Lipids Study Guide
Check out awesome, educational VR rooms on Inspirit’s mobile app (available for iOS and Android devices)🤩
Introduction
Lipids is another word for fats stored in the body. The human body has the ability to store caloric energy in the form of fat which can be used for future purposes. For instance, it can help us survive even during times of famine. Normal fat reserves are a sign that the human body’s metabolic processes are efficient and that the person is healthy.
What do Lipids include?
Lipids belong to the organic compounds family and are mostly insoluble in water.
- These contain oils, lipids and fats and perform a very vital role.
- They are a structural component of the cell membrane.
- They are an energy storehouses and signaling molecules.
Lipids are of three main types. These are triacylglycerols, phospholipids, and sterols.
1. Triacylglycerol
- This makes up 95% of the lipids in our diet and is found in fried foods, whole milk, vegetable oil, cream cheese, etc.
- Olives, avocados, nuts, and corn contain triacylglycerols naturally.
- These are what we commonly refer to as oils and fats.
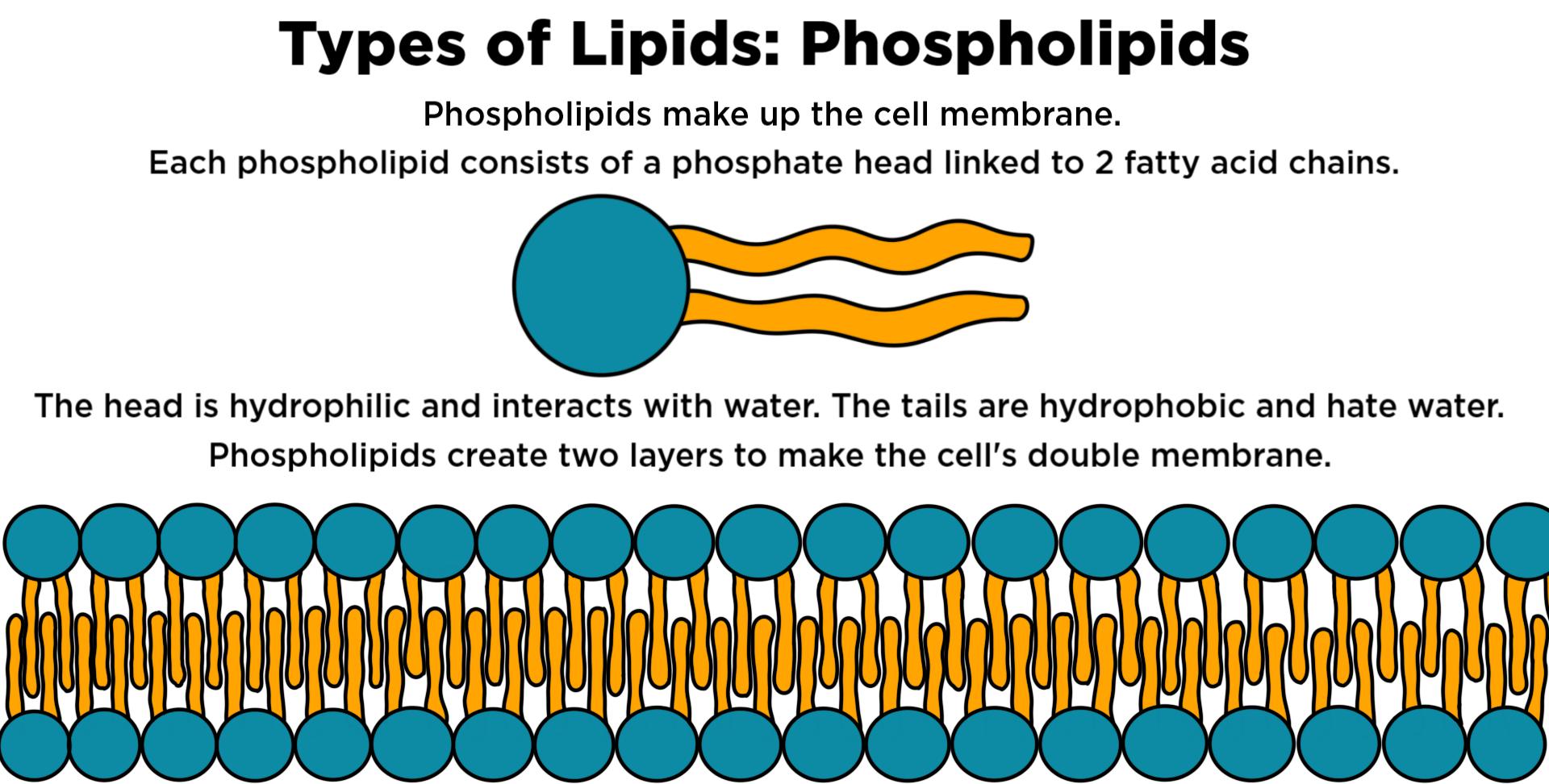
2. Phospholipids
- Phospholipids make up just 2% of the dietary lipids.
