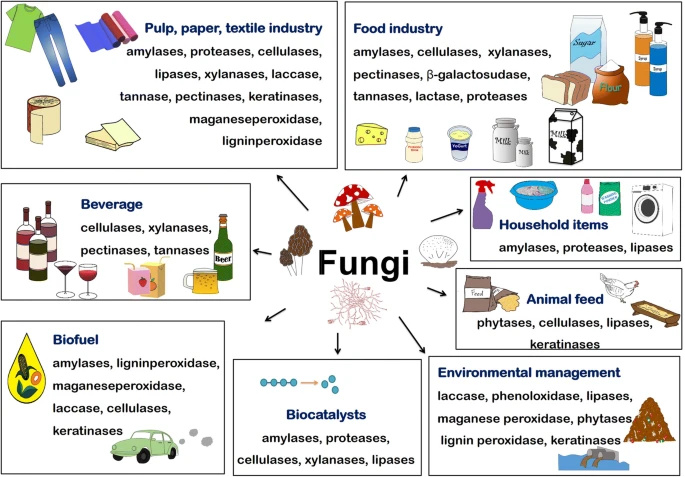
Uses of Fungi Study Guide
Introduction:
Fungi are abundant in the soil and air, as well as in lakes, rivers, and oceans, on and among plants and animals, in food and clothes, and the human body. In collaboration with bacteria, Fungi break down organic matter and release carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus into the soil and environment.
- Many domestic and commercial operations rely on fungi, including the production of bread, wine, beer, and some cheeses.
- A fungus may also be eaten; for example, certain mushrooms, morels, and truffles are considered an exquisite delicacy.
- Mycoproteins (fungal proteins) generated from the mycelia of specific fungi are used to manufacture high-protein dishes.
Medical Uses of Fungi:
- Fungus-derived penicillin was effectively utilized to treat a bacterial illness for the first time. Many formerly deadly bacteria-related disorders become curable as a result.
-
Griseofulvin, a commonly used antifungal drug, is generated from fungus. Dermatophytes are treated with griseofulvin. Following topical treatment, it accumulates in the hair and skin.
-
Another complex chemical with a limited spectrum of action against yeasts and yeast-like organisms is sordarin. The chemicals block protein production and have proven a popular therapy for various human fungal diseases.
-
Several fungi produce Cyclosporin A as a metabolite. It is a potent immunosuppressant in animals, and it’s widely used in humans after bone marrow and organ transplants.
-
Alkaloids found in ergots function by stimulating the sympathetic nervous system. This causes noradrenaline and sclerotin to be inhibited, causing blood vessels to widen.
-
Ergot alkaloids are used to treat various ailments, the most prevalent of which are migraines. During the commencement of an attack, the vasodilator action helps to relieve tension. The medications also aid in the reduction of blood pressure.
-
Aspergillus terries, a soil-borne fungus, generate the secondary metabolite lovastatin, whereas Phomma species produce squalestatin.
-
Statins have proved effective in decreasing low-density lipoproteins (LDL), the “bad” cholesterol, from blood vessels lowering the risk of arterial blockage, heart attack and diabetes.
Agriculture:
-
Fungi, as animal pathogens, aid in the control of pest populations. These fungi can only infect insects; they do not infect animals or plants.
-
Fungi are being researched as possible microbial insecticides, with a few already on the market. For example, the fungus Beauveria bassiana is studied as a potential biological control agent for the emerald ash borer’s recent expansion.
-
The mycorrhizal interaction between fungus and plant roots is critical for farmland production. 80–90% of trees and grasses would die if they didn’t have a fungal companion in their root systems.
- Gardening supply stores sell mycorrhizal fungi inoculants, which organic agriculture proponents encourage as soil additions.
Fungi as Food
- Fungi have an important role in human nutrition. Delicacies include morels, shiitake mushrooms, chanterelles, and truffles. Agaricus campestris, or meadow mushroom, is used in various cuisines.
-
Molds of the genus Penicillium ripen many pieces of cheese. They begin in a natural setting, such as the caves of Roquefort, France, where wheels of sheep milk cheese are piled to collect the molds that give the cheese its blue veins and pungent flavor.
-
Fermenting grains to make beer and fruits to make wine is an old technique humans have performed in most civilizations for millennia.
-
Ancient people collected wild yeasts from the environment and fermented carbohydrates into CO2 and ethanol anaerobically. Isolated wild yeast strains from several wine-making locations are now available for purchase.
-
In the late 1850s, Louis Pasteur played a key role in producing a stable brewer’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, for the French brewing business.
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, often known as baker’s yeast, is a key component of bread, which has been a necessity of human life for thousands of years.
-
Humans used to let the dough gather yeast from the air and rise over hours or days until separate yeast became accessible in modern days.
-
In the same way, sourdough bread is created today, a little portion of this leavened dough was retained and used as a starter (source of the same yeast) for the following batch.
Conclusion:
- Humans use fungi for various functions, including eating and food preparation.
- Fungi can also produce citric acid, antibiotics, and human hormones.
- Fungi are also used as study models.
- To grow, most grasses and trees need to form a mycorrhizal association with fungus.
- Yeasts have been used to make beer, wine, and bread for thousands of years.
- Because certain fungus prey on insects, they can be utilized as natural insecticides.
FAQs:
1. What are the 5 uses of fungi?
- Fungi are a vital source of food.
- Yeast is a unicellular fungus used in the production of bread in bakeries.
- Vitamin B is also produced by yeast.
- Like bacteria, fungi are excellent decomposers.
- A fungus called Penicillium notatum produces penicillin, an essential antibiotic.
2. What are the 2 examples of useful fungi?
Mushroom and yeast are 2 examples of useful fungi. Many species of mushrooms are edible and are an important source of food. Yeast is used in various fields, and some species are used to make bread and cheese.
3. How are fungi used in medicine?
- Many fungal secondary metabolites have significant commercial value.
- Antibiotics are produced naturally by fungi to kill or reduce the development of bacteria, hence reducing competition in the natural environment.
- Fungi can be used to isolate important medicines like penicillin and cephalosporins.
- Micafungin, an antifungal drug, mycophenolate, which prevents tissue rejection, and rosuvastatin, which lowers cholesterol, are all examples of fungus in medicine.
4. What is the role of fungi in our daily life?
Fungi have a crucial role in human life. In most ecosystems, fungi play a major role in decomposition. Fungi are used as food in the form of mushrooms and agents of fermentation in creating bread, cheeses, alcoholic drinks, and a variety of other foods.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the uses of fungi! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
Sources:
- Use of Fungi https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/8.15/primary/lesson/human-uses-of-fungi-bio/ Accessed on 8 Dec 2021
- Human Uses of Fungi https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_Introductory_Biology_(CK-12)/08%3A_Protists_and_Fungi/8.15%3A_Human_Uses_of_Fungi Accessed on 8 Dec 202
- Importance of fungi https://www.britannica.com/science/fungus/Importance-of-fungi Accessed on 8 Dec 2021
- Importance of Fungi in Human Life https://opentextbc.ca/biology2eopenstax/chapter/importance-of-fungi-in-human-life/ Accessed on 8 Dec 2021