Phospholipid Image Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
Each of our body’s cells is wrapped in a small membrane bubble. The consistency of this membrane is similar to that of salad oil! At first, it wasn’t very reassuring! Salad oil appears to be an extremely delicate barrier to erect between a cell and the outside world. Fortunately, the plasma membrane proves to be an excellent fit for its purpose. What precisely is it supposed to do? The plasma membrane establishes the cell’s boundaries and permits it to interact with its surroundings in a controlled manner. Phospholipids, which form a semi-permeable boundary between the cell and its environment, are required for the plasma membrane to fulfill these functions.
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
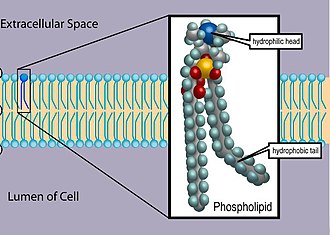
Phospholipids are polar lipids composed of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, and a phosphate group esterified to an organic molecule.Since they are amphipathic, which means they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas, they are well-suited for this task.The hydrophilic (or “water-loving”) component of a phospholipid is its head, which comprises a negatively charged phosphate unit and a tiny group that may or may not be charged or polar.
PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER
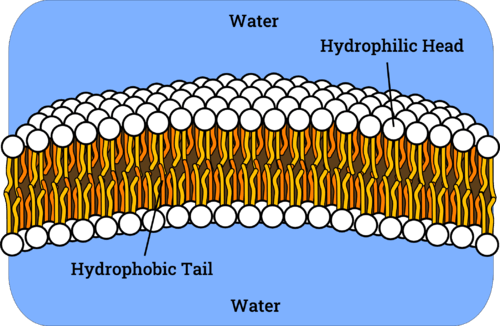
- In a membrane bilayer, the hydrophilic heads of phospholipids face outwards, touching the aqueous fluid both inside and outside the cell. Because water is polar, it creates electrostatic connections with phospholipid heads easily.
- Longer, nonpolar fatty acid tails make up the hydrophobic component.
- Fatty acid tails can interact easily with other nonpolar molecules, even though they have difficulty interacting with water.
- As a result, it is more energy efficient for phospholipids to bury their fatty acid tails into the core of the membrane, where they will be protected from the aquatic environment.
- Since water and other polar or charged molecules cannot easily traverse the hydrophobic interior of the membrane, the phospholipid bilayer generated by these interactions serves as a good barricade between the interior and exterior of the cell.
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANE
