Menstrual Cycle Study Guide
Introduction
Every month, the female body undergoes natural changes, referred to as a menstrual cycle. Menstruation begins at puberty and stops at menopause. The cycle lasts on average 28 days; however, it can last anywhere from 20 to 40 days. The initial day of a cycle corresponds to the start of a menstrual period, and the end day corresponds to the start of the next period.
First Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle usually begins between 8 and 15 when a girl reaches puberty (average age of 12). It normally begins two years after physical changes in the female body, such as the development of breasts and pubic hair, have occurred.
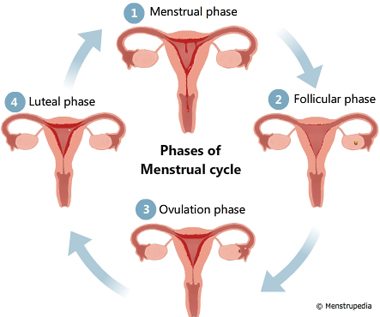
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
There are four basic phases of the menstrual cycle:
1. Menstruation
-
Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine wall’s internal lining and other fluids from the body through the vaginal canal.
-
It normally lasts three to seven days; however, this might vary from month to month and depend on the individual.
2. Follicular phase
- The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and concludes when ovulation occurs.
- The pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain) produces a follicular stimulating hormone(FSH) during this stage.
- This hormone causes the ovary to develop 10 to 20 follicles containing an immature egg.
- These follicles produce estrogen, which thickens the endometrial lining to receive a fertilized egg.
- Only one follicle often matures and goes to the ovarian surface, while the others disintegrate and are absorbed back into the body.
3.Ovulation
Ovulation usually happens 12 to 16 days before the next period, although not always in the middle of the cycle. The production of a mature egg by either of the ovaries is called ovulation.When estrogen is released during the follicular phase, the brain produces the gonadotropin-releasing hormone, which induces the pituitary gland to generate more luteinizing hormone.The mature egg is retrieved from the follicle (cyst) and transported from the ovary to the fallopian tube in this way.
If fertilization does not occur during this phase, the egg enters the uterus and disintegrates within 6 to 24 hours.
4. Luteal phase
- The follicle from which the mature egg emerges (now known as the corpus luteum) produces a substantial amount of progesterone and some estrogen during this period.
- The two hormones work together to build and maintain the endometrial lining.
- The yellow body or the corpus luteum disintegrates, and progesterone levels drop if fertilization does not occur, leaving the lining vulnerable.
- The lining then fades away, marking the start of a new menstrual cycle.
Terminologies of the menstrual cycle:
– Menarche: It is the age at which a teenage girl’s menstruation begins.
– Amenorrhea: It is a condition in which a woman does not have a period for six months or more. When a teenager does not start having a period, it is called primary amenorrhea, and when a woman ceases having periods, it is called secondary amenorrhea.
– Oligomenorrhea: is a condition in which a woman’s periods are irregular and occur every 35 days to every 6 months.
– Dysmenorrhea: The presence of painful periods.
– Perimenopause: is the time preceding menopause, which can last anywhere from a few months to a few years. During perimenopause, a woman’s ovulation is irregular, and her periods are irregular, ranging from monthly to every few months. She may also suffer menopausal symptoms like hot flashes regularly.
– Menopause: occurs when a woman’s ovaries cease ovulating and produce enough hormones, resulting in a year of no periods. Hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and other symptoms may accompany menopause.
Conclusion:
- Every month, a woman’s body undergoes natural changes in preparation for pregnancy, referred to as her menstrual cycle.
- The menstrual cycle usually begins between the ages of 8 and 15 when a girl reaches puberty (average age of 12)
- There are four basic phases of the menstrual cycle- menstruation, follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase.
FAQs:
1. What are the menstrual cycle days?
The duration of the menstrual cycle varies from woman to woman. The average duration of the period is around 28 days, but a range of 21-40 days is considered normal.
2. What causes the menstrual cycle to change dates?
The most common cause of this is age-related hormonal imbalances. Some other factors may also include stress, change in lifestyle, certain medical conditions, or side effects of certain drugs.
3. How do you calculate your cycle?
The duration of one’s menstrual cycle can be measured by the number of days from the first day to the first day of your next period.
4. What are the four stages of the menstrual cycle?
- Menstruation
- Follicular phase
- Ovulation
- Luteal phase.
5. When does a girl ovulate?
Ovulation generally occurs 12-14 before the next period.
6. What is menopause?
Menopause is when a woman’s ovaries cease ovulating and produce enough hormones, and she goes a year without having a period. Hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and other symptoms may accompany menopause.
7. What happens in the body of a female during the menstrual cycle?
During the monthly menstrual cycle, the uterus prepares for implantation of the zygote. This includes an increase in the thickness and glandularity of the uterus. If fertilization does not occur, the progesterone and estrogen level in the blood falls, shedding the uterine wall. The tissue, along with blood, passes through the cervix and comes out through the vagina.
8. What is the longest menstrual cycle?
Although the typical menstrual cycle has an average duration of about 28 days, this number varies from woman to woman. In some, the menstrual cycle can also extend up to 40 days. Lack of menstrual for more than 40 can be indicative of pregnancy.
9. Does every girl get their period?
The menstrual cycle is a natural process. Most girls get their periods towards the end of puberty. If the menstruation has not started till the age of 15, this could indicate primary amenorrhea.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Menstrual Cycle! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Menstrual Cycle. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.64/primary/lesson/menstrual-cycle-bio/. Accessed on 30 Nov, 2021.
- What is the Menstrual Cycle?. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.64/related/lecture/what-is-the-menstrual-cycle/. Accessed on 30 Nov, 2021.
- Normal Menstruation. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/10132-normal-menstruation. Accessed on 30 Nov, 2021.
- Menstrual cycle: What’s normal, what’s not. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/menstrual-cycle/art-20047186. Accessed on 30 Nov, 2021.