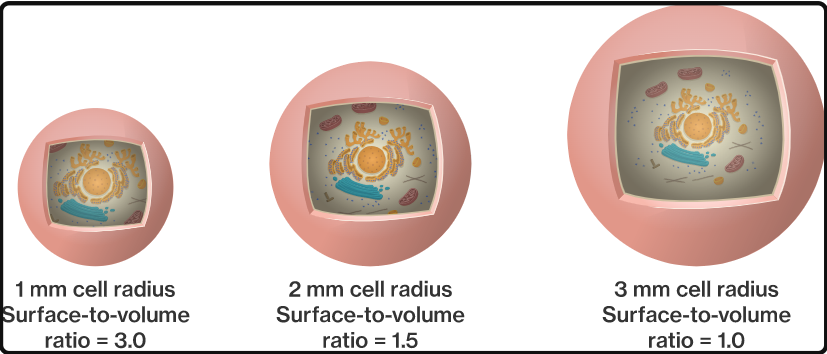
The important point is that the surface area to the volume ratio gets smaller as the cell gets larger.
As a result, if the cell develops beyond a certain point, not enough material can cross the membrane quickly enough to meet the increased cellular volume. When this happens, the cell must either split into smaller cells with better surface area/volume ratios or stop functioning. That’s why cells are so tiny.
Determinants of cell size
- All living things have a logical explanation for their form and function, and cells are no exception.
- The reason cells can only grow to a specific size is due to the surface area to volume ratio.
- In this context, surface area refers to the portion of the cell’s outside known as the plasma membrane.
- The volume is the amount of space inside the cell.
- The surface area divided by the volume is the ratio.
- This displays how much surface area is accessible in relation to the size of the cell.
- The cell is very large if the surface area to volume ratio is low.
- When the ratio is high, the surface area exceeds the volume, and the cell is tiny.
- The greater the surface area to volume (SA/V) ratio is, the more efficient the cell becomes.
Conclusion:
- Cells are far larger than atoms, yet they are still quite tiny.
- The smallest known cells are mycoplasmas, a type of minuscule bacteria; some of these single-celled creatures are spheres as small as 0.2 m in diameter (1m = roughly 0.000039 inches)
- Surface area-to-volume ratios affect the exchange of materials between cells or organisms and the environment.
FAQs:
1. What is the smallest and largest cell size?
Bacteria have the tiniest cells, ranging in size from 0.1 to 0.5 micrometers. On the other hand, the biggest cell is 170 mm 130 mm and is an ostrich egg.
2. How is cell size measured?
An eyepiece graticule can be used to measure cell size. The scale is ruled on the graticule, and one can determine the distance measured for each graticule division. The graticule may then be used to measure cells.
3. What is the size of blood cells?
Normal human RBCs are biconcave in form, with a diameter of around 7-8 µm and a thickness of about 2.5 µm.
4. Why are cells small in size?
Cells are so small that they may optimize their area-to-volume ratio. Smaller cells have a higher ratio, allowing more molecules and ions to be moved across the cell membrane per unit of cytoplasmic volume.
5. What is a cell?
A cell is defined as “the tiniest, most fundamental element of life, responsible for all of life’s operations.” All living things are made up of cells, which serve as structural, functional, and biological components. A cell may duplicate itself on its own, and as a result, they are referred to as the building blocks of life.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Cell Size! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
Sources:
- Cell size and shape https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-biology-advanced-concepts/section/3.5/#:~:text=Eukaryotic%20cells%20normally%20range%20between,the%20largest%20of%20them%20all. Accessed on 21 Dec, 2021
- Variation in cells https://www.ck12.org/biology/variation-in-cells/ Accessed on 21 Dec, 2021
- Cell size https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-college-human-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/4.3/primary/lesson/variation-in-cells-chumbio/ Accessed on 21 Dec, 2021