Soap Scum Formation Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
A chemical reaction can occur when two materials are combined. The atoms and molecules of the different substances interact and generate new substances. For instance, when two liquids are blended and solidified, a precipitate is the solid formed as a result. The interaction between dissolved soap and “hard” water is a well-known example of a precipitate-forming reaction. It is important to note here that the difference in the product (scum in hard water and lather in soft water) is because of the difference in the chemical properties of hard water. So, what is this hard water anyway? And which property of hard water is responsible for scum formation? Let’s find out.
HARD WATER:
- The mineral content of hard water is high.
- It is generated when water percolates through the sediments of magnesium and calcium carbonates found in chalk and limestone.
- It does not froth with soap and is therefore unsuitable for laundry.
- The hardness of water is hazardous to boilers because it causes salt build-up, which affects the boiler’s performance.
- Although hard water is safe to drink, prolonged exposure can cause various issues.
TYPE OF HARDNESS OF WATER
1. TEMPORARY HARDNESS:
Water becomes briefly hard attributed to the prevalence of magnesium and calcium carbonates. The hardness in the water can be eliminated in this scenario by boiling it.
2. PERMANENT HARDNESS:
Permanent hardness is defined as the presence of soluble magnesium and calcium salts in the form of chlorides and sulfides in water, which cannot be eliminated by boiling.
WHAT IS SCUM?
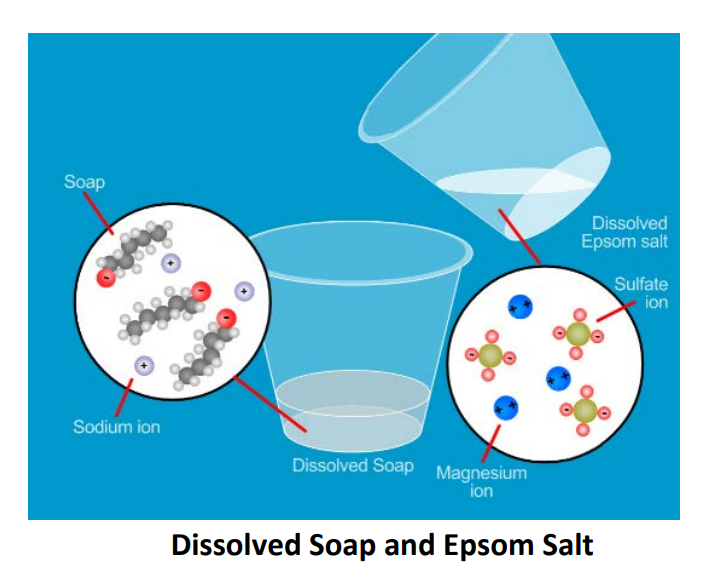
Soap scum, sometimes known as lime soap, is a white substance of calcium stearate, magnesium stearate, and other alkali metal fatty acid derivatives.
HOW IS SCUM FORMED?
- In hard water, calcium and magnesium salts are typically present.
- A precipitate is generated when soap molecules combine with calcium and magnesium salts.
- As an off-white coating, this precipitate begins to float on the water’s surface. This layer is known as scum.
- In hard water, soaps lose their cleansing effectiveness due to the production of scum.
CONCLUSION:
- Soap scum, sometimes known as lime soap, is a white substance of calcium stearate magnesium stearate.
- Citric acid softens hard water, adjusts pH levels, and improves the performance of detergent soap.
FAQs:
1. How is soap scum formed?
When hard water and soap are combined, the magnesium ion combines with the soap molecules to generate a solid precipitate that does not dissolve. This precipitation of soap scum inhibits the soap’s ability to produce bubbles.
2. What is soap scum?
Soap scum, sometimes known as lime soap, is a white substance of calcium stearate, magnesium stearate, and other alkali metal fatty acid derivatives. The introduction of soap, as well as other anionic surfactants to hard water, produces these compounds.
3. What pH is soap scum?
Soap scum is a coating that tends to be on the alkaline side of the pH scale (from eight to 14).
4. How does citric acid remove soap scum?
Citric acid softens hard water, adjusts pH levels, and improves the performance of detergent soap.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Soap Scum Formation! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our app to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Harness of Water: https://byjus.com/jee/hardness-of-water-types-and-removal/ Accessed 27 Feb 2022
- Inquiry in Action: https://www.acs.org/content/dam/acsorg/education/k-8/inquiry-in-action Accessed 27 Feb 2022
- Formation of Scum: https://www.doubtnut.com/question-answer-chemistry/explain-the-formation-of-scum-when-hard-water-is-treated-with-soap-647113539 Accessed 27 Feb 2022