Cardiovascular Diseases Study Guide
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), also known as heart diseases, are the leading cause of death globally. The term cardiovascular disease comprises blood vessel diseases that include coronary artery disease, arrhythmias or heart rhythm complications, congenital heart defects, and heart infections.
Heart diseases are typically a result of arteries building-up fatty deposits (atherosclerosis). Contracting or tightening the blood vessels is a typical type of heart disease.
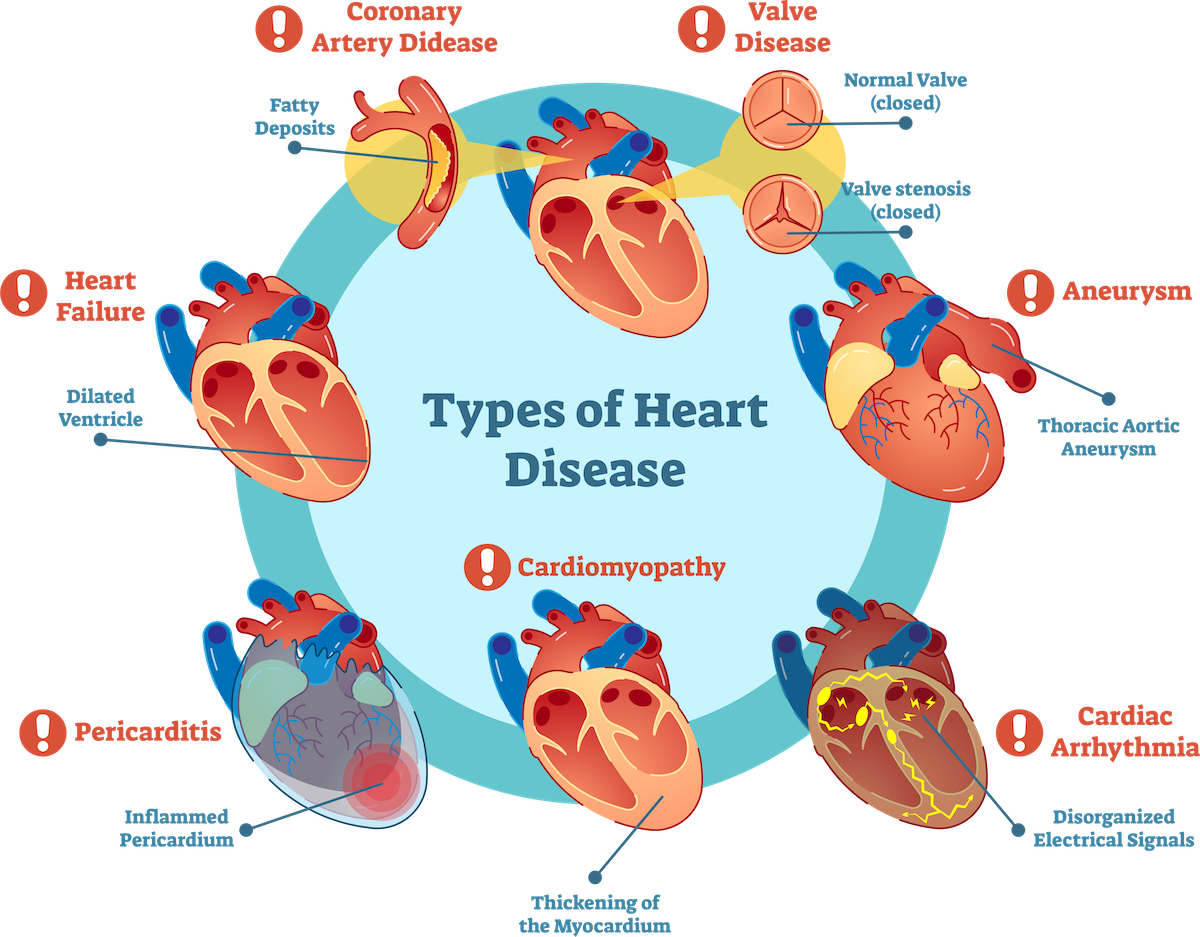
Types of Heart Disease
1. Coronary Artery Disease
Most common cause of heart attacks, that occur due to the buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries (main arteries that carry blood to the heart)
2. Congestive Heart Failure
Long-term condition that worsens over time. It results in a weaker and even enlarged heart over time, causing the patient to feel tired and weak most of the time
3. Heart valve Disease
Occurs when the valves in the heart do not function as they should. This can be due to enlarged valves, extra valve tissue that blocks blood flow, or improper opening and closing of the valves, leading to backward blood flow
4. Cardiomyopathy
Causes muscle tissue to become weak that can ultimately lead to heart valve disease and heart failurePericarditis: The pericardium, a tissue surrounding and supporting the heart, becomes swollen and inflamed. This can be acute or chronic, and when untreated, can result in heart failure.
