Protozoa Study Guide
Introduction
- Protozoa are heterotrophic, unicellular eukaryotic creatures. They can either live freely or as parasites.
- There are around 65000 protozoan species classified into several categories.
- They don’t have a cell wall.
- Protozoa go through several phases throughout their life cycle.
- Some stages of the life cycle are contagious.
General characteristics of Protozoa
- Protozoa can be found in the aquatic environments, both freshwater and saltwater.
- Some are free-living, while others live as parasites on plants and animals.
- They are mostly aerobic. However, some are anaerobic and can be found in the rumen or human gut.
Protozoa Size and Form
- Protozoa vary widely in size and shape, ranging from microbial to big enough to be seen with the naked eye.
- The shell of unicellular foraminifera can grow to be 20 cm in diameter.
- They are unicellular and have eukaryotic cells.
Some specialized interior structures carry out metabolic duties:
-
The nucleus has a dispersed appearance due to scattered chromatin
-
The plasma membrane encloses the cytoplasm and additional locomotory projections such as flagella, pseudopodia, and cilia.
-
Some genera have a membranous envelope called pellicle, which gives a definite shape to the cell.
-
Food vacuoles are present, from which ingested food emerges. Ciliates have a gullet, a bodily cavity that opens to the outer world.
-
The central vacuole is present for osmoregulation, which involves the removal of excess water.
-
Membrane-bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, and other specialized structures.
-
Protozoa are heterotrophic.
-
Phagocytosis is the process through which they consume food.
-
Most protozoa species have flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia for locomotion. Sporozoa, which lack a locomotory structure, have subpellicular microtubules that aid in sluggish movement.
-
Most protozoa have a life cycle alternating between a latent cyst stage and a proliferating vegetative stage.
-
The cyst stage may live in arid environments without water or nutrients, and it may still be viable.
-
The vegetative stage is contagious, and it is at this stage, they feed and multiply.
Reproduction-
They primarily reproduce asexually. They reproduce by binary fission, longitudinal fission, transverse fission, and budding.
Protozoa classification
Protozoa is a class of unicellular heterotrophs and belongs to the Kingdom Protista.
Protozoa are classified into four primary groupings based on their anatomy and the section of their body that is involved in locomotion:
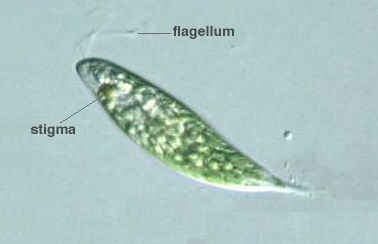
1. Mastigophora or Flagellates:
- These organisms can be parasitic or free-living
- They contain flagella for mobility
- Flagella rotate in a propeller-like fashion thus propelling the protist forward
- They have a cuticle or pellicle covering their body
- Freshwater species have a contractile vacuole
- Reproduction is via binary fission (longitudinal division)
- Examples: Trypanosoma, Trichomonas, Giardia, Leishmania, and others
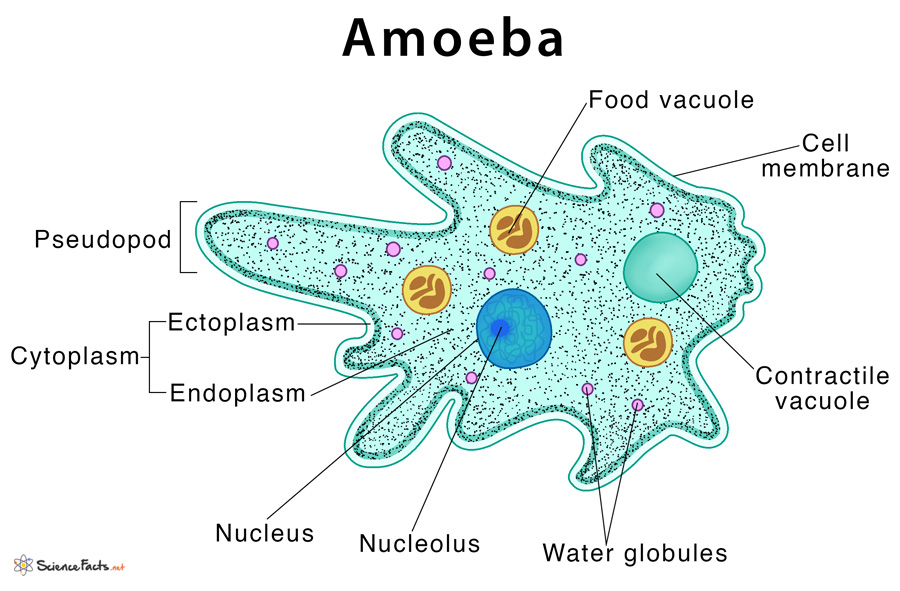
2. Sarcodina or Amoeboids:
- They dwell in freshwater, seawater, or damp soil and migrate via pseudopodia.
