Decomposition Reaction Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
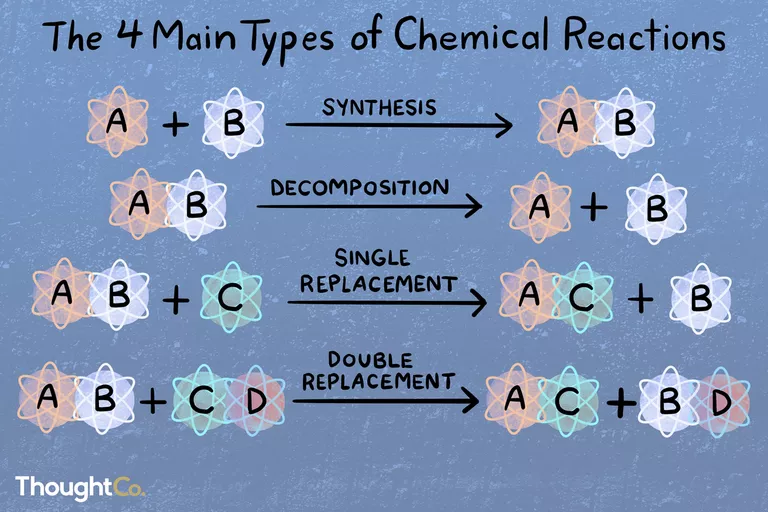
We’ve studied chemical reactions where one or more than one reactant is involved, which yields products. One of the ground rules is that the left side is the reactants, while the right side is the products. However, chemical reactions can be further divided into various types, of which decomposition reactions are a major type.
WHAT IS A DECOMPOSITION REACTION?
If in a chemical reaction, two or more than two products are obtained with only one reactant, then the chemical reaction is known as a decomposition reaction. The general form of any decomposition reaction would be:
AB → A + B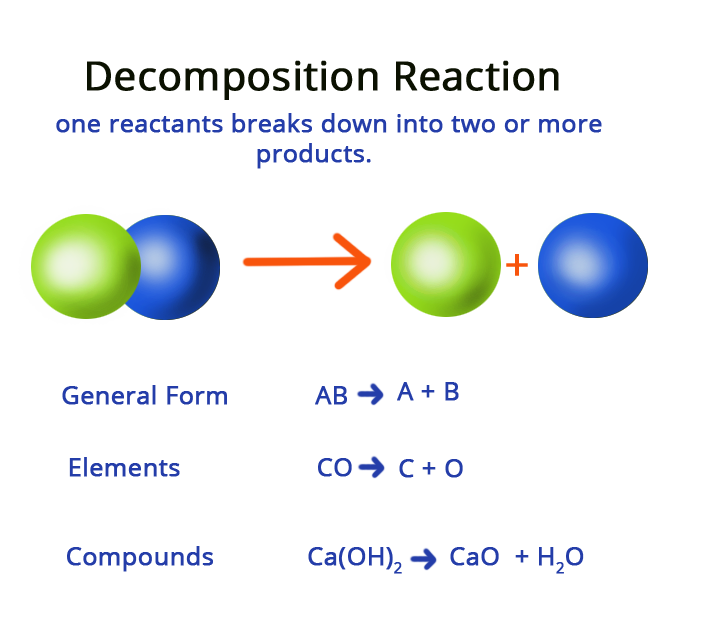
Decomposition equations can also be termed as analysis reactions or even chemical breakdowns. The opposite of decomposition reaction would be synthesis, where more than one reactant combines to form a complex product. Decomposition reactions could be easily recognized by looking for single reactants with more than one product.