5. Arrhythmia
The heart beats in a certain rhythm, and if it varies from this steady rhythm over a long period of time, it can cause a serious condition called arrhythmia. People can be born with arrhythmias, and it can potentially lead to cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Diseases
-
The typical heart disease symptoms comprise chest pain (angina), numbness, shortness of breath, coldness, or weakness around the arms and legs.
-
The arrhythmias symptoms include a type of flutter in the chest; tachycardia or a racing heartbeat; a slow or a weak heartbeat, or bradycardia; and fainting.
-
The cardiovascular problem may be marked by blue or pale gray skin.
-
Also, a thick heart muscle, termed cardiomyopathy, can result in bloating and breathlessness, amongst other symptoms.
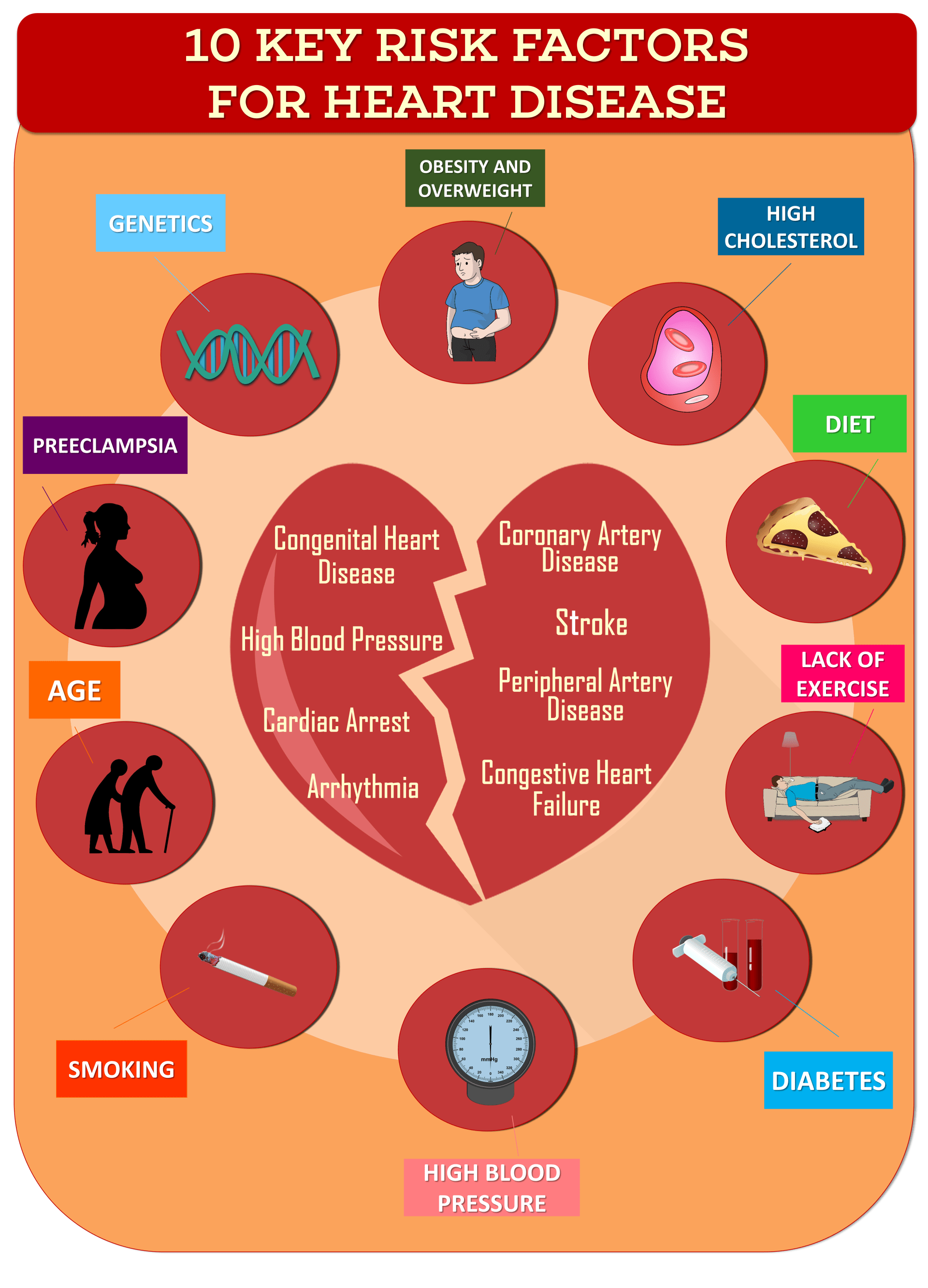
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
High blood pressure, age, diabetes, poor diet or exercise habits, smoking, substance abuse, obesity, and other chronic kidney diseases also contribute to cardiovascular problems.