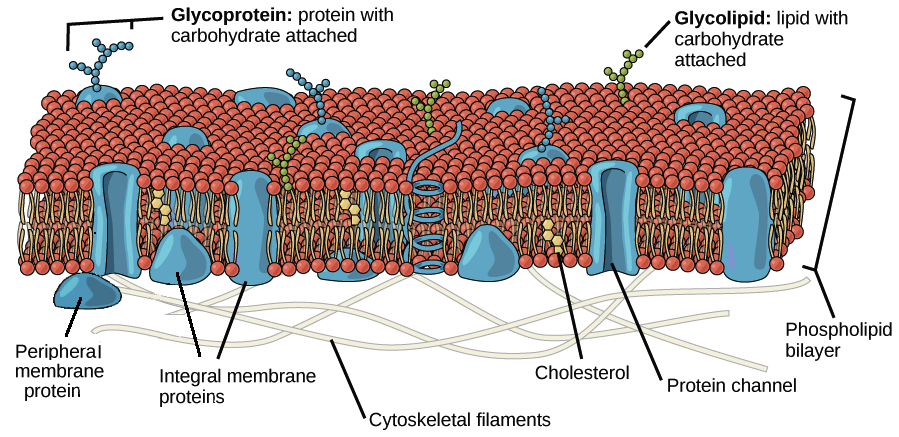
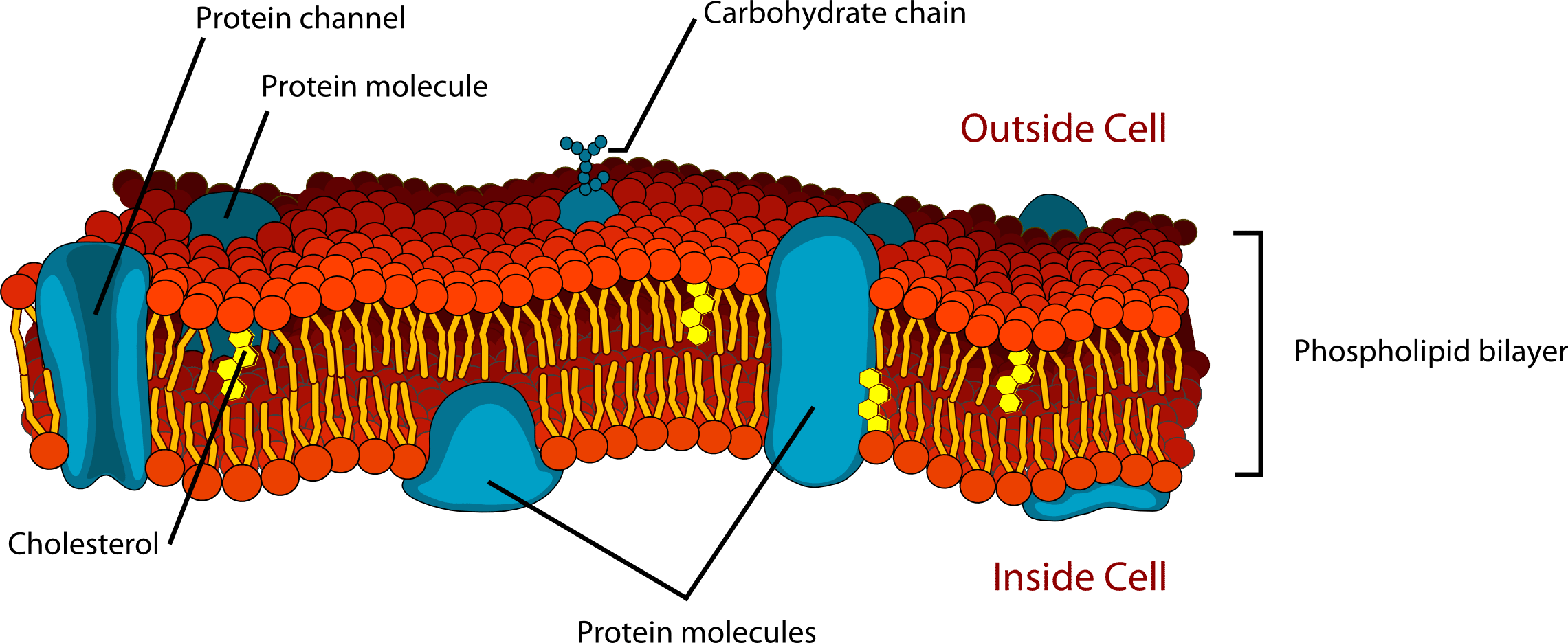
- Bilayers of phospholipids are essential constituents of cell membranes.
- The lipid bilayer creates a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell, preventing chemicals and ions from passing through.
- The cell membrane does, however, play an essential role in allowing selective transmission of particular materials into and out of cells.
- Integrating various protein molecules in and through the lipid bilayer achieves this.
- These proteins create channels that allow specified ions and chemicals to pass through.
- Connected carbohydrates on the exterior of the lipid bilayer allow several membrane proteins to make hydrogen bonds with water.
CONCLUSION:
- Phospholipids are polar lipids composed of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, and a phosphate group.
- Bilayers of phospholipids are essential constituents of cell membranes.
FAQs:
1. What does a phospholipid look like?
The phospholipid has two tails emerging from the head and is structured like a thumbtack. The phosphate group is at the top, while the two fatty acids are at the bottom. The heads are hydrophilic and are proximal to the membrane’s inner and outer surfaces.
2. Which is a phospholipid?
Phospholipids are polar lipids composed of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit and a phosphate group esterified to an organic molecule.
3. What is a phospholipid, and what is its function?
Phospholipids are lipids that include phosphoric acids, nitrogen bases, alcohol, and fatty acids in a compound form. These compound lipids are important components of the cellular membranes and give them a fluid appearance.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Phospholipid Images! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our app to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Structure of the Plasma Membrane: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/cell-structure-and-function/plasma-membranes/a/structure-of-the-plasma-membrane Accessed 27 Feb 2022
- Phospholipids: https://www.thoughtco.com/phospholipids-373561 Accessed 27 Feb 2022
- Phospholipids: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introchem/chapter/phospholipids/ Accessed 27 Feb 2022