Immunodeficiency Study Guide
Introduction
The main protectors of our body, the white blood cells, are released by the immune system. These white blood cells are divided into B cells and T cells. Antigens, which are invaders, are combated by B and T cells.
B cells produce antibodies that are particular to the sickness that your body identifies. T lymphocytes eliminate alien or abnormal cells. Some of the antigens include bacteria, viruses, cancer cells, and parasites.
Immunodeficiency makes it difficult for your body to fight infections and illnesses. This condition makes it much easier for your body to be attacked by external pathogens and for you to get viral and bacterial illnesses.
Immunodeficiency diseases can be inherited or acquired. Acquired diseases, often known as secondary disorders, occur later in life. Acquired disorders are more common than congenital disorders, which are present from birth.
What is an immunocompromised disease?
- Immunocompromised people have a reduced ability to fight infections and other diseases.
- This may be caused by certain diseases or conditions, such as AIDS, cancer, diabetes, malnutrition, and certain genetic disorders.
- It may also be caused by certain medicines or treatments, such as anticancer drugs, radiation therapy, and stem cell or organ transplant (also called immunosuppression).
Symptoms of Immunodeficiency Disorders
- Infections tend to occur and recur frequently in people with immunodeficiency disorders
- Typically, respiratory infections (such as sinus and lung infections) are the first to appear and reoccur often
- Most people ultimately suffer serious bacterial infections that persist, recur, or cause problems
- Catching a cold several times does not necessarily indicate that the individual has a disorder
- Infections of the mouth, eyes, and digestive tract are common
- Thrush, a fungal infection of the mouth, may be an early sign of an immunodeficiency disorder
- Sores may form in the mouth
- People may have chronic gum disease (gingivitis) and frequent ear and skin infections
- People with certain immunodeficiency disorders may have many noticeable warts (caused by viruses)
- Other symptoms differ according to the intensity and length of the illnesses.
- Many patients have fevers and chills and a loss of appetite and weight
- Abdominal discomfort may occur, potentially resulting from an enlarged liver or spleen
- Infants and young children who have persistent diarrhea may not grow and develop normally
- Immunodeficiency may be more severe if symptoms appear in early childhood rather than later in life.
Common causes of Immunodeficiency Syndromes
A variety of factors can cause immunodeficiency. The most prevalent causes worldwide are HIV, malnutrition, and unhygienic environments. However, around one in every 500 patients have intrinsic or primary immunodeficiency. Here are the most prevalent problems.
Autoimmune disordersSeveral autoimmune diseases damage the immune system. Among these conditions are:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- IBD (Irritable Bowel Disease)
- Psoriasis
As you can see, several autoimmune illnesses are caused by the body attacking itself. These circumstances, however, can make the immune system less efficient, leading to immunodeficiency or immune system disorders.
Acquired immunodeficiencies
There are several acquired causes of immunodeficiency, which means that immunodeficiency is the outcome of another ailment. These acquired immunodeficiencies are most frequently associated with:
- Malnutrition
- Stress after surgery
- Diabetes
- Cancer of the lymph nodes
- Anesthesia influences
- Chronic viral infections
When these disorders create immunodeficiency, the first approach is to seek therapy for the underlying ailment. After that, you must treat the immunodeficiency to guarantee that your body can fight infections and viruses.
Signs of a Weak Immune System
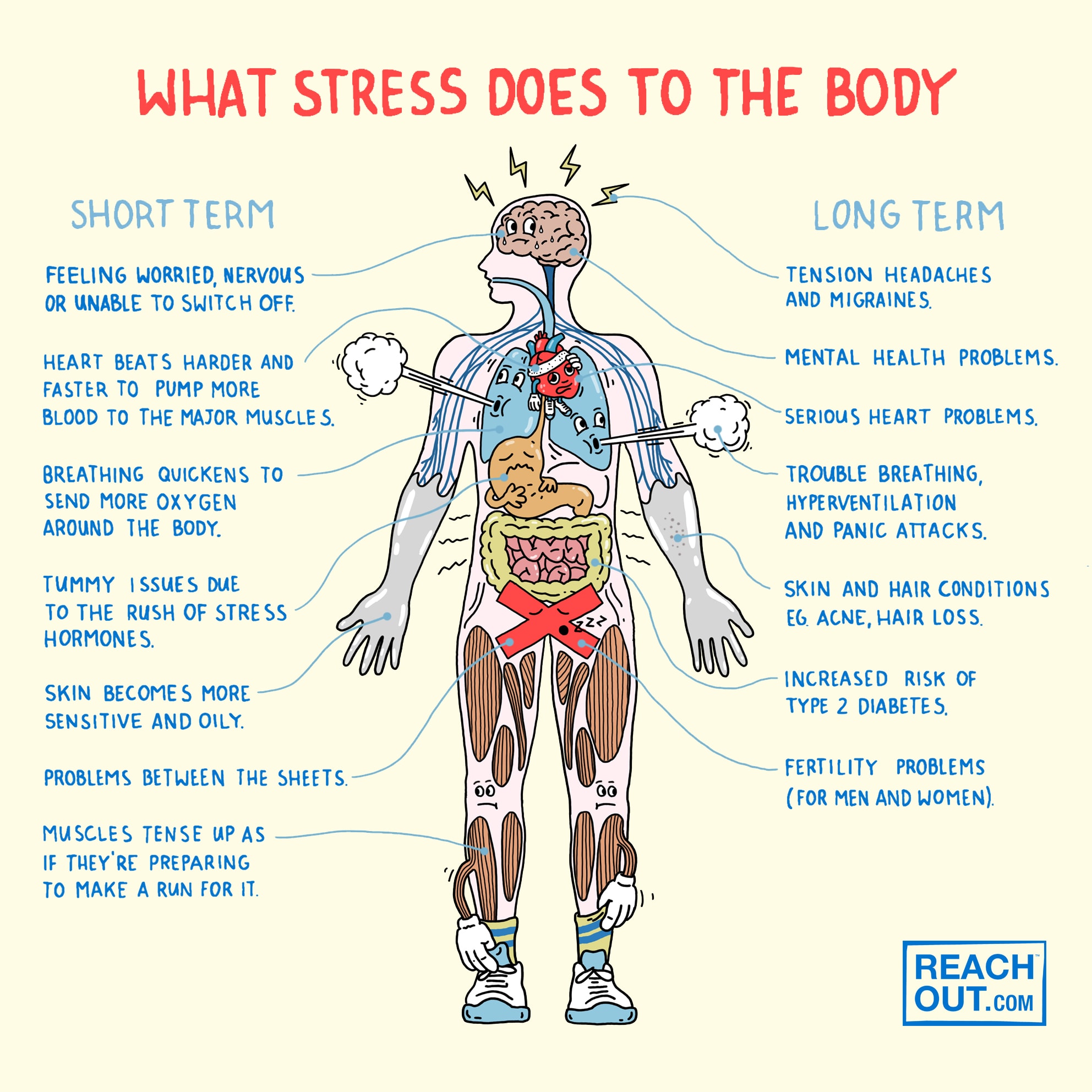
1. Stress Levels
Long-term stress impairs your immune system’s reaction. Stress reduces the body’s lymphocytes, white blood cells that assist the body fight illness. The lower your lymphocyte numbers, the more vulnerable you are to viruses such as the common cold.
2. Cold
Adults are entirely typical to sneeze and snuff their way through two or three colds every year. Most people recover in seven to ten days. It takes the immune system three to four days at that period to develop antibodies and fight off troublesome viruses. However, contracting common cold regularly – or having a cold that won’t go away – is a clear indication that your immune system is straining to keep up.
