Prenatal Development Study Guide
Introduction
Child development is something that is believed to start from infancy. However, the pregnancy development stages are also a crucial mode of the development process. Prenatal development stages are a span of remarkable changes that then sets the stage for future growth. The brain grows in the prenatal period, and it then continues to grow and change through the initial years of childhood.
Prenatal Development Stages
The prenatal stages are divided into 3 parts:
- The first and second week after fertilization is the germinal stage.
- From the third, all to the 8th week is the embryonic stage.
- The period from the 9th week to birth is the fetal period.
Germinal Stage
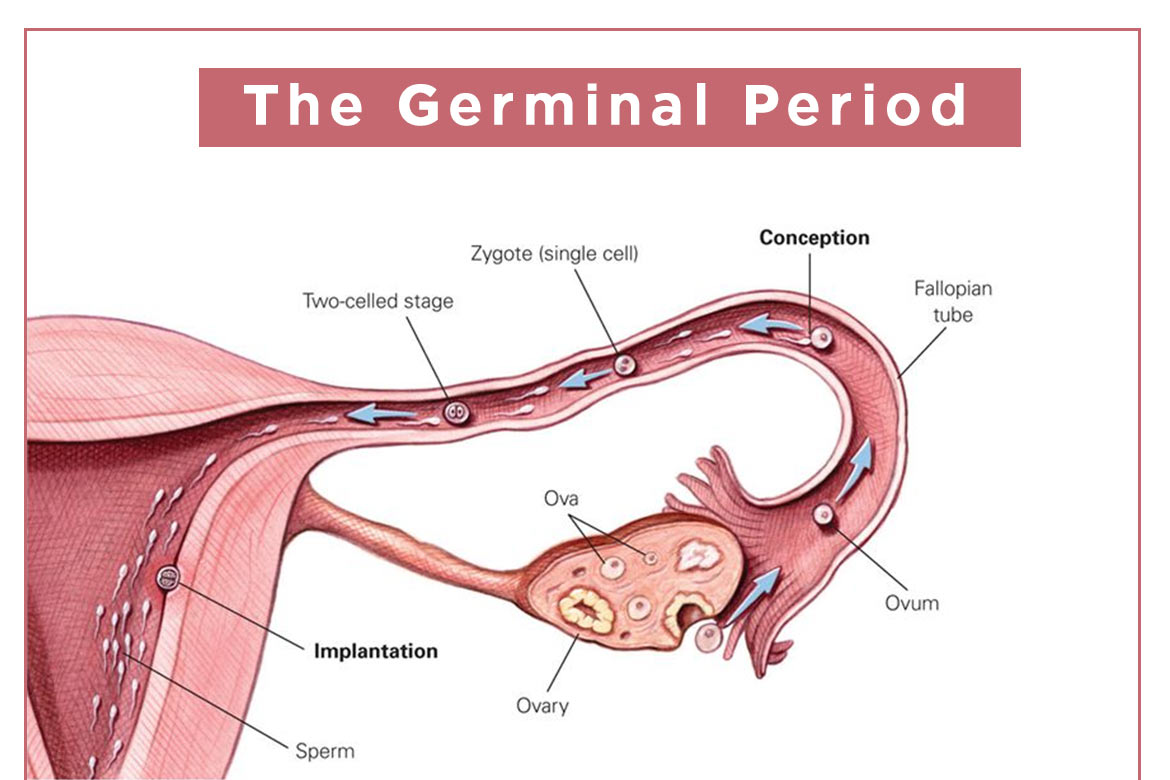
- The germinal stage is the first of the stages of prenatal development. It starts from fertilization when the egg and the sperm meet in one fallopian tube.
- The egg that is fertilized is the zygote. After some hours of fertilization, the single-celled zygote makes a passage down from the fallopian tube and reaches the uterus.
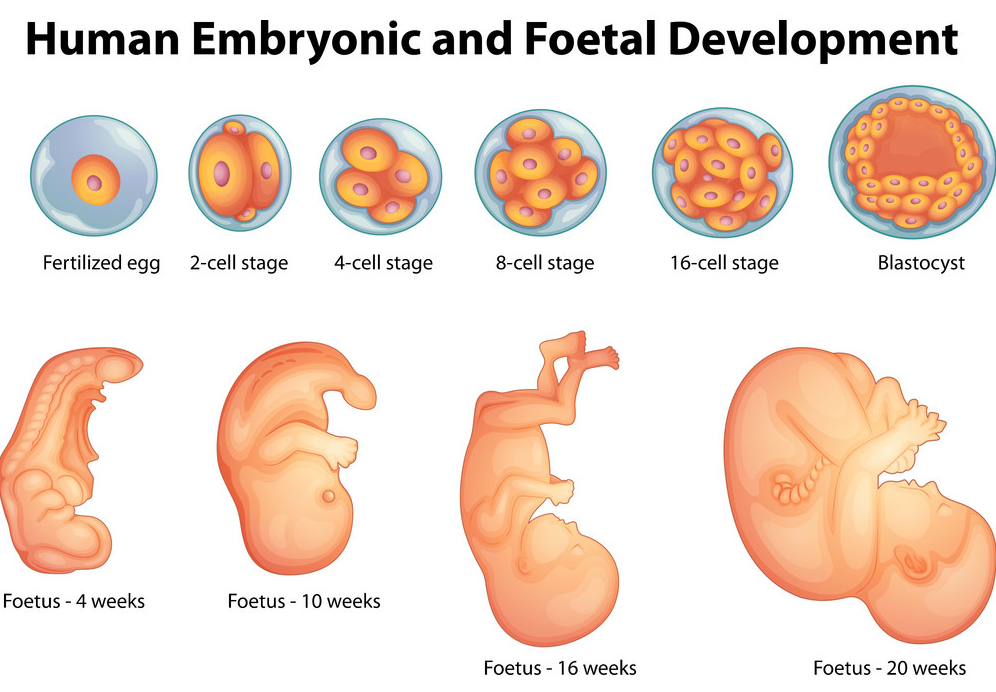
- The cell division starts 24 to around thirty-six hours after the fertilization. The zygote divides itself into 2 cells through mitosis and then doubles itself. Half of the zygotes will not survive more than two weeks, though.
