Urinary System Study Guide
Introduction
The urinary system forms a major part of the excretory system of the body. It consists of the kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. The urinary system takes blood into the kidneys and filters it to remove the cellular metabolic waste collected from all the organs to form urine. The urine is stored in the urinary bladder until it can be eliminated from the body.
Parts of the Urinary System
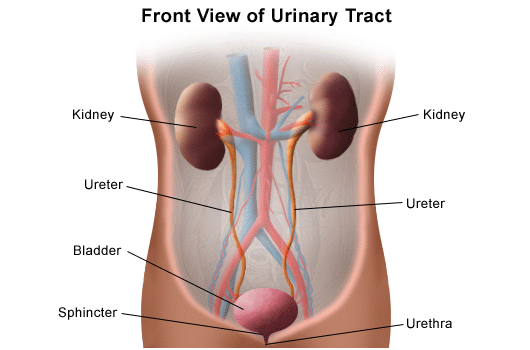
The urinary system can be primarily divided into: the kidneys, the ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. This diagram of the urinary system shows all the organs and their respective positions:
Kidneys
The kidneys are dark, bean-shaped structures measuring 10-12 cm in length and 5-7cm in width. They weigh about 120-170 grams. The anatomy of the kidney can be simplified into 2 major structures:
-
Outer renal cortex: This part of the kidney houses the glomerulus and the convoluted tubules. The renal capsule surrounds the outer cortex and provides space for the glomerulus’s renal artery, veins, and capillaries.
-
Inner renal medulla: The inner renal medulla is the smooth part within the kidneys that houses the renal pyramids and Loop of Henle. Each kidney has over a million functional units called nephrons which do the filtering.
This kidney diagram labeled gives a simple view of the internal structures of the kidneys:
Ureter
- The ureter’s function is to connect each kidney to the renal pelvis.
- The ureters are a thin muscular tube that helps in pushing the urine to the urinary bladder.
- In the general urinary system diagram, the ureters are long, tube-like structures.
Urinary Bladder
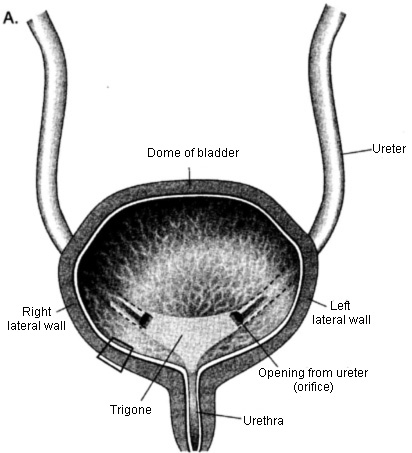
- The urinary bladder is a muscular organ that stores the urine until it can be passed.
- It sits above the pubic bone and has a capacity of 400-600ml in a fully grown adult.
- The urinary bladder function is to hold the urine until it can reach full capacity and discharge it in a process called micturition.
- A muscular tissue that lines the bladder contracts to squeeze the urine out of the urethra.
Here is the diagram of the urinary bladder showing the structures that make up the organ:
Urethra
- The urethra is a muscular tube that starts from opening the urinary bladder and runs through the pelvic region to open outside of the body.
- The function of the urethra is to work in tandem with the urinary bladder to squeeze urine out of the body by relaxing the sphincter.
Conclusion
- The urinary system organs work together to produce, store and excrete urine out of the body.
- The kidneys filter the blood in its nephrons to separate the waste and send it in urine.
- The urine flows down the ureters and collects in the urinary bladder.
- When urinating, the brain triggers the micturition process and relaxes the sphincter in the urethra to pass the urine.
FAQs:
1. What are the 7 functions of the urinary system?
The 7 urinary system functions are:
- Removing cellular metabolic waste
- Removing toxins, medicines, or other ingested substances
- Balance the fluids in the body
- Balance the electrolyte levels in the body
- Regulate blood pressure by releasing hormones
- Regulate red blood cell production
- Control calcium and phosphorous levels in the blood
2. What are the 3 main parts of the urinary system?
The 3 main parts of the urinary system are the kidneys, the ureters, and the urinary bladder.
3. What is the functions invloved in the urinary system?
The kidneys filter blood to make urine which is passed through the ureters into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder holds the urine until it can be excreted through the urethra.
4. Which is the main organ of the urinary system?
The kidneys are the main organs of the urinary system as they do all the filtering of the blood.
5. Where is the kidney located in the body?
The kidneys are located just below the ribcage in the backside of the body.
6. What is urine made of?
Urine is made up of water, all the waste products produced by the body, such as uric acid, urea, and electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and sulfates.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Urinary System! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
Sources:
- Picture of the Kidneys. https://www.webmd.com/kidney-stones/picture-of-the-kidneys. Accessed on 25 Nov, 2021.
- The Truth About Urine. https://www.webmd.com/urinary-incontinence-oab/truth-about-urine. Accessed on 26 Nov, 2021.
- Urinary System. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.42/primary/lesson/urinary-system-bio/. Accessed on 26 Nov, 2021.
- Anatomy of the Urinary System. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/anatomy-of-the-urinary-system. Accessed on 26 Nov, 2021.