Mammals – Ancestors and Evolution Study Guide
Introduction:
The Late Triassic age was when the mammals arose approximately 200 million years ago. The earliest known mammals were called morganucodontids — tiny creatures that lived amongst the dinosaurs. There were many other mammals around at that time, but these mammals were the only ones who managed to survive and prosper.
Mammalian ancestors
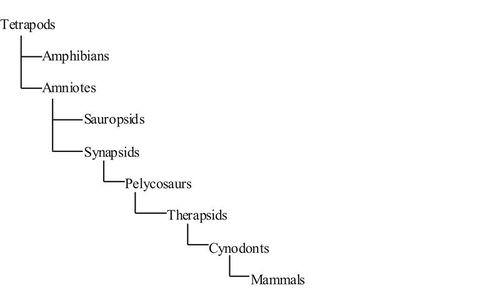
Mammals evolved from the subclass Synapsida of the reptilian order Therapsida. The therapsids were also called mammal-like reptiles.
Amniotes were the first vertebrate organisms who were completely terrestrial as their eggs possessed internal membranes, which enabled the developing embryo to take in oxygen while being in the water. Thus, they could lay their eggs on dry land.
The amniotes further evolved into:
(i) Sauropsids — from which dinosaurs, birds, crocodiles, snakes, and turtles descended
(ii) Synapsids — from which came the mammals
The therapsids emerged from the synapsid pelycosaurs during the middle Permian era and became the dominant land vertebrates. The therapsid clades include Biarmosuchia, Dinocephalia, Anomodontia, Gorgonopsia, Therocephalia and Cynodontia.
Mammalian evolution
There was a catastrophic extinction of about seventy percent of the terrestrial vertebrate animals about 252 million years ago, including several plant species. This affected the food chains in different ecosystems around the world. The establishment of newer ecosystems and their stabilization took over 30 million years.
From the catastrophic extinction, two groups were formed:
→ The mammals, mostly nocturnal insectivores, carnivores, or omnivores
→ The tritylodonts, that were primarily herbivores
- Mammals were initially known as the “crown-group animals,” and Mammaliaformes consisted of the final ancestors of the Morganucodontidae and the Mammalia or the Mammaliamorpha.
- The crown-group mammals were also called “the true mammals” and could distinguish between the red, green, and blue shades of colors as they possessed opsins in the cones within their retinas.
- The mammalian features evolved into middle ears, jaws, and lactating glands, as seen in the tritylodontids, morganucodontans, who show evidence of lactation.
- They developed sharp teeth to capture other animals or eat plants and crunchy insects.
- A special tooth called a tribosphenic molar was formed in some marsupials(ones that carry their young ones in small pouches) and placentals (ones that give birth to well-developed offsprings).
- Some also developed saw-blade premolars (as seen in the multituberculates) and intricate molars to chomp and grind plants.
- They also had a digestive system modified depending on the animal’s diet. Most of the carnivores have large intestines, the horse has a huge voluminous intestine, while the ruminants have a multi-chambered (normally four-chambered) stomach.
- The marsupials, like the koalas, kangaroos, and opossums, were probably the first mammals who developed “nipples” that had concentrated milk ducts and could feed their young ones at any time.
- A placenta in mammals is another distinct feature as the fetus is fed through it within the mother’s body, and the fetus’s immune system is thus separated from that of the mother.
- The mammals also developed hair or fur along with whiskers. These were developed to protect from low temperatures or insulation from changing weather conditions.
- It was an evolved insulation technique without the need to spend energy to produce body heat. Their limbs changed from sprawling hindlimbs to proper erect limbs used to climb, walk, run, etc.
- They were warm-blooded in that they could produce heat internally, maintain the warm temperature constantly throughout the body and maintain a high metabolic rate by features like endothermy, homeothermy, and tachymetabolism.
- There were respiratory turbinates or thin convoluted bone structures in their nose lined with a mucous membrane used to warm the inhaled air.
- They also developed a bony secondary palate which enables them to breathe and eat simultaneously.
- A diaphragm that allowed them to breathe well during any physical activity was formed, and a large brain was used to think and make decisions.
Conclusion
- The evolution of mammals began around 325 million years ago when the synapsids or reptiles dominated the Permian Period when the entire land existed as the single “Pangaea.” Additional features like warm blood, lactating glands, hair, fur, teeth, erect limbs, etc. were evolved over millions of years.
- The crashing asteroid 66 million years ago changed the advancement of several mammalian ancestors like those with non-tribosphenic teeth.
- It was the end of the era for many other animals and plants.
FAQs:
1. What are the ancestors of mammals?
Amniotes or synapsids were known to be the ancestors of mammals.
2. Do all mammals have a common ancestor?
Yes, all mammals are known to have evolved from the synapsids.
3. From what mammals did humans originally evolve from?
Humans have evolved from the great apes.
4. When did the evolution of mammals begin?
The evolution of mammals began 178 million years ago.
5. Do mammals and reptiles have a common ancestor?
Yes, mammals and reptiles have a common ancestor.
6. How did mammals develop?
Mammals developed from the subclass Synapsida of the reptilian order Therapsida, also called mammal-like reptiles.
7. Did mammals evolve from amphibians?
No, mammals evolved from reptiles.
8. Why are mammals successful in terms of evolution?
Mammals are successful. They can survive in various habitats as they are warm-blooded, possess large brains, adapt to any condition, and have teeth, which can adjust to different diets.
9. Did mammals evolve from birds?
No, mammals did not evolve from birds. They evolved from reptiles known as synapsids.
10. Why did mammals become dominant on Earth?
An asteroid attack occurred about 66 million years ago, which destroyed all the dinosaurs and other animals. Mammals managed to survive and adapt to various types of habitats.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Mammals – Ancestors and Evolution! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- The Rise of Mammalshttps://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/rise-mammals Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Evolution of mammalshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolution_of_mammals Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Evolution and classificationhttps://www.britannica.com/animal/mammal/Evolution-and-classification Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Mammal Ancestorshttps://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/12.31/primary/lesson/mammal-ancestors-bio/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021
- Mammal Evolutionhttps://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/12.32/primary/lesson/evolution-of-early-mammals-bio/ Accessed on 6 Dec 2021