STIs: How They Spread Study Guide
Introduction:
-
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are also called sexually transmitted disease (STD).
-
STDs are acquired by sexual contact with the virus, bacteria, and parasites that cause the STI to pass the infection from one to the other person.
-
The germs are passed through blood, semen, and vaginal and bodily fluids.
-
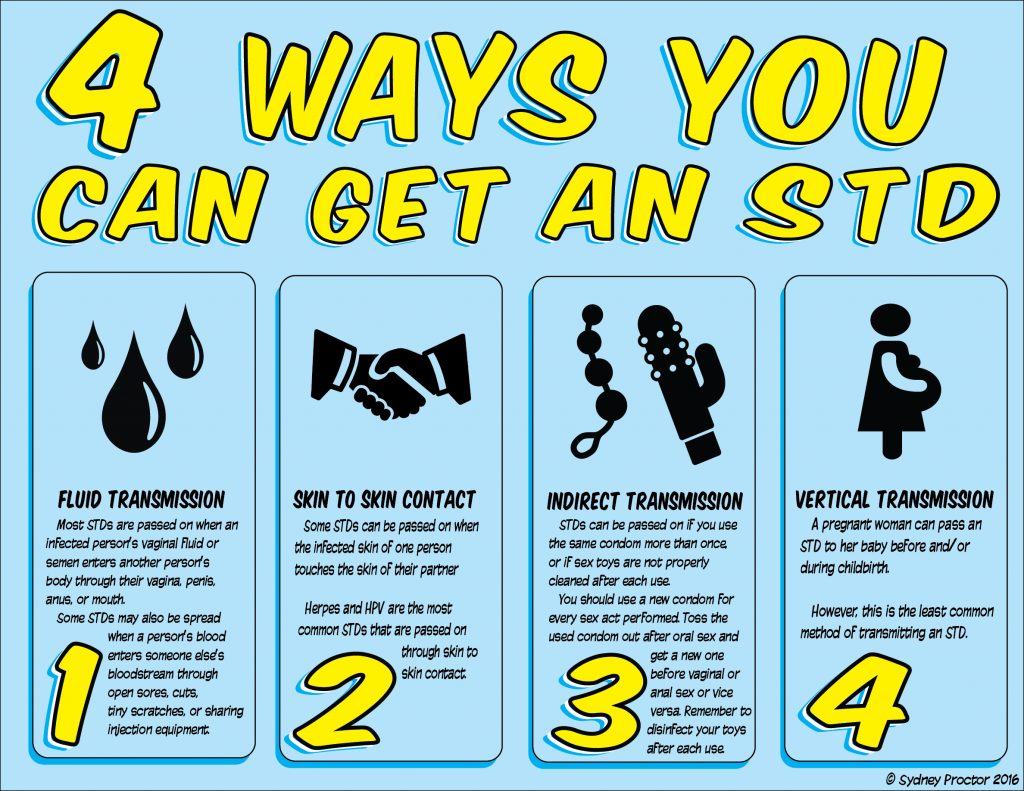
At times the infections are passed non-sexually as well. A mother can pass on the STI to her child during pregnancy or childbirth. The STIs can also spread when needles are shared or through blood transfusion.
-
STIs may not always be symptomatic. You may have a sexually transmitted infection from those who are healthy and may not even know that they have an infection and thus show no STD symptoms.
Causes of STIs
- The main cause of an STI are viruses and bacteria that grow in moist and warm places in the body.
- The virus is passed from one person to the other through sex.
- The infection can spread from the mouth, vagina, penis, or anus.
- The infection can be minor, or it can also be painful.
- Some infections are life-threatening as well.
Some common STIs:
- Chlamydia
- Syphilis
- Genital Warts (HPV)
- Gonorrhea
- Hepatitis B (HBV)
- Genital Herpes
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
- Trichomoniasis
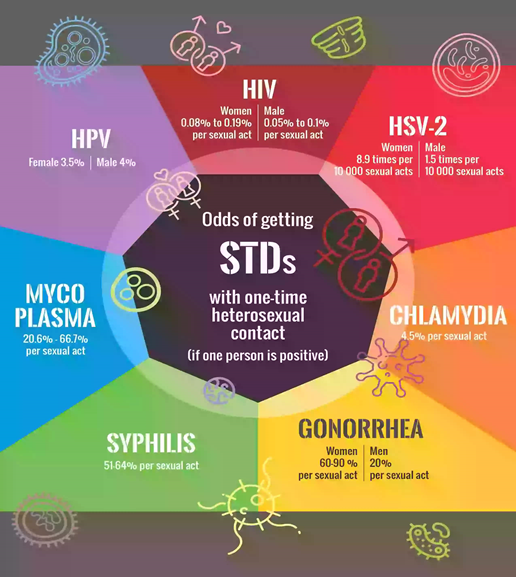
How do these Diseases spread?
