Oxidation Reactions Study Guide
INTRODUCTION:
You may have observed that chip and snack packages have more air in them. Because oxygen is an extremely reactive gas, it might oxidize the fats or oils in the snack, causing it to deteriorate. When fats or oils are oxidized for a long time, they develop an unpalatable taste and odour. Nitrogen gas, in fact, is utilized in the packing of chips and other snacks to keep food from deteriorating. Wondering what oxidation is? Let’s find out.
WHAT IS OXIDATION?
The removal of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion during a process is known as oxidation. The oxidation number (also called the oxidation state) is the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom. The opposite process is called reduction. When the oxidation number of a compound, atom, or ion increases, it is said to be oxidized.
HISTORICAL DEFINITION OF OXIDATION
When oxygen was added to a chemical, it was referred to as oxidation because oxygen gas was the very first recognized oxidizing agent. However, adding oxygen to a substance usually results in electron losses and a rise in oxidation state; the concept of oxidation has been broadened to cover different chemical processes.
OXIDATION OF ALKANES:
- An alkane can be oxidized to the equivalent alkene when exposed to high temperatures in the presence of an adequate catalyst.
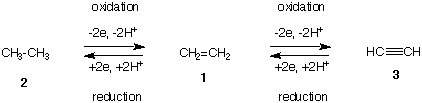 Source
Source - The most reduced form of a hydrocarbon is the alkane, whereas the most oxidized form is the alkyne.
OXIDATION OF HYDROCARBONS:
Now let’s discuss the oxidation of hydrocarbons in respect of the addition of oxygen to the compound:
- In organic chemistry, oxidation reactions include the introduction of oxygen to a molecule, which modifies the functional group of that chemical.
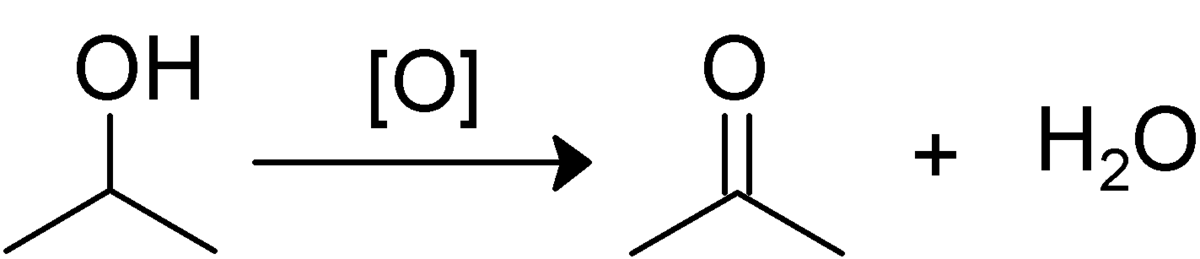
- When alcohol is oxidized, it produces either an aldehyde or a ketone.
- The oxidation result is a ketone instead of an aldehyde whenever the alcohol to be oxidized is a secondary alcohol. For instance, the oxidation of 2-propanol gives propanone.
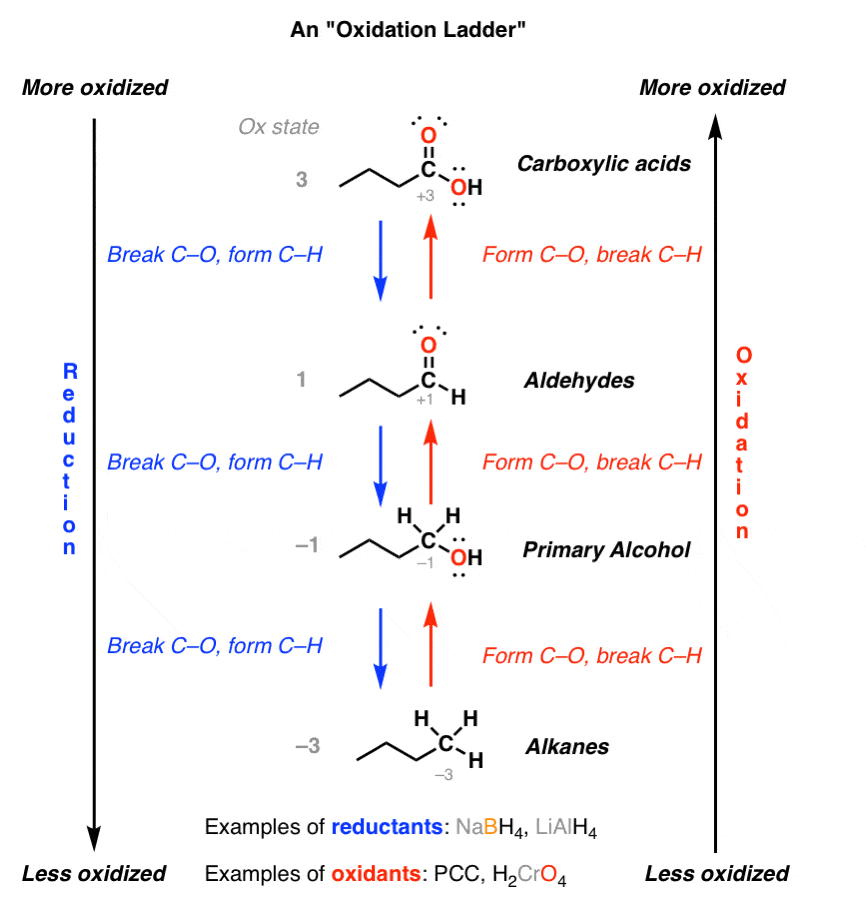
After you’ve mastered oxidations and reductions, you’ll find that some compounds’ reactions can occur in a logical order.
- The alkane could be converted to primary alcohol by oxidation.
- The alcohol could be converted to an aldehyde by oxidation.
- The aldehyde could be converted to a carboxylic acid by oxidation.
This is what we call an oxidation ladder.
CONCLUSION:
- The removal of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion during a process is known as oxidation.
- In organic chemistry, oxidation reactions include the introduction of oxygen to a molecule, which modifies the functional group of that chemical.
- The oxidation result is a ketone instead of an aldehyde whenever the alcohol to be oxidized is a secondary alcohol.
FAQs:
1. What is the oxidation of propanol?
Propanol is oxidized to the aldehyde propanal by sodium dichromate acidified in dilute sulphuric acid. The color shift of the dichromate solution as it has been reduced from orange to green indicates the oxidation of the alcohol to an aldehyde.
2. Can 2-propanol be oxidized to a carboxylic acid?
A carboxylic acid can be formed when propanol (primary alcohol) is oxidized. Different alcohol kinds react to oxidation in different ways. 2-propanol is a secondary alcohol that may be converted to a ketone by oxidation but not carboxylic acid.
3. Which compound is formed by the oxidation of 2-propanol?
The oxidation result is a ketone instead of an aldehyde when the alcohol to be oxidized is secondary. Propanone is produced by oxidizing the most basic secondary alcohol, 2-propanol.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Oxidation Reactions! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Oxidation Reactions. https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/oxidation-reactions/lesson/Oxidation-Reactions-CHEM/. Accessed 1 Feb 2021.
- Oxidation Definition and Example in Chemistry. https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-oxidation-in-chemistry-605456. Accessed 1 Feb 2021.
- Oxidation: Definition, Classification, and Examples. https://researchtweet.com/oxidation-definition-classification-examples/. Accessed 1 Feb 2021.