3. Slow healing of wounds
When you have a burn, cut, or scrape, your skin goes into damage management mode. Your body strives to protect the wound by delivering nutrient-rich blood to the site of the damage to aid in the regeneration of new skin. Healthy immune cells are required for this healing process to take place. However, if your immune system is weakened, your skin will not be able to repair. On the other hand, your wounds persist and are difficult to cure.
How can you avoid immunodeficiency disorders?
The strategies for avoiding and treating infections differ depending on the immunodeficiency condition. People who have an immunodeficiency condition owing to a lack of antibodies, for example, are at risk of bacterial infections.
The following measures can help lower the risk:
- Taking care of one’s personal hygiene (including conscientious dental care)
- Not eating raw or undercooked food
- Not ingesting potentially tainted water
- Avoiding interaction with infected individuals
- Maintain good hygiene. After using the restroom and washing your hands with light soap before eating.
- Take proper care of your teeth. Brush your teeth twice a day, at the very least.
- Eat healthily. A healthy, well-balanced diet can help keep illnesses at bay.
- Engage in some physical activity. Maintaining a healthy level of fitness is critical to your overall health. Inquire with your doctor about the activities that are acceptable for you.
- Get adequate rest. Try to sleep and wake up at regular timings every day, and obtain the same number of hours of sleep each night.
- Control your tension. According to certain research, stress might impair your immune system. Massage, meditation, yoga, biofeedback, and hobbies can help you manage your stress. Find out what works best for you.
- Avoid becoming exposed. Avoid persons who have colds or other diseases, and avoid crowds.
- Inquire with your doctor about vaccines. Determine which ones you should have.
Conclusion:
- Immunocompromised people have a diminished capacity to fight infections and other disorders.
- Certain diseases or circumstances, such as AIDS, cancer, diabetes, malnutrition, and certain genetic abnormalities, may contribute to this.
- Certain medicines or therapies, such as anticancer drugs, radiation therapy, and stem cell or organ transplant, may also cause it.
FAQs:
1. What are some common immunodeficiency diseases?
Some of the common immunodeficiency diseases are listed below:
- Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome (ALPS)
- APS-1 (APECED)
- CARD9 deficiency and other syndromes of susceptibility to candidiasis
- Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)
- Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)
2. What can cause a weak immune system?
A weakened immune system can be caused by various reasons such as food, certain drugs, infections, or having an autoimmune illness. If you experience frequent colds, difficulties fighting infections, persistent exhaustion, or stomach problems, you may have a compromised immune system.
3. What are 3 possible reasons for immunodeficiency?
Malnutrition, poor hygienic conditions, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are the most prevalent causes globally.
4. What is low immunity called?
Low immunity is known as ‘Immunodeficiency.’
5. What are the signs of a weak immune system?
Signs of a weak immune system include frequent cold, infections, digestive problems, delayed wound healing, skin infections, fatigue, organ problem, delayed growth, a blood disorder, and autoimmune diseases.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Immunodeficiency! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Immunodeficiency https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.53/primary/lesson/immunodeficiency-bio/ Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.
- immunocompromised.https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/immunocompromised Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.
- 6 Signs You Have a Weakened Immune System.https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2020/march/weakened-immune-system Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.
- Immunodeficiency Disorders.https://www.healthline.com/health/immunodeficiency-disorders Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.
- Overview of Immunodeficiency Disorders. https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-in/home/immune-disorders/immunodeficiency-disorders/overview-of-immunodeficiency-disorders Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.