Mold Study Guide
Introduction:
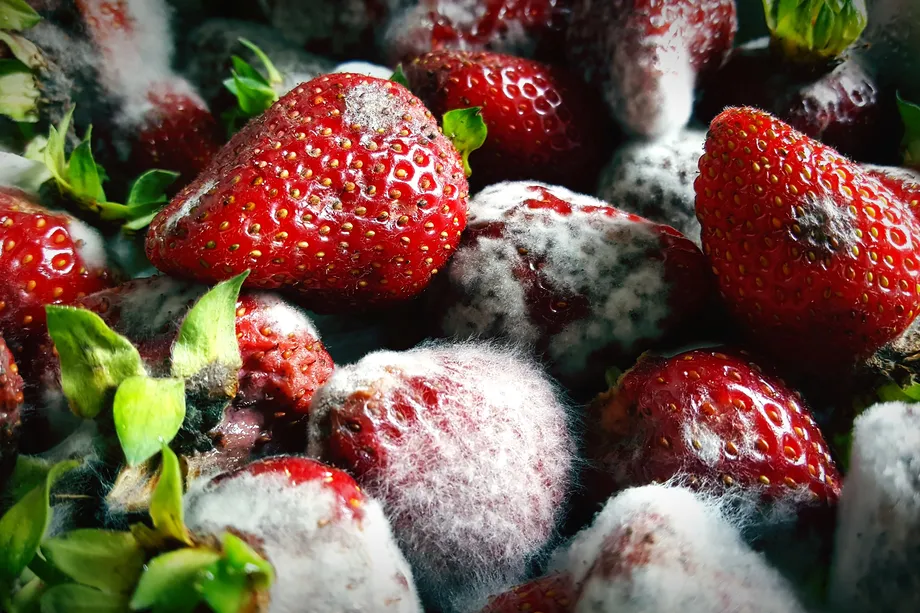
Have you ever experienced that moment of dismay when you open your fridge expectantly, only to find that your favorite tasty ice cream is covered with a hairy gray substance or a blackish layer? It is most likely to be mold or mould – a type of fungi that deteriorates food amongst others. Mold affects food and is also seen on house walls or other moist or dark places in buildings. However, mold has its place in the ecosystem with its contribution.
What is Mold?
Mold is a living organism that resemble fungi-like protists. These fungi appear like they are neither plant nor animal.
Mold is heterotrophic, meaning it cannot make its food as plants do, and mold must gain nutrients from other organic substances. However, unlike animals, mold does not really ‘eat’ its food, and it must absorb nutrition from other organisms. To do this, mold secretes enzymes that break down the food substance into smaller organic molecules that can be absorbed. If you’ve ever grabbed a piece of moldy fruit, you may have felt the soft and mushy area that has essentially been digested.
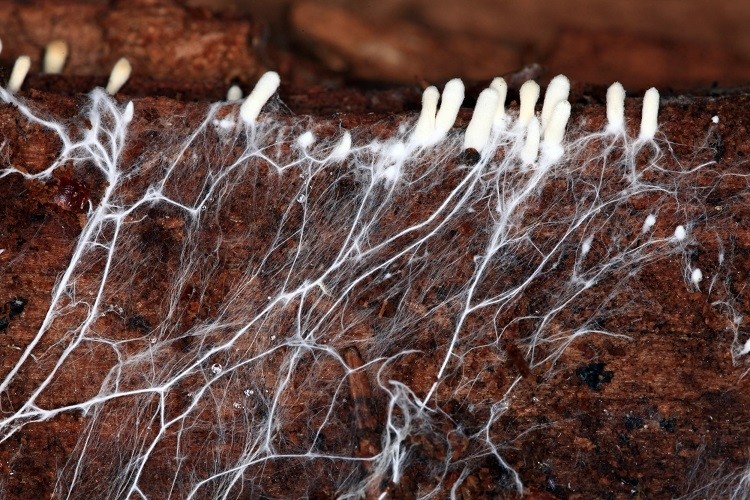
Mycelium molds are a vast group of thread-like structures called hyphae, and are observed on food surfaces and other affected damp surfaces. It appears like a grassy lawn. Like individual blades of grass making up a lawn, many hyphae make up a mycelium, which explains its ‘hairy’ appearance. It is also important to note that mold is multi-cellular.
Is mold a living thing?
Mold is a living organism that belongs to the Fungi family. Mold acquires energy from digesting other substances and reproduces via spores, living organism status.
Mold mostly reproduces through asexually produced spores, although some types of mold also produce spores sexually. These spores are invisible and are carried through the air. Once these spores come in contact with a favorable environment (dark, moist), they start to grow quite rapidly!
Types of Mold
There are three main classifications of mold, depending on its how hazardous they are to our health:
1. Allergenic: Causes an allergic reaction such as eye irritation, skin irritation, or asthma.
2. Pathogenic: Can cause disease, and it’s often hard to pinpoint this type.
3. Toxigenic: Produces substances that are toxic and can lead to dangerous or deadly health conditions.
Examples of Mold
There are more than 100,000 types of mold. The common examples of mold, and where they are usually found are explained below.
Acremonium
- This is a mold that’s commonly found in buildings that have been affected by water seepage.
- It is slow-spreading, making it easier to detect and remove compared to other molds.
