Connect with our sales team.
Get Started
DNA
Launch
Subject: General Bio
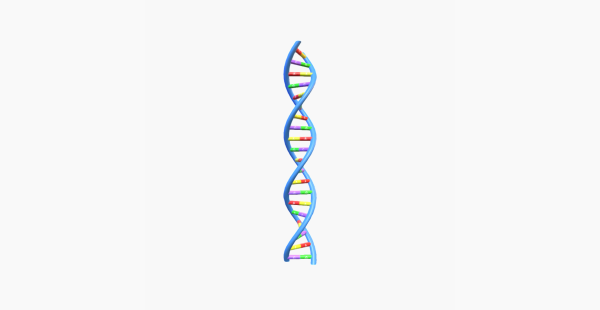
DNA strand
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic blueprint for all living organisms, composed of two strands forming a double helix structure. Each strand consists of a backbone of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules, with nucleotide bases attached to the sugar molecules.
Adenine (A)
Adenine (A) is a nucleotide base that pairs with thymine (T) in the DNA double helix. Adenine is one of the two purine nucleotide bases, along with guanine, that forms the building blocks of DNA. The chemical structure of adenine makes it particularly susceptible to oxidative damage, leading to possible errors in DNA replication and transcription.
Guanine (G)
Guanine (G) is a nucleotide base that pairs with cytosine (C) in the DNA double helix. It is one of the two purine nucleotide bases, along with adenine, that forms the building blocks of DNA. It can be damaged, leading to mutations and cancer, but DNA repair mechanisms can remove and repair damaged guanine.
Cytosine (C)
Cytosine (C) is a nucleotide base that pairs with guanine (G) in the DNA double helix. A chemical reaction can sometimes cause cytosine (C) to become uracil (U). This can lead to mutations and genetic instability, but cells have DNA repair mechanisms that can remove and repair damaged cytosine.
Thymine (T)
Thymine (T) is a nucleotide base found in DNA that pairs with adenine (A) through hydrogen bonds to form a complementary base pair. Thymine (T) plays a critical role in DNA replication and transcription, as it is responsible for maintaining the sequence of genetic information.
Ready to transform your classroom with immersive learning technology? Connect with our sales team.
Get Started
DNA
Launch
Subject: General Bio
Animated
Breakable
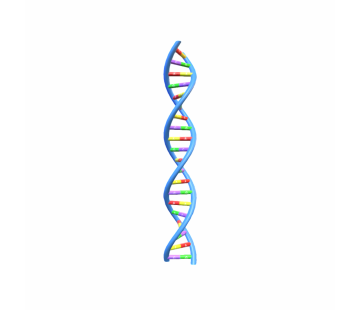
VR ReadyWeb ReadyDNA strand
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic blueprint for all living organisms, composed of two strands forming a double helix structure. Each strand consists of a backbone of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules, with nucleotide bases attached to the sugar molecules.
Adenine (A)
Adenine (A) is a nucleotide base that pairs with thymine (T) in the DNA double helix. Adenine is one of the two purine nucleotide bases, along with guanine, that forms the building blocks of DNA. The chemical structure of adenine makes it particularly susceptible to oxidative damage, leading to possible errors in DNA replication and transcription.
Guanine (G)
Guanine (G) is a nucleotide base that pairs with cytosine (C) in the DNA double helix. It is one of the two purine nucleotide bases, along with adenine, that forms the building blocks of DNA. It can be damaged, leading to mutations and cancer, but DNA repair mechanisms can remove and repair damaged guanine.
Cytosine (C)
Cytosine (C) is a nucleotide base that pairs with guanine (G) in the DNA double helix. A chemical reaction can sometimes cause cytosine (C) to become uracil (U). This can lead to mutations and genetic instability, but cells have DNA repair mechanisms that can remove and repair damaged cytosine.
Thymine (T)
Thymine (T) is a nucleotide base found in DNA that pairs with adenine (A) through hydrogen bonds to form a complementary base pair. Thymine (T) plays a critical role in DNA replication and transcription, as it is responsible for maintaining the sequence of genetic information.