Radioactivity: Definition and Types Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
Have you ever wondered why danger signs surround radioactive sites? Radioactive reactions can be quite explosive and have fatal repercussions to the human body.
Radioactivity was first discovered by Henri Becquerel in 1896. Later, Marie Curie studied the radiation of different compounds, and discovered that uranium and thorium are radioactive elements.
This guide teaches you more about the highly interesting corner of chemical reactions – radioactivity.
WHAT IS RADIOACTIVITY?
- Radioactivity is defined as the spontaneous emission of radiation from highly energized particles or photons resulting in nuclear reactions.
- This process is also known as radioactive decay, or radioactive disintegration.
- There is a different form of radioactivity that is harmful and not harmful.
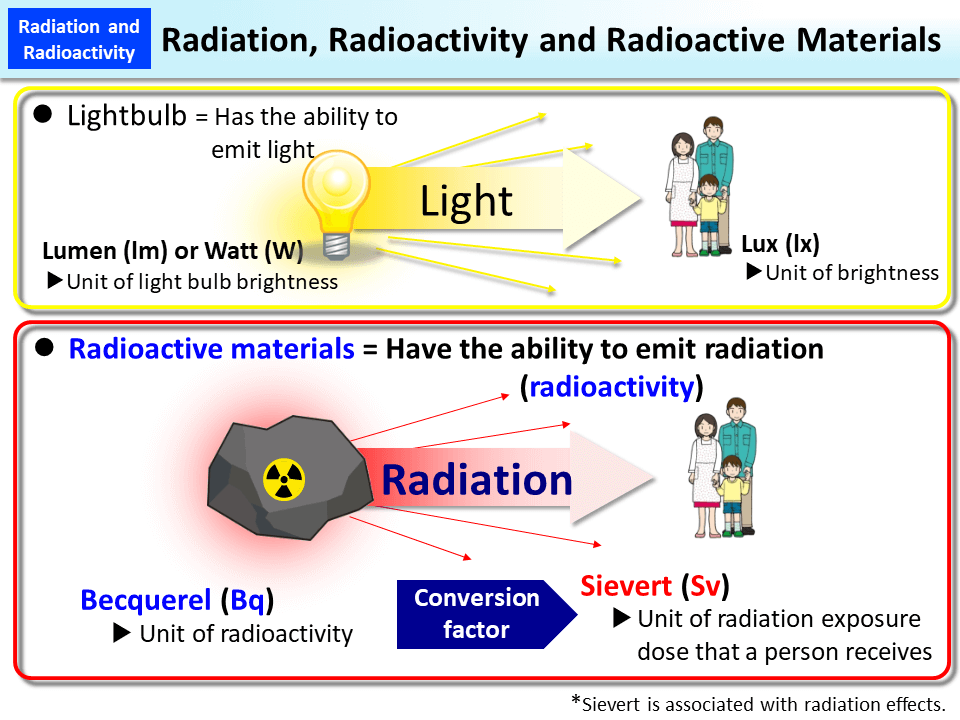
- One of the biggest examples is a light bulb: it emits radiation in the form of light and heat, but there is no radioactivity taking place.
- A substance that consists of unstable nuclei of the atom is considered to be radioactive.
Since Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity, the SI unit of radioactivity is becquerel (Bq).
WHAT IS RADIOACTIVE DECAY?
We hear about the concept of ‘radiation’ all the time, especially in medical terminology. Radiation occurs when an unstable, high-energy nucleus of an element releases some of that energy to get to a more stable state (similar to when you consume way too much sugar and need to work off all of that energy!). Radioactive decay is one of the ways this excess energy is expelled.
The rate of decay of a group of atoms can be anticipated by the half-lives or decay constants. Half life refers to the time taken by the radioactive sample to fall to half its original value.
TYPES OF RADIOACTIVE DECAY
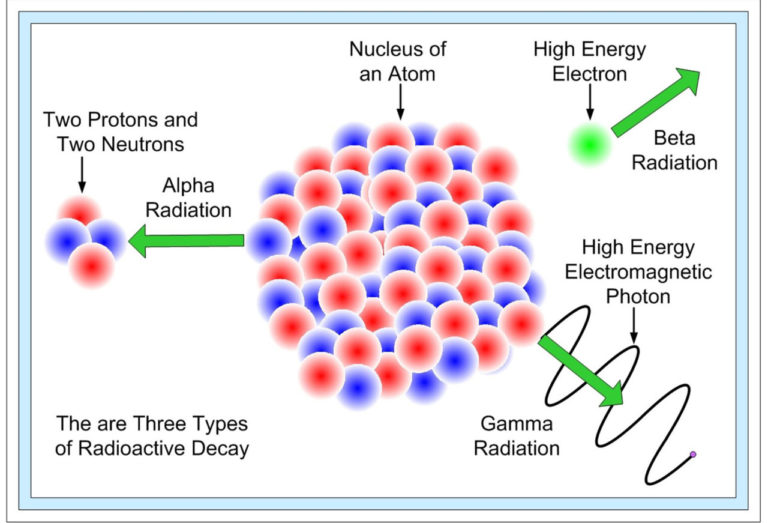
There are mainly three types of radioactive decay that were discovered first. All these types were named after the ability to penetrate matter. Later additional types of decay were discovered. The types of radioactive decays are as follows:
- Alpha Decay
- Alpha decay (A = 4, Z = 2) is those particles that can penetrate the matter at the shortest distance.
- It is emitted from the nucleus; hence, it has a daughter nucleus (A – 4, Z – 2).
- Beta Decay
- Beta-decay occurs with a nucleus having too many neutrons and too many protons; the protons or neutrons transform into another.
- Beta decay is again differentiated into two types – Beta minus and Beta plus.
- Gamma Decay
- Gamma decay is considered those particles which can penetrate the matter at the greatest distance.
- It occurs after one of the decays, like the alpha or the beta decay, takes place.
- As the nucleus is left in an excited state, it tries to become stable, so it releases a gamma-ray photon; this helps the atom to lower its energy and attain stability.
SUMMARY
- Radioactivity is widely applied in the medical world. It helps in the diagnosis and therapy of various diseases
- The three types of radioactivity decay are Alpha, Beta, and Gamma decay.
- It is highly dangerous; hence, it needs to be used under careful observation.
FAQs
Q. What is radioactivity caused by?
The radioactivity occurs due because the atoms remain in a very unstable state. The nucleus present in the atom remains in a very exciting stage. So, to attain stability, radioactivity occurs.
Q. How long does it take for radioactivity to disappear?
Some of the radioactive elements disappear within minutes or even hours, but some of their decay very slowly. Some of the elements like Strontium-90 have a half-life of 30 years.
Q. How can radioactivity be avoided?
To avoid radioactivity, you need to go far away or distance yourself far away from the source of the radioactivity. For shielding, you can consider barriers made with concrete or lead. It protects from gamma rays.
Q. What happens if you are exposed to radioactivity?
Exposure to very high levels of radiation can cause critical health effects like skin burns and radiation sickness. It can also have an outcome of long-term health effects such as cardiovascular disease and cancer.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Radioactivity: Definition and Types! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
SOURCES
- Definition of Radioactivity: https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-radioactivity-606338 Accessed 19th April 2022.
- Radioactivity: https://www.britannica.com/science/radioactivityAccessed 19th April 2022.
- Applications of Radioactivity: https://www.britannica.com/science/radioactivity/Applications-of-radioactivity Accessed 19th April 2022.