Cnidarians Study Guide
Introduction:
The cnidarians are part of the animal kingdom, and examples are jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, and hydrozoans. The species can be found throughout the world and are quite diverse. When the cnidarian gets damaged, these can regenerate their body parts, making them immortal.
Facts about cnidarian
Even though the scientific name is ‘Cnidaria’, they go by their common names. Here are some interesting facts about Cnidaria.
- The phylum cnidaria is invertebrates, and their size ranges from ¾ of an inch to 61/2 feet in diameter.
- These can grow to a length of 250 feet.
- The weight of the species can be around 440 pounds.
- The lifespan of Cnidaria is around 4000 years, and these live on a carnivore diet.
- Cnidaria can be found all around the world’s oceans.
Cnidaria description
Cnidaria is of two kinds. These are polypoid and medusoid.
- The polypoid Cnidaria can be distinguished by tentacles and have a mouth that faces up something like the coral or the anemone. The body forms of cnidarians are attached to a colony of the animals or a substrate.
- The medusoid types are like jellyfish, which have a body or a belly on the top, mouth hanging, and tentacles down.
The cnidarian habitat and distribution
Cnidaria are a diverse species in their habitat, and these can be found across the world’s oceans. They are found in temperate polar and tropical waters. Depending on their species, the cnidarian’s habitats can be found across several water depths and close to the shore. These can survive in shallow waters, deep-sea and coastal habitats.
The cnidaria behavior and diet
Cnidaria are carnivorous, and they make use of their tentacles to feed on the plankton and other smaller water organisms. They use their stinging cells to fish when the trigger at the cnidocyte end is activated. This causes the thread to unfurl outwards, turning it inside out. The thread then wraps around and stabs the prey tissue, injecting a toxin.
Some of the Cnidaria, like the corals, are inhabited by algae that go through photosynthesis. This is a process through which it gets carbon to the Cnidaria host. In a group, the Cnidaria can regenerate and reorganize their bodies. This may mean that these are immortal. The oldest of the Cnidaria are the corals in the reef known to live for over 4000 years. There are, however, some kinds of polyp that live just for 4 to 8 days.
Cnidaria offspring and reproduction
Different Cnidaria species reproduce in various ways. These can reproduce asexually, which is by budding. In this process, a new organ grows from the main organism. Or they could reproduce sexually, like when spawning happens. The male and the female release the sperm and the egg in the water column, producing the free-swimming larvae.
The life cycle of the Cnidaria is complex, and this varies within classes. The archetypal life cycle of the Cnidaria starts as zooplankton, and this develops into the sessile polyp stage. The polyps are then attached to the seabed, which buds off into a water-free swimming medusa stage. However, some species stay as polyp-like coral reefs.
Conservation
Cnidaria, like the jellyfish, is likely tolerant to climatic change. Some are thriving and take over the habitat of other forms of life. Corals are, however, threatened because of the environmental damage and the acidification in the oceans.
Cnidaria and humans
Cnidaria may interact with humans in various ways. These are sought in recreational activities like the scuba divers who go to the reefs to see the corals. It is important to know that not all Cnidaria are safe. If you go near them, they may sting.
Some could even be fatal. There are certain Cnidaria that can be eaten. These could be collected for trade to keep in aquariums or make jewelry.
Conclusion:
- Cnidarians in the cnidarian phylum include corals, jellyfish, and sea anemones.
- The animals can be found in the shallow waters of the ocean
- If you step on them, then these animals can sting you. This is one of the cnidarian’s characteristics. It is because they have nematocysts which are the stinging cells.
- The nematocysts are used to catch food.
- When you touch the nematocysts, this releases a poison thread that can paralyze the prey.
- Cnidarians are the simplest of the higher organisms, and they are also the prettiest.
FAQs:
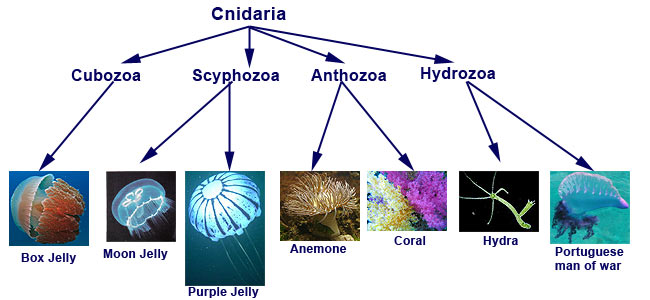
1. What are 5 examples of cnidarians?
- Anthozoa is Corals and sea anemones
- Scyphozoa is the Swimming Jellyfish
- Staurozoa is the Stalked Jellyfish
- Cubozoa, which is the Box jellyfish
- Hydrozoa is the Hydroids and siphonophores
2. What are the characteristics of Cnidaria?
- Aquatic
- Mostly marine
- Organisms
- Have tentacles with stinging cells called nematocysts
3. Why are cnidarians important?
They are predators in the ocean sea. They are a crucial part of the marine ecosystem where they engage in a symbiotic relationship with the other organism. Their predatory activity ensures a delicate balance in the ocean’s food chain.
4. How do cnidarians breathe?
Gas exchange in cnidarians happens through direct diffusion.
5. How do cnidarians move?
They move by jet propulsion.
6. How do cnidarians feed?
The cnidarians use their cnidae and the associated toxin to capture food.
7. Where are cnidarians found in the world?
The cnidarians can be found in all the ocean habitats.
8. How do cnidarians sense their environment?
The nerve net in the cnidarian serves as a sensory locator. The nerve cell stretches around the animal’s body and lets the cnidarian detect any chemical changes. They use these senses to capture the prey and to move in response to stimuli. The expansive nerve net is known as the diffuse nerve net.
*We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Cnidarians! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App and check out our awesome VR room for this guide – we promise it makes studying much more fun 😎*
Sources:
- Cnidarian Factshttps://www.thoughtco.com/cnidaria-phylum-profile-2291823 Accessed on 3 Dec 2021
- cnidarianhttps://www.britannica.com/animal/cnidarian Accessed on 3 Dec 2021
- Cnidarianshttps://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-middle-school-life-science-2.0/section/9.3/primary/lesson/cnidarians-ms-ls/ Accessed on 3 Dec 2021