EXAMPLES OF DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS
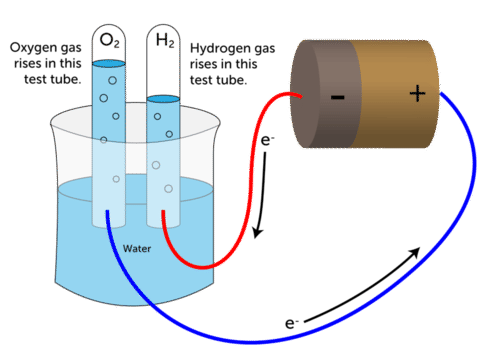
If you pay attention, decomposition reactions are happening every day in your life. One would be the electrolysis of water to form hydrogen and oxygen gas.
2 H₂0 → 2 H₂ + O₂Another example would be the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen.
2 H₂0₂ → 2 H₂O + O₂Another decomposition reaction example would be heating green copper carbonate; it decomposes to form copper oxide as well as carbon dioxide.
CuCO₃ → CuO + CO₂(g)The compound would change from light green to black material.
TYPES OF DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS
There are three types of decomposition reactions, mainly:
-
Thermal Decomposition: A thermal decomposition reaction is activated by heat. This type of decomposition reaction is an endothermic one. A notable example of a thermal decomposition reaction would be the decomposition of calcium carbonate to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide.
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ -
Electrolytic Decomposition: For the reactants to decompose into more than one product, electrical energy supplies this reaction with activation energy. Water electrolysis, as mentioned above, is a notable example.
-
Photolytic Decomposition: The reactant absorbs energy from photons to break the chemical bonds and then form products. An example of this kind of decomposition reaction would be the decomposition of ozone to form oxygen.
O₃ hv → O₂ + O
If a catalyst aids any decomposition reaction, then they could be termed catalytic decomposition reaction.
Double Decomposition reaction
In double decomposition reaction we have two reactants forming two products.
Let us understand with an example:
- AB + CD → AD + CB A is cation and B is anion similarly C is cation and D is anion. A combines with D and C combines with B. There is generally a process of writing the cations first and then the anions for easy understanding.AB combines with CD to form AD and CB.Both the reactants exchange their anions and cations and form two different products which is a double decomposition reaction.
- NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2OSodium hydroxide meet to react with hydrochloric acid gives us sodium combining with chlorine and hydrogen combining with hydroxyl and forming a water moleculeAcid reacts with the base to form salt and water.
Applications
- A decomposition reaction is used to yield quicklime for cement.
- It is used to weld using a thermite reaction.
- To get relief from acid indigestion.
- To identify any sample based on decomposition reaction and products obtained.
- Another major application of this reaction would be to extract pure metals from their chlorides, oxides as well as ores.
CONCLUSION
- A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction where, with one reactant, you get two or more products.
- An easy way to figure out a decomposition reaction is by looking at the number of products.
- Decomposition reactions are of three types- thermal decomposition, photolytic decomposition, electrolytic decomposition.
FAQs
1. What is the decomposition of copper carbonate?
It is a thermal decomposition reaction where heating green copper carbonate, it decomposes to form copper oxide as well as carbon dioxide.
2. What is the balanced equation for copper carbonate?
The balanced equation for copper carbonate would be
CuCO₃ → CuO + CO₂(g)
3. What is the Opposite of Decomposition Reaction?
Decomposition reactions are those in which a compound breaks down to form two or more substances. These reactions require a source of energy to proceed. Thus they are the exact opposite of combination reaction in which two or more substances combine to give a new substance with the release of energy.
__4. Are all decomposition reaction Endothermic? __
Endothermic reactions are those in which heat is applied to the compounds in order for the reaction to occur. A decomposition reaction occurs when a single substance (compound) breaks down into two or more products. Because a single substance cannot break down on its own, it requires energy, and because energy is given to the reactant in all cases of decomposition reactions, each decomposition reaction is referred to as an endothermic reaction.
However, in the case of decomposition of vegetable matter, when microbes react on animal or plant waste, a lot of energy is released, resulting in the release of gases, thus classifying the reaction as exothermic. There can be certain exceptions in which decomposition reaction can be exothermic too.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Decomposition Reaction! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
]]>