Muscular Contractions Study Guide
Introduction
Contraction of muscles is the muscles’ shortening, tightening, and lengthening when you do some activity. You can feel the muscles contraction when you hold them, or you pick up something. You also feel it when you exercise or stretch!Contraction and relaxation of muscles go hand-in-hand. Muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation when the contracted muscles get back to their normal state.
What causes muscle contraction?
Muscles play various roles in the body, and there are many reasons why the contraction of muscles is important.
- It offers stability to the connective tissues and joints. The muscles could shorten and lengthen involuntarily, as well as when the body needs them to.
- Muscle contraction also happens to produce heat and to maintain the temperature of the body. Around 40% of the body’s temperature gets connected to muscular work.
- Shivering is a basic response that your body has to colder temperatures. Shivering causes the skeletal muscles to get activated, which end up warming your body.
- Muscular contraction lets you maintain posture. You can sit and stand only because of muscle contraction.
How do muscles contract?
Muscles contain fibers which are called myosin. Based on how you use your muscles, the myosin fiber will either get tightened up or shortened, or it could stretch and loosen. To make a muscle movement, a signal is sent from the brain. This signal travels through the nervous system to the muscles. The muscle then contracts, and this makes your bone move. All of these take place super fast!
Muscle Fibre Structure
To understand the mechanism of muscle contraction, it is first important to understand the structure of the muscle fibers. Muscle contraction happens when the thick and thin myosin filaments slide past each other.
Each muscle fiber is made of many myofibrils, which are composed of two kinds of protein filaments – thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments. The actin filament is anchored to structures that are called Z lines.
The sarcomere is the region that lies in between two Z lines. In the sarcomere, the myosin filament overlaps the actin filament. The myosin filament is made of tiny cross bridges which attach to the actin filament.
Sliding Filament Theory
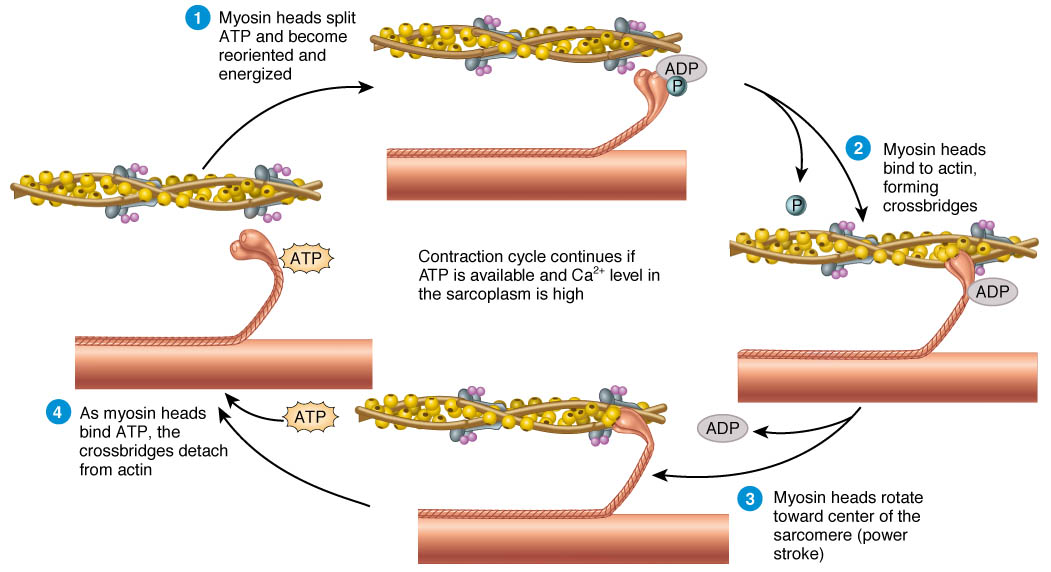
The most widely used theory on how muscle fibers contract is the sliding filament theory. As per this theory, the myosin filament uses energy from the ATP to walk through the actin filament with the cross-bridges. This pulls the actin filament together. This movement pulls the Z lines closer, and this causes the sarcomere to get shortened.
When every sarcomere in the muscle fiber gets shortened, then this causes the fiber to contract. The muscle fiber could either contract fully, or it may not contract at all. The total number of fibers that contract determines the muscular force strength. The force is greater when more fibers contract.
Conclusion
It is important to note that the muscle contraction process does not occur by itself. They need a stimulus from the nerve cell, which tells them when to contract.
For instance, when you wish to raise your hand:
- The brain sends the electrical signals through the nerve cells, the motor neurons in the shoulder and arms.
- The motor neurons then stimulate the muscle fibers present in the shoulder and arm, which contract and cause the arm to rise.
- The involuntary contraction of the stomach and cardia muscles is also controlled totally by the nerves.
FAQs:
1. What are the 4 types of muscle contractions?
The four types of muscle contractions are:
- Isometric is a muscle contraction where the length of the contracted muscle does not change.
- Isotonic is a muscular contraction where the length of the muscle will change.
- Eccentric muscular contraction is an isotonic contraction, but here the muscle lengthens.
- Concentric muscular contraction is an isotonic contraction in which the muscle shortens.
2. What happens during muscular contraction?
During the muscle contraction, the muscle gets stimulated as per the sliding filament theory. This happens through the muscle length, and it generates a force but at the insertion and origin. This makes the muscle shorten and change the joint angle.
3. What is another word for muscular contractions?
Muscular shrinking is another word for muscle contraction.
4. What is the most common type of muscle contraction?
The concentric contraction is the most common type that causes muscle tension when it shortens. When the muscle shortens, it creates a force to move an object.
5. What is the opposite of a muscle contraction?
The opposite of muscle contraction is muscle relaxation.
6. What is the synonym of contraction?
The synonym of contraction is shrinking.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Muscular Contractions! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
Sources:
- Types of Muscle Contractions. https://www.webmd.com/fitness-exercise/types-of-muscle-contractions#1. Accessed 25 Nov, 2021.
- Muscle Contraction. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.10/primary/lesson/muscle-contraction-bio/. Accessed 25 Nov, 2021.
- Muscle Contraction and Locomotion. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-biology/chapter/muscle-contraction-and-locomotion/. Accessed 25 Nov, 2021.