Causes of Heart Diseases
-
A waxy build-up of fatty molecules, cholesterol, and minerals that can adversely impact one’s health is termed plaque. Plaque builds up with time in the inner linings of spoiled arteries resulting from high cholesterol and hypertension.
-
When blood vessels are filled with plaque, circulation is choked or blocked; thus, preventing oxygen and nutrients from reaching the heart.
-
Several risk factors affect one’s chances of developing cardiovascular disorders. Some of these can be controlled while some cannot. For example, heredity and age cannot be controlled by anyone, and the risk naturally increases once one ages.
-
However, there are various other factors that one can control or prevent, such as obesity, smoking, high cholesterol, physical inactivity, hypertension, diet, etc.
-
The risk factors of cardiovascular diseases, such as unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, can play a huge role in one’s health. For example, leading an inactive life and consuming an unhealthy diet can primarily affect one’s chances of contracting a cardiac disease.
-
Also, drinking excessively, smoking, and not handling stressful situations or diabetes are factors that result in cardiovascular disease.
-
Diabetes and Depression
Based on the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, persons with type 2 diabetes have twice the chance of developing cardiovascular disease. If one has type 2 diabetes, this results in high blood glucose levels, increasing plaque quantity. This is the reason blood sugar should be managed carefully.Depression is another factor that contributes to the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Depression prevents one from leading an active and healthy lifestyle leading to unhealthy habits, such as drinking and smoking.
Conclusion:
- Identifying those with the highest risk of CVD and ensuring that they receive the necessary treatment can most definitely avoid premature deaths.
- Everyone must access non-transmissible disease medicines and basic health care in all primary health care facilities to ensure that people who require treatment and counseling can get it.
FAQs:
1. What are the four most common cardiovascular diseases?
The four most common heart diseases are:
- Heart attack: Also named myocardial infarction, this is one of the most common types of cardiovascular disease.
- Coronary heart disease: This disease is a medical condition connected to the arteries carrying blood rich in oxygen to the heart.
- Congenital heart defect: This disorder is associated with a flaw in the heart structure or major blood vessels.
- Cyanotic heart disease: This disorder is often categorized by low oxygen levels.
2. What is considered a cardiovascular disease?
A cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term for diseases or disorders affecting blood vessels or hearts. This disease results from a build-up of fatty deposits within the arteries (atherosclerosis).
3. What causes cardiovascular disease?
The primary causes of stroke and heart disease are physical inactivity, unhealthy diets, tobacco use, and drinking.
4. What are the early warning signs of heart disease?
Specific symptoms such as ankle swelling, chest discomfort, shortness of breath may be the early warning signs of heart disease.
5. Can cardiovascular disease be cured?
Cardiovascular disorders can’t be cured; however, treatment can help manage the symptoms and decrease the chances of heart attacks. The therapy comprises lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and exercise.
6. What are the symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
Some of the symptoms of cardiovascular disease include:
- Chest tightness, chest pain, chest pressure, or chest discomfort (angina).
- Pain, weakness, or coldness around legs or arms.
- Pain in the jaw, neck, throat, back, or upper abdomen.
7. What are the six main risk factors for cardiovascular disease?
The six main risk factors of cardiovascular heart disease are:
- High Blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
8. How can I improve my heart health?
Regular exercise and maintaining healthy eating habits can help improve your heart health.
9. What food causes blocked arteries?
Food high in saturated fat mainly causes blocked arteries.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Cardiovascular Diseases! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun!
Sources:
- Cardiovascular diseases. https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases/#tab=tab_2. Accessed Nov 26, 2021
- Cardiovascular Diseases https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/guide/diseases-cardiovascular. Accessed Nov 26, 2021
- Cardiac Disease https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/Cardiac-Disease.htm. Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Cardiovascular Diseases. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.27/primary/lesson/circulatory-system-diseases-bio/. Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- What Causes Cardiovascular Disease? https://heartbeetcomplete.com/what-causes-cardiovascular-disease/. Accessed Nov 26, 2021