Amphibians – Reproduction Study Guide
Introduction
Organisms belonging to Class Amphibia under the Chordata Phylum are called Amphibians. There are about 3000 species at present. These are multicellular vertebrate species that live on land as well as water. They are also the 1st type of cold-blooded animals to exist on this planet.
General characteristics of Amphibians:
- They can live on both land as well as water.
- They are generally found in warm environments.
- Skin is smooth and rough without scales
- Presence of glands make it moist.
- Body is divided into the head and trunk.
- Tail may or may not be present.
- They have a three-chambered heart.
- Breeding occurs in water.
- They have two pairs of limbs for locomotion.
Reproduction In Amphibians:
Most amphibians generally require water for breeding, but some also lay eggs on the land. These creatures that lay eggs on land have developed various adaptations to keep the eggs moist. Some amphibians can even survive in brackish water. But to date, there is no proof that any amphibian can lay eggs in purely marine conditions.
Reproduction of amphibians occurs through sexual reproduction. It involves the fusion of eggs produced in female ovaries, and sperms generated by male testes. But in the case of frogs, fertilization is generally external while it is internal in the case of salamanders and caecilians.
Several frogs lay their eggs in the wild and do not require any water medium to breed and lay their eggs. They reproduce via direct development, whereby they have evolved mechanisms to be completely independent of free-standing water. Frogs generally use mating calls to communicate with each other in order to reproduce their young ones.
Unlike frogs, salamanders and caecilians do not have a larynx. They can grunt but it is generally not useful for mating. Most salamanders use the sense of smell to find a mate. The males generally emit an odor, display their colors and postures to attract females.
In caecilians, the fertilization is internal, whereby the male is seen extruding an intromittent organ, the phallodeum, and inserting it into the female cloaca. Amphibian fertilization probably takes place in the oviduct. Majority of salamanders also engage in internal fertilization.
When it comes to the environment, amphibians in the tropics breed almost in any season of the year. But when it comes to temperate regions, breeding is generally seasonal and mostly happens in the spring season. This breeding is triggered by increasing temperature and rainfall.
Generally, they lay a large number of eggs at a single time and often do so in groups. They all deposit their eggs in the same place at the same time. This is the mass action technique. This is a technique of survival mechanism. This mechanism will overwhelm the predators and make sure that at least some of the eggs will survive.
- Amphibian eggs are usually covered in a jelly-like substance that protects the eggs and keeps them moist.
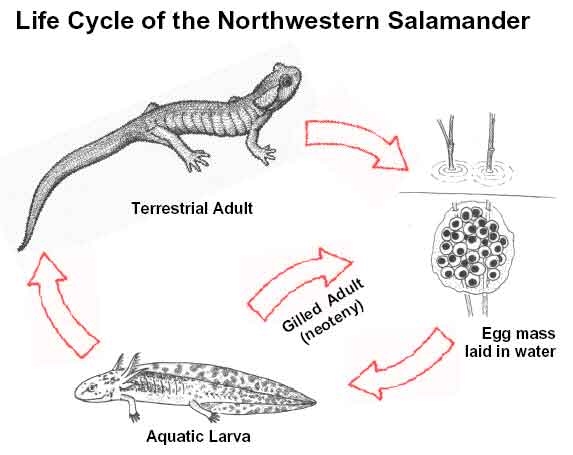
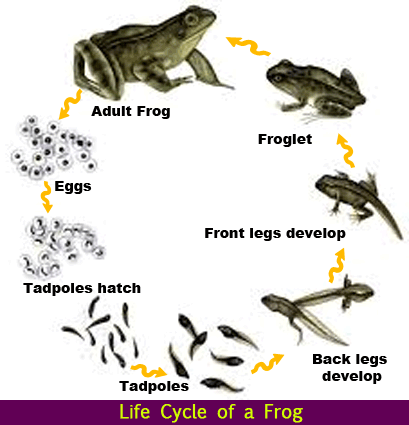
- Most of the amphibian species go through a larval stage that is different from the adult form of the species.
- After the larvae hatch, it slowly develops gills to provide locomotory movement in the aquatic environment. In the early stages, they bear a strong resemblance to fish.
- The larvae then start to undergo metamorphosis, whereby they change into the adult form and limbs, and lungs start to develop.
- Here they start to lose their gills, tails, etc. and adapt to the land environment.
- Once these changes are complete, the juvenile species are ready to emerge out of the water and live their second phase of life.
Three other types of development occur in the case of amphibians, they are:
-
Internal development– Internal development is when the embryo develops inside the female’s body and emerges at a later developmental stage, either as a larva or in its post-larval juvenile stage.
-
Direct development– Direct development occurs when the species do not go through the larval stages. They either directly hatch their eggs or are born necessarily as smaller and sexually immature versions of their parents. For example, a few frogs, salamanders, caecilians, etc.
-
Another type of development that is seldom seen is a mechanism in species like the ‘Silvery salamander.’ They undergo a form of asexual reproduction called parthenogenesis. The eggs of these species do not undergo fusion and fertilization. Instead, the eggs develop into a new organism without the help and contribution of genetic material from the sperm. The result of this form of development is that the offspring are the exact clones of their mothers, and hence they are all females.
Conclusion:
- As amphibians reside in both land and water, their reproduction system has also adapted accordingly.
- As Amphibians do not produce amniotic eggs, they lay their eggs in water so they don’t dry out.
- Amphibians reproduce sexually but some species are able to reproduce asexually as well.
FAQs:
1. How do amphibians reproduce?
Amphibians reproduce sexually by laying eggs that generally lack a shell.
2. Can amphibians reproduce asexually?
Most amphibians reproduce through the sexual mode of reproduction. But there are some species such as the Silvery Salamander that can undergo a form of asexual reproduction called parthenogenesis.
3. Do amphibians lay eggs or give birth?
Amphibians are usually oviparous – egg-laying, but a few species are also known to have the viviparous mode of reproduction. For example – Gegeneophis seshachari, a caecilian is a legless amphibian.
4. What is the difference between reproduction in mammals and amphibians?
Internal fertilisation occurs in mammals during sexual reproduction, while external fertilization occurs in amphibians most of the time.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Amphibians-Reproduction! Join our discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Do not forget to download our App and check out our awesome VR Room – we promise it makes the exercise of studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Reptiles. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/studyguides/biology/reptiles-study-guide.html?encodedID=SCI.BIO.827&courseContextID=5292077. Accessed 3 Dec 2021.
- Amphibian Reproduction – Advanced. https://www.ck12.org/biology/amphibian-reproduction/lesson/amphibian-reproduction-advanced-bio-adv/. Accessed 3 Dec 2021.
- Amphibian Reproduction and Development. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_Introductory_Biology_(CK-12)/12%3A_Vertebrates/12.13%3A_Amphibian_Reproduction_and_Development. Accessed 3 Dec 2021.
- Amphibian Reproduction. https://study.com/academy/lesson/amphibian-reproduction.html. Accessed 3 Dec 2021.