Alternaria
- Is found both indoors and outdoors.
- It is usually observed in damp places such as dead plant material, grass with dew, and overwatered soil.
- This mold variety spreads during dry and windy conditions.
Aspergillus
- These molds range from yellow-green to blue-green hues.
- Aspergillus has a cotton or wool texture.
- This mold produces allergic reactions, and its effects can lead to serious conditions such as Aspergillosis – a type of lung disease.
Aureobasidium
- Aureobasidium have colors ranging from black to softer cream or pink hues.
- They are commonly found in bathrooms and kitchens, growing in the tile grout or caulking.
Chaetomium
- Colonies of Chaetomium are found in damp and humid locations of buildings or areas that don’t get sunlight and have poor ventilation.
- Chaetomium mold can have both allergenic and pathogenic effects.
Cladosporium
- This type of mold is found in basements or attics.
- Cladosporium has a velvet texture and is olive-gray.
- It causes an allergic reaction, especially in infants. It is also known to cause infections in the fingernails, toenails, and eyes.
Fusarium
- Fusarium can be found in various colors, from tans and whites to brighter pinks and purples.
- Fermented fusarium, also called Quorn, is used as a meat substitute by many vegetarians and vegans.
Mucor
- Mucor is a yellow or white mold with a cottony texture
- It’s usually found in the air in schools, offices, and homes.
Penicillium
- Penicillium can be identified by its musty odor.
- It’s often found in blue-green, white, yellow, or pink hues and has a powdery texture.
- It can be found indoors with moisture and often contaminates leather and cloth items.
- By studying penicillium, scientists found a component of the fungi named Penicillin – an antibiotic commonly used to treat infectious diseases.
Stachybotrys Are green to black and sticky to touch. This fungus is found in damp places throughout the home. Bathroom ceilings, wet carpets, laundry rooms, and basements are often home to black mold. Commonly referred to as “black mold”, Stachybotrys can cause severe illness.
Moldy Facts
No one likes to see mold in their homes! It is useful to understand this fungus, and to enable its prevention or effective removal when it shows up.
- Mold can be seen in many places
- There are over 100,000 different types of mold and grow on a variety of surfaces
- Mold growth starts in 24 – 48 hours after the introduction of spores on a moist surface
- Painting over mold doesn’t remove it
- Mold can even grow on Christmas trees!
- Bleach does not kill mold very effectively – in fact vinegar might be a better bet!
- Insurance policies do not cover mold
Conclusion:
- Mold is a living organism that belongs to the kingdom Fungi.
- Mycelium Molds are the vast group of thread-like structures called hyphae commonly observed on food surfaces and other affected damp surfaces.
- Depending on its health hazard, mold is categorized as Allergenic, Pathogenic, and Toxigenic.
- Common mold examples are Acremonium, Alternaria, Aspergillus, Aureobasidium, Chaetomium, Cladosporium, Fusarium, Mucor, Penicillium Stachybotrys.
- It is good to be aware of certain facts about Algae, as these will enable its prevention or effective removal.
FAQs:
1. Is it mould or mold?
It means the same. Americans spell it like mold, whereas the British spell it as Mould.
2. What does mold do to a person? Is mold harmful to humans?
People who have touched, inhaled mold or mold spores may have allergic reactions such as a runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, watery eyes, skin rash, and itching (dermatitis). Molds can trigger asthma attacks in people who are allergic to molds, causing wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
3. Can you get sick from mold in your house?
In some cases, mold in homes can make you sick, especially if you have allergies or asthma. Mold exposure can irritate your eyes, skin, nose, throat, and lungs, irrespective of vulnerability to allergies.
4. What kills mold?
- A bleach solution can kill mold. Mix one cup of bleach in a gallon of water, apply to the surface, and rinse.
- Mix a solution of ammonia and water in equal measure. Spray on the surface, wait two to three hours, then rinse.
5. Can mold grow in your lungs?
The mold spores can colonize (grow) inside lung cavities from chronic diseases, such as sepsis, tuberculosis, emphysema, or advanced sarcoidosis. The fungus fibers might form a lump by combining with white blood cells resulting in blood clots.
7. How do you stop mold from growing?
Following measures prevent mold growth:
- Reduce humidity levels in homes as low as possible (not more than 50%)
- Ensure good flow of natural air
- Detect and plug water leaks in your home’s roof, walls, or plumbing, so mold does not have moisture to grow.
- How do I know if my house has mold? Do all houses have mold?
- If the home has water stains, discoloration on walls, floor, or ceilings, or there is visible bubbling, cracking, or peeling paint or wallpaper, it is a sign of mold.
9. Is there a mold detector?
There are a handful of test kits offered available for detecting mold. The kit detects airborne mold spores. Samples must be sent to the lab for analysis, with results expected in 5-7 days.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Mold! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Moldhttps://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/8.6/primary/lesson/molds-bio/ Accessed on 9 Dec 2021.
- mold
- https://www.britannica.com/science/mold-fungus Accessed on 9 Dec 2021.
- What is Mold? – Definition, Types & Causes
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-mold-definition-types-causes-examples.html Accessed on 9 Dec 2021.
- 12 Common Types of Mold Found in the Home
- https://www.apartmentguide.com/blog/types-of-mold/ Accessed on 9 Dec 2021.