Scientific Methods, Experiments, and Theories Study Guide
Introduction
This guide covers 5 basic concepts: evolution, cell theory, gene theory, homeostasis, and laws of thermodynamics. As we take a sneak peek into some foundational concepts, it is observed that biology branches into three categories: medical science, the study of plant-based medicines; botany, the study of plants; and zoology, which is the study of animals.
Understanding Biology
A basic understanding of biology is vital for us to learn about life on this earth! The father of biology is considered to be a greek philosopher named Aristotle. His theory of biology is also referred to as ‘Aristotle’s biology’, which encompasses various biological processes like temperature regulation, metabolism, inheritance, information processing, and embryogenesis.
Biology is the study of evolutionary relationships among organisms and the varied diversity of life on Earth. The approach to biology deals with fundamental units of life.
It comprises concepts such as how life grows, develops, how life responds to its environmental surroundings to maintain internal stability, evolution, reproduction, etc.
Biology concepts include the following:
- The study of cells as the basic unit of life
- Units of heredity such as DNA and RNA
- Consumption and transformation of energy
- Internal stability in every living organism
For undergoing any study, adopting a proper scientific method helps acquire knowledge the right way from the right sources.
What is the Scientific Method?
It is a technique used to mathematically and experimentally prove a hypothesis. Precisely, the construction and testing of a scientific hypothesis. It is only through scientific methods that several scientific theories have been derived and found for modern-day study.
- It involves testing the hypothesis and revising the output based on the research findings, the outcome of tests, and experiments.
- Thereby coming up with a revised hypothesis which is finalized on testing the revised hypothesis several times from different approaches.
- Sometimes the knowledge gained is useful in solving specific problems; other times, it is interesting but lacks practical application.
- The scientific method generally requires a systematic and logical search for information via observation and experimentation.
The scientific method’s basic steps are to:
- State a problem based on observations
- Develop a research question or questions
- Form a hypothesis
- Experiment to test the hypothesis
- Collect information
- Record and analyse data
- And form a conclusion.
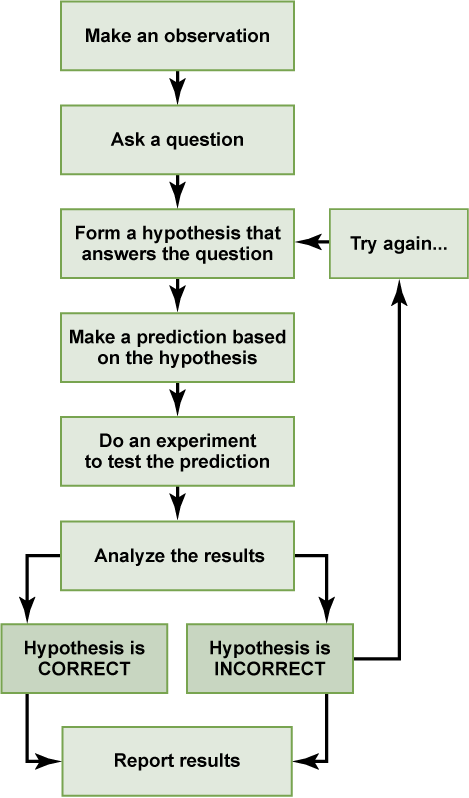
Steps of the Scientific Method
Learning and research in this field involve a minimum of 6 basic steps of the scientific method in order, as mentioned below:
- Careful observations
- Asking questions and being skeptical about observations
- Making assumptions or deriving hypotheses
- Forecast or prediction a behavior
- Test the prediction
- Reproduce the experiment until there is no deviation from the original observation and theory
However, there also need to be exceptions to the scientific method:
- You must be able to test and prove its opposite outcomes for each hypothesis. That is estimating a possible negative outcome.
- There should be a basis for every reasoning. There are two types of reasoning which are deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning uses true premises to reach a logical conclusion, whereas inductive reasoning uses an opposite approach.
- Every experiment must include a dependent variable that does not change and an independent variable that does not change.
- An experiment involves an experiment group and a control group where the two groups are compared, which is the foundation of science. If there is no reproducibility, then there is no science.
Observation
-
The scientific method begins with stating a problem based on observation. At this point, the scientist recognizes that something has occurred and that it occurs regularly. As a result, the scientist formulates a question or states a problem that needs to be investigated.
-
The next step in the scientific method is to look for resources that may contain information about the question or problem at hand. In this stage, the scientist conducts a literature review and collaborates with other scientists to learn about the topic at hand.
Hypothesis, Experimentation, and Analysis
-
Following that, a hypothesis is formed, which means that the scientist proposes a possible solution to the question while acknowledging that the answer may be incorrect.
-
The hypothesis is tested by the scientist using experiments with experimental and control groups. Experiment data is collected, recorded, and analysed.
Theory
If a hypothesis is tested and confirmed frequently enough, the scientific community refers to it as a theory. The theory is then put to the test in a series of additional experiments using rigorous experimental methods. Other scientists may not only repeat the experiments but may also conduct additional experiments to challenge the findings.
Conclusion:
Biological studies have been developed using scientific methods to come to verifiable and proven conclusions that form a part of all the research and findings in every scientific field.
FAQs:
1. How many steps in the scientific method?
There are 5-7 steps to prove your scientific hypothesis by testing it several times in different scenarios.
2. Why is the scientific method important in biology?
Any problem-solving in our day-to-day life opens an opportunity to use the scientific method. Like any other scientific method, each problem is approached by identifying the issue or drawback, making observations based on the number of times, duration, specific properties, and more. Every part of the research to solve the problem is to arrive at the proven answer. Scientists have been able to acquire all the biological knowledge through the scientific method. It is an orderly way of gaining information through observation and experimenting.
3. What are the six basic steps of the scientific method?
The six steps of the scientific method are as below:
- Observe
- Ask questions
- Make assumptions
- Predict behavior or output
- Test the output
- Reproduce the experiment
4. Which of the following concepts is not one of the unifying theories of biology?
- One or more living cells make the composition of all living organisms.
- Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently.
- The basic unit of structure and organization in organisms is the cell.
- All cells come from pre-existing living cells.Option 2 is the answer.The basic principles of biology are cell theory. This theory is credited to Theodor Schwann and Mattias Schleiden, who are German scientists. In cell theory, it is known that cells depend upon the parent cell for enzymes used for replication. Hence option two is the correct answer.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Scientific Methods, Experiments, and Theories! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun 😎
Sources:
- Steps of Scientific method in order. https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1931/2017/05/30180407/figure-01-01-05.png. Accessed Nov 26, 2021
- Scientific Method. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/1.1/primary/lesson/scientific-investigation-bio/. Accessed Nov 26, 2021.
- Scientific Method-Biology. https://www.cliffsnotes.com/study-guides/biology/biology/the-science-of-biology/scientific-method. Accessed Nov 26, 2021.