Plant Evolution Study Guide
Plant Evolution
Like any other living being, plants also undergo a series of evolutionary steps. Over time they adapted, changed, and became what we see today. The evolutionary history of plants has been preserved in fossils. These fossils date back to some 400-500 million years back. It is believed that the evolutionary development of the plant kingdom is basically due to the invasion of the photosynthetic multicellular organisms to the continents.
The fossil records of the plants have helped us immensely in dating the evolutionary landmarks of plants changing their characteristics over time. Today we have almost 500,000 species of plants that have evolved from a single ancestor!
The Early Plants
Botanists worldwide have a common belief that plants have evolved from aquatic algae.
- Early plants were small, unicellular, with simple branching.
- One major evolution was that the ancestors of green plants, i.e., algae could be unicellular or multicellular, but today’s plants cannot be unicellular.
- It is believed that the earliest plants were similar to stonewort.
- But today’s modern plants and stonewort differ a lot. Stonewort has stalks, whereas today’s plants have stiff stems. Today we have roots, but stonewort has hair-like structures called rhizoids and not roots. From water being their only habitat to today’s green Earth, plants have had a very long journey of evolution.
- With time their evolutionary changes included the structure of the plant’s body, tolerance to ecological conditions, systematic diversity.

Evolution in Plants: Terrestrial
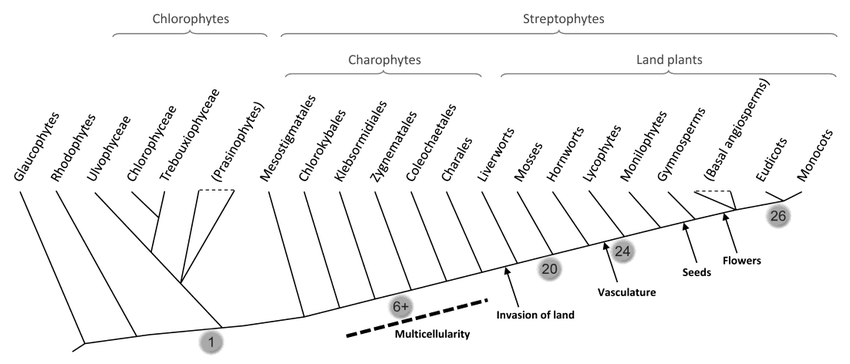
Plants are believed to be amongst the earliest organisms to leave the water and colonise land. According to the fossil history of the plants, botanists estimate their land presence is around 450 million years old. The first terrestrial plants were most probably in the form of tiny plants resembling liverworts. To survive their terrestrial journey, plants had to go through many adaptations.
- Stomata – In earlier plants, a waxy layer called cuticle helped seal water in the plants, and also it prevented gases from entering or escaping the plant. Later, small pores on the leaves of land plants called stomata evolved to retain water and exchange gases.
- Vascular Tissues- Vascular tissues are a major landmark in plant evolution. They helped the plants to transport water and mineral nutrients. Before, there was no need for any such tissue as earlier plants (algae) already lived in water and only got all their nutrients. But now, something was needed to provide water supply and nutrients from the ground to the plant and distribute the food prepared in the leaves to all the parts of the plants. The first fossil record of vascular plants (i.e., land plants with vascular tissues) appeared in the Silurian period.
- Leaves- The first leaves were very small, and became larger over time. Leaves are the main source of food for plants as they are rich in chlorophyll
- Flowers- According to fossil evidence, the evolution of flowers first made its appearance about 125million years ago and then rapidly diversified.
- Reproductive Adaptations- Before coming on land, the earlier plant types released their embryos in the water. Still, after coming on land, the embryo after fertilization started developing in the female part of the plant itself. This adaptation was common in all kinds of plants. Other reproductive adaptations that evolved in plants include ovules, pollen, pollen tubes, and pollination by animals.
- Seeds and Pollens- Seed plants appeared about one million years ago. Seeds and pollen are two major evolutions. Seeds protect the embryo and provide it with nutrients to support the early growth of the sporophyte.
Conclusion
- The evolution in plants is a series of evolutionary adaptations that helped them sustain, survive and diversify on the land.
- The ancestors of the earliest plants are believed to be green algae.
- Plants are considered the earliest organism to leave the water and thrive on land.
- The evolution of Vascular tissue was a very major evolution for the plants.
FAQs:
1. How have plants evolved?
Plants have evolved from unicellular water-dwelling algae to multicellular photosynthetic terrestrial plants. This has only been possible because of the many evolutionary adaptations plants adopted over time.
2. What are the four major periods of plants evolution?
The broadly categorized four major periods of plants evolution are:
- The Pre Cambrian Era
- The Paleozoic Era
- The Mesozoic Era
- The Cenozoic Era
3. What is the evolution in plants?
Evolution in plants biology is the study of the biological evolution of plants from being water-dwelling to land inhabiting with the help of many adaptations.
4. Do plants undergo evolution?
Yes, plants have been going through evolution since millions of years ago. From being unicellular to today’s diversified multicellular green plants dominating the whole land is visible proof of the plant’s evolution through time.
5. What is the importance of plant evolution?
The evolution in plants, i.e., from being algae to the photosynthetic multicellular green plants and their presence on the land, has eventually helped Earth be ready for animal and human life. It would not have been possible without the evolution of plants.
6. What are some examples of evolution in the plant world?
Vascular tissues, seeds, flowers, and stomata are major examples of evolution in the plant world.
7. When did plants first evolve?
Plants first evolved around 500 million years ago, i.e., during this time, the record of the first terrestrial plants existed. Earlier plants were similar to algae, and later with time and many evolutionary adaptations, they marked their presence on land and have diversified since then.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Plant Evolution! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>