- These are water-soluble and are found in animals and plants.
- They are a protective barrier around the cells of the body as they form the cell membrane and organelle membranes present in the cells.
3. Sterols
- The most popular of sterol is cholesterol.
- The body gets only a tiny amount of cholesterol through food as our body produces most of it.
- Cholesterol is a crucial component of the cell membrane and also synthesizes the sex hormone, bile salts, and vitamin D.
The role of Lipids in the human body
Lipids are stored or synthesized to support the cells and assist in several essential processes. There are many external uses of lipids. Along with protecting the cells, here are some crucial ways lipids work in the body.
Nervous System – Lipids are found in the myelin sheaths, an integral part of our nervous system. They protect the nerve cells as they are made of fatty tissue sleeves. They also increase impulse conduction.
Vitamin Absorption- Lipids let the body use the vitamins, especially helping the body absorb the fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
Hormone Production- Lipids produce certain hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol. These play a role in developing sexual characteristics and controlling metabolism and the immune system. It also helps balance the sodium and water levels, improves the body’s resilience, prevents inflammation, and improves its ability to heal.
Other uses of LipidsAlong with their use in the body, lipids are used in specific industries like cosmetics, skincare, and pharmaceuticals.
- These are used in the cosmetic industry to make several skincare and beauty products like creams and lotions.
- Lipids are used to manufacture steroids used to treat diseases like cancer or to regulate hormones. These may also be added to some drugs to make them last longer or improve drug absorption.
Conclusion
- The main kinds of lipids are triglycerides and sterols like cholesterol.
- The body requires these at healthy levels.
- Any deviation in lipid values from the normal body range is a cause of concern as it can lead to many health issues.
- Lipids play a crucial role in protecting the cells and allowing absorption of some vital vitamins.
- Excess lipids in the body can lead to liver and heart diseases.
FAQs:
1. What are four examples of lipids?
The four types of lipids are wax, fat and oil, steroid, and phospholipid.
2. What are lipids and their function?
Lipids are inorganic compound and are insoluble in water. They function as energy-storing molecules and as chemical messengers.
3. What are lipids and their importance?
Lipids are fats, and these serve many essential roles in the body. They act as a structural component of the cell membrane. They also function as energy storehouses and are important signaling molecules.
4. What is a lipid in the human body?
Lipids are waxy, fatty, and oily compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They are a crucial components of the human body’s homeostasis function and contribute to several vital body processes.
5. Is cholesterol a lipid?
Cholesterol is a type of lipid, also known as fat.
6. Why are lipids essential to the body?
Lipids play a diverse role in the functioning of the human body. They are a source of energy to the living organisms, and an important component of the cells structural building material. They provide more than double the power compared to proteins and carbohydrates based on weight.
7. What happens if you lack lipids?
Insufficient lipids in your body may cause the body to develop dry rashes, a weak immune system, hair loss, and issues related to vitamin deficiencies.
8. What are the terrible effects of lipids?
The body needs healthy energy and fats to carry out its functions. However, too much saturated fat could cause cholesterol levels to build up in the arteries, raising harmful cholesterol levels. This then increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
9. What foods are rich in lipids?
Corn, canola, olive, sunflower oil and soy, peanut butter, some fish, seeds, nuts, dairy products, and animal meat are some foods that are rich in lipids.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Lipids! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun 😎
Sources:
-
What Are Lipids? https://med.libretexts.org/Courses/American_Public_University/APU%3A_Basic_Foundation_of_Nutrition_for_Sports_Performance_(Byerley)/06%3A_Lipids_Basics_-_Another_Energy_Source_for_the_Athlete/6.02%3A_What_Are_Lipids. Accessed on 25 Nov, 2021.
-
What Is a Lipid?. https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-a-lipid-5084584. Accessed on 25 Nov, 2021.
-
Lipids. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/1.12/primary/lesson/lipids-bio/. Accessed on 25 Nov, 2021.
-
The Functions of Lipids in the Body. http://pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu/humannutrition/chapter/the-functions-of-lipids-in-the-body/. Accessed on 25 Nov, 2021.