STIs can be transmitted through:
- Direct contact with a sore or lesion
- Close public contact like in the case of pubic lice
- Exposure to infectious blood
- Contact with semen or vaginal fluid of an infected person
- Sharing of needles with an infected person
Types of STIs
STIs are of three types: bacterial, parasitic, and viral.
-
Bodily fluids like semen, vaginal secretions, blood, saliva can contain the virus.
-
A person can also get an STI when he comes in contact with the fluid that contains the virus or bacteria. It is thus recommended to use condoms to avoid coming in contact with bodily fluids during sex.
-
STIs like herpes can pass through direct skin-to-skin contact. It happens through anal, oral, or vaginal sex. It can also pass from the mouth to the genitals when one has oral sex.
-
STIs like hepatitis and HIV can pass through the infected person’s blood. If the infected sexual partner has an open sore, they can pass it. Also, when needles are shared, one is exposed to STI’s.
-
Parasitic STIs like pubic lice pass through close contact with the infected person. It can be transmitted disease through clothing and sheets when one comes in close contact with pubic hair.
-
It is important to know that STIs do not spread through casual contact. Sharing clothes, shaking hands, or sharing a toilet seat do not cause STIs.
Risk and Diagnosis
-
Anyone can get STD. It is, however, more common among young adults and teenagers, that do not take adequate precautions while engaging in sexual activity. Drug users who share needles are also prone to STIs.
-
STIs can be diagnosed by a healthcare professional. They will take a fluid sample of the penis or vagina and a blood test to confirm the problem, and a lab test will confirm if you have a viral or bacterial STI.
-
Blood tests are done to show if you have a disease that has infected your blood.
-
Urine samples show if the bacteria is present in your urine.
-
Fluid samples show if you have any active sore, and this can help to diagnose the infection.
Prevention
It is important to avoid the risk factors of STIs. This is the only way to prevention of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Use a dental dam or a condom to reduce the risk of catching the infection through bodily fluids.
- Using oil-based lubricants as water-based lubricants may make the condoms break.
- It is important to undergo regular testing, especially before having sex with a new person.
- There are vaccines to protect against HPV and hepatitis
- Using sterile and safe needles also keeps you healthy and saves you from infections.
- Make sure to stay safe, and get regularly tested!
Treatment
The kind of STD disease determines its treatment. Treatments could help relieve the symptoms, cure the infection or prevent the symptoms from flaring up again. It is possible that STI can pass on to the partner even during the treatment.
- Some common STI treatments are antibiotics. Infected people should complete the full antibiotic course and not have sex unless the treatment is complete.
- Antiviral medications can prevent outbreaks. Here the infected person can still transmit the disease to a partner.
- Lotions and creams may be prescribed in sores or to treat pubic lice.
- Anyone who feels that they could have STI should contact the doctor. It is important to follow all the treatment guidelines to avoid the spread of STIs.
Conclusion:
- STIs are sexually transmitted diseases
- There can also be sexually transmitted diseases passed without sexual intercourse, through the use of infected needles, and blood to blood contact
- Using condoms and taking preventive measures can prevent the spread of STIs
- One should get checked regularly to see if they have STI
- STI spreads through skin to skin contact, bodily fluids, and also by sharing sheets
FAQs:
1. What are the 4 ways most STIs are spread?
Vaginal sex, oral sex, anal sex, and needles are the 4 ways that spread STI.
2. How can you tell if someone has an STI?
The common symptoms are:
- Clear, greenish, white, or yellowish vaginal discharge.
- Discharge from penis.
- Vaginal odor.
- Vaginal itching.
- Itching inside the penis.
- Painful sexual intercourse.
- Painful urination.
3. Can you get an STI from a toilet?
The virus cannot thrive on a hard surface outside the human body. Thus you cannot get STI from a toilet.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about STIs – How they Spread! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- How to Prevent Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs). https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/how-to-prevent-stis#:~:text=A%20person%20with%20an%20STI,your%20health%20can%20be%20affected. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sexually-transmitted-diseases-stds/symptoms-causes/syc-20351240. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- What are Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) or Diseases (STDs)?. https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/s/sexually-transmitted-infections. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- STIs. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.72/primary/lesson/sexually-transmitted-infections-bio/. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.
- STDs: How do you get one?. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/327267#summary. Accessed 2 Dec, 2021.