Skeletal Muscles Study Guide
Introduction:
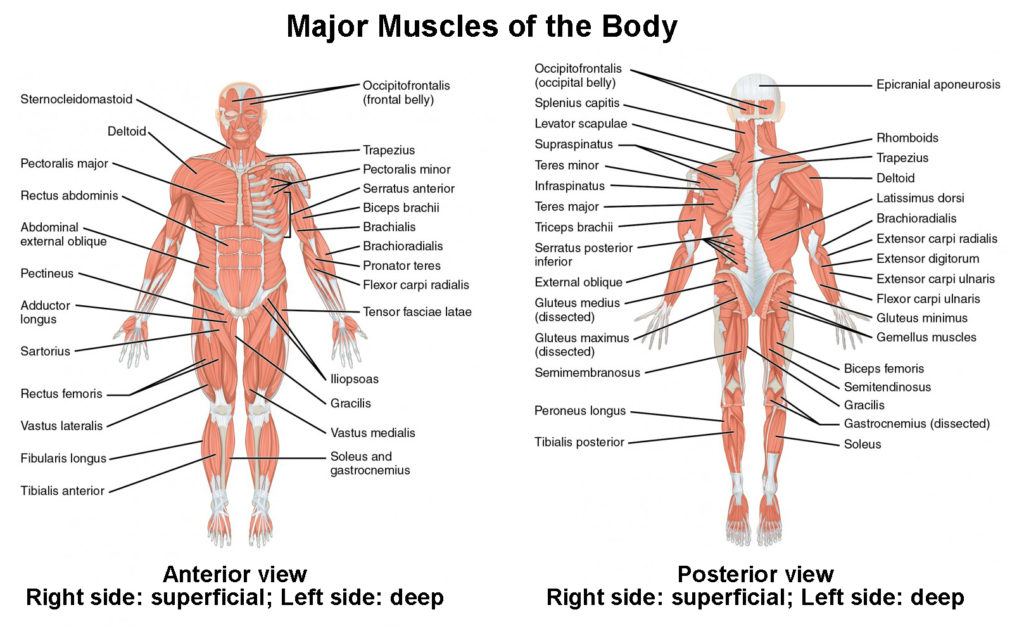
Skeletal muscles are the muscles attached to the bones helping them in movement. These voluntary muscles are found in all the body parts with bones and can move under our will and control. Skeletal muscles examples include head, neck, extremities, spine, chest, and pelvis.
Skeletal Muscle Functions:
- It helps in chewing and swallowing, and aids digestion.
- It helps in breathing by aiding the contraction and relaxation of the ribs of the chest concerning the lungs.
- It helps to maintain body posture.
- It helps to move the body parts in relation to each other.
- It helps in the movement and protection of joints by holding them in appropriate positions.
Skeletal Muscle Structure:
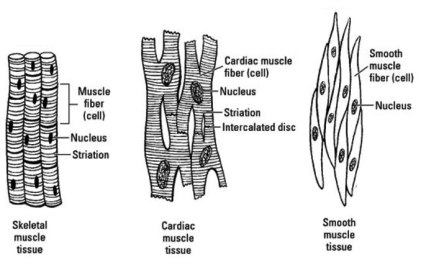
Skeletal muscles like smooth and cardiac muscles appear as bands under the microscope and are also called striated muscles. So the structure of skeletal muscle is typically a structure of striated muscle type. These muscles are long and thin fibers that are multinucleated with alternating red and white lines.
The structure of skeletal muscle includes both macroscopic and microscopic features.
Macroscopic features:
Four hundred types of skeletal muscles in the body range in different shapes, sizes, and functions. Most of the skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and ligaments.
Microscopic features:
- The skeletal muscles are bulky structures that are clusters of muscle cells at the basic level
- These muscle cells group themselves into compartments at hierarchical levels and are surrounded at each hierarchy by a connective tissue sheath:
- Muscle cells group themselves as muscle fibers and are surrounded by endomysium sheath
- These muscle fibers are grouped to form a bundle supplied by nerves and blood vessels and are surrounded by perimysium sheath, and
- The fascicles are grouped to form the muscle tissue which is surrounded by the endomysium sheath.
Muscle Cells and Fibres
-
The two types of muscle fibers are aerobic and anaerobic: red, slow twitching with sustained muscular activity, and white, fast-twitch with rapid and transient muscular activity, respectively.
-
The myofibrils of muscle fibers are made of two types of proteins- thin actin proteins and thick myosin proteins. This alternating protein arrangement in the muscle fibers gives the striated appearance under the microscope for skeletal and other striated muscles.
-
The muscle fibers or the muscle cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, and the cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm. They have more representation by specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum that stores higher calcium levels and is called sarcoplasmic reticulum.
-
Calcium is the messenger chemical involved in the contraction and relaxation of muscles.
The functional unit of the muscle cell or muscle fiber is called the sarcomere, which is the complex arrangement of the proteins constituting the muscle.
- The midline of the sarcomere is the M-line consisting of myomesin.
- The sarcomeres end with a Z-band made of titin proteins.
- I-bands flank the Z-band on both sides of the A-band, in the middle.
- The I-band are thinner regions composed of actin proteins, while the A-band has actin and myosin proteins.
- In the middle of the A-band, is an H-zone with a paler region than the A-band but not the I-band composed of only myosin proteins.
Conclusion:
The skeletal muscle is a complex of all the muscles which performs tasks like walking, running, and lifting through two simple and alternating processes – contraction and relaxation.
FAQs:
1. What is the skeletal muscle function?
It helps in the coordinated movement of the bones to will and control. The muscles in the extremities are typical examples of skeletal muscles.
2. What are the three types of skeletal muscles and examples?
The skeletal muscle is represented by the limbs’ muscles of the heart represents the cardiac muscles, and the stomach muscles represent the smooth muscles.
3. What is the strongest muscle in the human body?
The strongest muscle of the human body is the muscle of the jaw that helps in mastication.
4. Where is a skeletal muscle found?
The skeletal muscles are always found in association with the bones of the body.
5. What are the six major functions of muscles?
The six major functions of the skeletal muscles are to
- Move the skeletal bones,
- Provide support and posture to the body
- Support the soft tissues to stay in position
- They are the hinges at work at entry, and exit points inside and outside the body
- Help maintain the body temperature
- Store nutrients like minerals such as calcium
6. What cells are found in skeletal muscle?
The skeletal muscle comprises the muscle fibers or myofibrils whose fundamental unit is the sarcomere.
7. What makes up skeletal muscle?
The skeletal muscles are sarcoplasm rich in sarcoplasmic reticulum enriched with calcium and have many nuclei, hence, multinucleate.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Skeletal Muscles! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun 😎
Sources:
- Skeletal muscle https://www.britannica.com/science/skeletal-muscle Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Structure o Skeletal Muscle https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/muscular/structure.html Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Skeletal Muscle https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21787-skeletal-muscle Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Skeletal Muscles. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.9/primary/lesson/skeletal-muscles-bio/. Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Skeletal Muscle https://courses.lumenlearning.com/nemcc-ap/chapter/skeletal-muscle/ Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Skeletal Muscle https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/skeletal-muscle Accessed Nov 26, 2021.