- Once the eighth cell point is reached, the cells start to differentiate on various characteristics, which determine the kind of cell they will finally become. When the cells start to multiply, they separate into separate masses. The outer cell becomes the placenta, and the inner cell becomes the embryo.
- The cell division occurs fast, and this is a week’s journey from the fallopian tube towards the uterine wall. The cells then develop into a blastocyst which is made of three layers. Each of these layers develops into a different human body structure.
- The ectoderm becomes the nervous system and the skin; the endoderm becomes the respiratory and the digestive system, and the mesoderm becomes the skeletal and muscle system.
- The blastocysts then reach the ureter and attach themselves to the uterine wall through implantation. This process happens when the cells sit in the uterine lining.
- The connective blood vessels and the membranes get formed, which offers nourishment. Implantation is not a sure-fire or automatic process.
When implantation takes place, the hormonal changes stop the period’s cycle, leading to many physical changes.
Embryonic Stage
- In the embryo period, the cell mass known as the embryo is formed. This is the start of the third week which is the embryonic periods’ start.
- The cell mass becomes distinct and looks like a human in this stage. The embryonic stage is important because it plays a major part in the child’s development. The neural tube is formed 4 weeks after fertilization. This tube develops into the CNS, including the brain and the spinal cord. The early development signs in the neural tube consist of the 2 ridges that emerge from every side of the neural plate.
- More ridges keep forming now, and once the tube is formed, it begins to develop into brain vesicles. The head starts to form in the fourth week, then led by the ears, mouth, nose, eye, etc.
- In the fifth week, the arms and the legs appear. In the eighth week, the major organs are formed. When the neurons are formed, they move to different brain parts.
- Once they reach the right location, they connect with the other neural cells.
Fetal Stage
- The embryo now has entered the further stage to grow into the fetus. Vital transformations in the brain take place. The fetal period starts from the ninth month until birth. The remaining growth and changes happen in this period.
- The body structure continues to develop. The neural tube grows into the spinal cord and the brain. Synapses begin to develop. Reflexes begin to emerge between the 9th and the twelfth week. The fetus can make its reflexes with its legs and arms.
- The sex organs are formed in the 3rd month, and by the end of this month, all body parts are formed. The fetus grows in length and weight, and the major part of its physical growth will happen in the latter part of the pregnancy.
- The third month of the prenatal period ends with the first trimester. In the 2nd trimester, the heartbeat grows strong, and the other bodily systems develop. The fetus also increases six times in size. The central nervous system and the brain also get very responsive at this stage. The brain matures and functions as that of a newborn.
- From the 7 months until the fetus’s birth, it develops and puts on weight and prepares to live outside the womb. The lungs contract and expand and prepare the muscles to breathe.
Conclusion:
- Prenatal development is how the baby develops from a single cell into an embryo and then to a fetus.
- The average length of prenatal development time is 38 weeks after fertilization.
- A single zygote develops into a full-term baby.
- The three fetal development stages of prenatal development are the germinal, embryonic, and fetal stages.
FAQs:
1. What are the 3 main stages of prenatal development?
The three stages are germinal, embryonic, and fetal development.
2. What do you mean by prenatal development?
Prenatal development is the process of development and growth within the womb. It is important because it prevents complications.
3. What affects prenatal development?
Chronic maternal illness, maternal infections, some toxin exposures, and several nutritional deficiencies are the major factors that affect prenatal development.
4. What do we mean by gestation?
The fetal development period from fertilization until birth is the gestation period.
5. How does fertilization happen?
When the sperm cell swims up through the vagina and enters a woman’s uterus, it joins with the woman’s egg cell. It then travels down through one of the fallopian tubes. this passes from the ovary to the uterus.
6. What is the most important week of pregnancy?
The first trimester from 0 to 13 weeks is very important.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Prenatal Development! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App and check out our awesome VR room for this guide – we promise, it makes studying much more fun 😎
Sources:
- Prenatal Development. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-psychology/chapter/prenatal-development/. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- Prenatal Development. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.67/primary/lesson/fetus-growth-and-development-bio/. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- Stages of Prenatal Development. https://www.verywellmind.com/stages-of-prenatal-development-2795073. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- Prenatal development. http://www.healthofchildren.com/P/Prenatal-Development.html. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.