Embryo Growth Study Guide
Introduction:
The human body is a complex living system. The reproductive system is a fascinating part of the human body. From the time of conception, fertilization of the egg through implantation, the embryonic stage, fetal development, and ultimately the birth of the baby. Each stage of baby growth during pregnancy, from embryo development to fetus development through the three trimesters, is critical to the baby’s normal development in the womb.
What is an Embryo?
An embryo is a human organism in the early stages of growth and differentiation, from fertilization to the beginning of the third month of pregnancy.
A newly developing human is typically referred to as an embryo until the ninth week after conception when it is referred to as a fetus.
Growth and Development of the Embryo:
Human life starts as a single cell and soon grows into an embryo. The blastocyst (an early stage embryo after 5-7 days of fertilization) is called an embryo after implantation occurs.
Following fertilization, the embryonic stage lasts through the eighth week. During this time, the embryo grows in size and becomes more complex. It develops specialized cells and tissues and starts to form most organs.
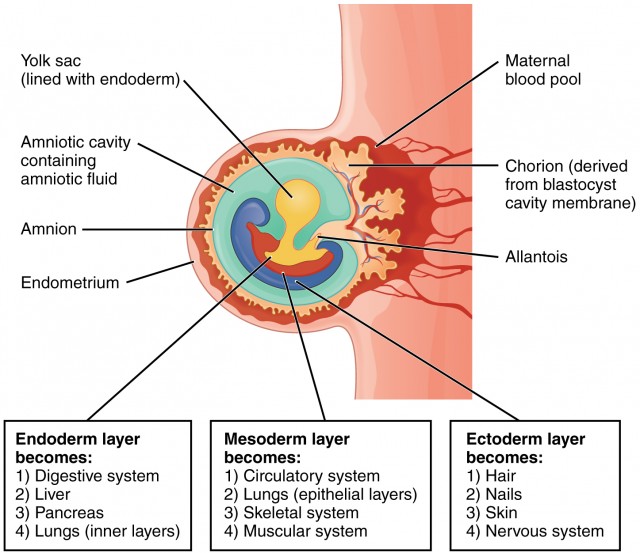
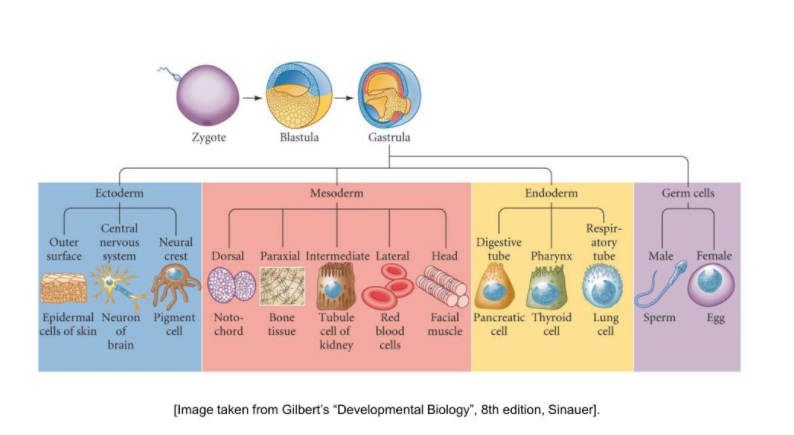
- Formation of cell layers: During the second week after fertilization, cells in the embryo migrate to form three distinct cell layers, called the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Each layer will soon develop into different cells and tissues!
-
Differentiation of cells: A zygote is a single cell. During the third week of fertilization, the embryo undergoes cellular differentiation. Cellular differentiation is the process by which unspecialized cells become specialized cells.
-
Differentiation occurs as certain genes are ‘expressed’ or “switched on” while other genes are switched off. Because of cellular differentiation, cells develop unique structures and abilities that suit them for their specialized functions.
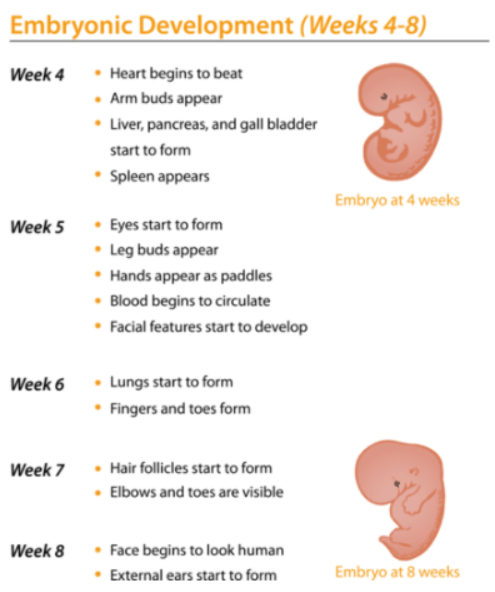
- Organ formation: After cells differentiate, all the major organs begin to form during the remaining weeks of embryo development. The figure below describes in detail the developments that occur in the embryo during these 4 weeks.