- They trap their food with pseudopodia
- Pseudopodia are cell surface extensions in the form of feet-like structures that propel the cell forward.
- There is no particular shape and no pellicle.
- The contractile vacuole is present in freshwater amoeboids
- Reproduction is via binary fission and cyst formation
- Examples: Amoeba, Entamoeba, etc.
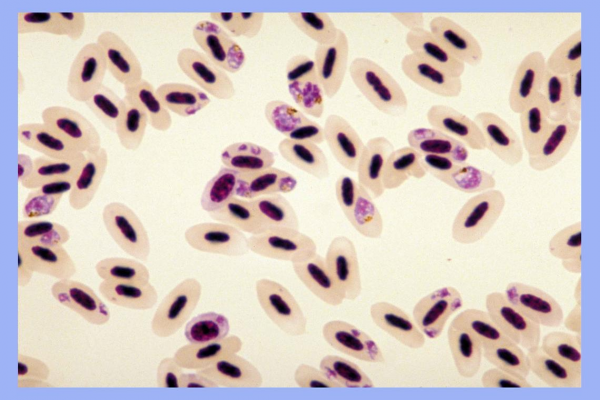
3. Sporozoa or Sporozoans
- They are are endoparasitic organisms.
- They lack a specialized organ for mobility;
- Reproduction is by sporozoite formation and these spores form into new protists.
- Examples include Plasmodium, Myxidium, Nosema, Globidium, and others.
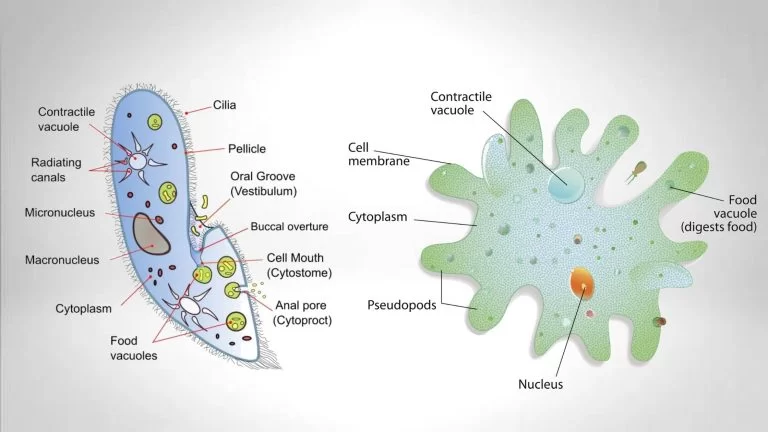
4. Ciliophora or Ciliates
- These are aquatic creatures that actively move thanks to thousands of cilia.
- Cilia are thin, very small tail-like projections that extend outward from the cell body
- They have a fixed form due to pellicle covering.
- They may have tentacles
- Contractile vacuoles are present
- Some species have an organ for defense called trichocysts
- They move with the assistance of cilia, and the movement of cilia also assists in getting food into the gullet
- They reproduce by transverse division and also generate cysts
Conclusion:
- Despite their single-celled organization, protozoa are an extremely successful group of creatures in various ways.
- Theey play an important function in food webs, notably the saprovore food web.
- Protozoa play a multifaceted ecological role, providing energy to predaceous micro-, meio-, and macrofauna and enhancing decomposition processes.
FAQs:
1. What are the 3 types of protozoa?
- Amoebas (representative: Ameba proteus)
- Flagellates (representative: Trypanosoma, Euglena)
- Ciliates (representative: Paramecium)
- Apicomplexa (representative: Plasmodium)
2. What are five examples of protozoa?
- Giardia
- Trypanosoma
- Trichonympha
- Entamoeba
- Plasmodium
3. What diseases are caused by protozoa?
Common infectious diseases caused by protozoans include:
- Malaria.
- Giardia.
- Toxoplasmosis.
4. Are protozoa bacteria?
Protozoa are one-celled creatures similar to bacteria. However, they are larger than bacteria and have a nucleus and other cell features, making them more comparable to plant and animal cells.
5. Are protozoa harmful to humans?
Protozoan infections cause illnesses that impact many creatures, including plants, animals, and some marine life. Many of the most common and deadly human illnesses, such as African Sleeping Sickness, amoebic dysentery, and malaria, are caused by protozoan infections.
6. What are two diseases caused by viruses?
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV/AIDS)Human papillomavirus (HPV)
7. Are protozoa heterotrophic or autotrophic?
Protozoa (animal-like protists) are heterotrophs that consume or absorb their food.
8. Are protozoa fungi?
Protists are unicellular eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Protozoa! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Protozoa: Structure, Classification, Growth, and Development. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8325/. Accessed 8 Dec, 2021.
- PROTOZOA. https://microbiologysociety.org/why-microbiology-matters/what-is-microbiology/protozoa.html. Accessed 8 Dec, 2021.
- Protozoa. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/8.4/primary/lesson/protozoa-bio/. Accessed 8 Dec, 2021.