Stages of Pregnancy Month-by-Month
The fetal development during stages of pregnancy is broadly divided into trimesters.
First trimester: The first trimester includes from conception to 12 weeks.
- Month 1: The fertilized egg grows with a water-tight sac forming around it. Called the amniotic sac, it gets gradually filled with fluid, which helps cushion the growing embryo.
- Month 2: Facial features development continues, as each ear appears as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds are forming that will eventually grow into arms and legs. Gradually forming of Fingers, toes, and eyes also takes place.
- Month 3: Arms, hands, fingers, feet, and toes are fully formed during this stage. The fetus starts opening and closing fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails start developing, and the external ears are formed.
Second trimester: The 2nd trimester is considered the best part of the pregnancy experience. By this time, morning sickness has probably stopped, and discomforts of pregnancy have disappeared or become almost negligible.
- Month 4: The fetal heartbeat may be audible (can be sensed through an instrument called Doppler). The fingers and toes are well-defined, while eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails, and hair have fully formed.
- Month 5: The Fetus moving around can be felt at this stage, called Quickening. Hair growth on the head starts.
- Month 6: In this month, the eyelids begin to part open.
- Month 7: The fetus’s growth continues as it develops body fat reserves. The fetus starts responding to stimuli, including sound, pain, and light, as hearing is fully developed.
Third trimester: Each week of this final development helps the fetus prepare for birth in the final trimester of the pregnancy. The fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat to help after birth.
- Month 8: The fetus’s maturity continues as it develops body fat reserves. More kicking can be observed. Rapid brain development takes place, and most internal systems are well developed.
- Month 9: The lungs are almost developed fully. The fetus shows coordinated reflexes and can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light, and touch.
Conclusion:
- New life takes shape from conception when the fertilized egg rapidly divides into many cells before it travels through the fallopian tubes and binds itself or implants to the uterus wall.
- The embryonic stage continues till 8 weeks, during which the development of specialized cells and tissues happens and most organs start forming.
- The fetal development from here on till the end of 3rd trimester facilitates the important part of the growth and development of the baby in the womb.
FAQs:
1. How much does an embryo grow each week?
The embryo is constantly and rapidly growing every week. It develops in size and complexity-developing specialized cells and tissues. It also starts to form most organs.
2. How quickly does an embryo grow?
During the first 8 weeks, the embryo grows rapidly and becomes a fully formed Fetus by the end of the first trimester. The fetus weighs approximately 15-30 grams, measuring 3-4 inches in length.
3. What is the growing embryo?
The embryo is growing in the 8 weeks following fertilization. During this period, the embryo grows in size and becomes more complex. The embryo develops specialized cells and tissues and starts to form most organs.
4. What happens when an embryo grows?
The embryo is constantly growing, with several remarkable changes beginning to form and grow at every stage. By the end of the 1st trimester, the embryo is called a fetus.
5. Is an embryo a baby?
An embryo is a baby in its early stage of development, in which critical organs and body structures are formed. The embryo is considered to be the early stage of human development. The terms embryo and fetus refer to the developing baby inside the mother’s womb.
6. Does an embryo have a heartbeat?
An embryo at 6 weeks does not have a fully formed heart. Rather, the embryo has a cluster of cells that eventually forms into a heart. This cluster of cells emits electrical signals, which can be detected on an ultrasound. Usually, the heartbeat can be detected by ultrasound somewhere between 6 ½ – 7 weeks.
7. What is the 14-day rule embryo?
The ’14-day rule is an international ethical standard for human embryo research that limits research on human embryos to a maximum period of 14 days after their creation through In-vitro fertilization or to the equivalent stage of development normally attributed to a 14‐day‐old embryo. It has been in place for decades and written into law in many countries.
8. How do I know implantation has occurred?
The following symptoms are indications that implantation has occurred.
- Cramps in stomach
- Spotting or implantation bleeding
- Sensitive breasts
- Mood swings
- Changing tastes
- Blocked nose
- Constipation
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Embryo Growth! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Source:
- Fetal Development: Stages of Growth. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7247-fetal-development-stages-of-growth Accessed on 1 Dec 2021
- Fetal development week by week. https://www.babycenter.com/pregnancy/your-baby/fetal-development-week-by-week_10406730 Accessed on 1 Dec 2021
- Introductory and General Biology. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology Accessed on 1 Dec 2021
- Embryo Growth. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.66/primary/lesson/embryo-growth-and-development-bio/ Accessed on 1 Dec 2021