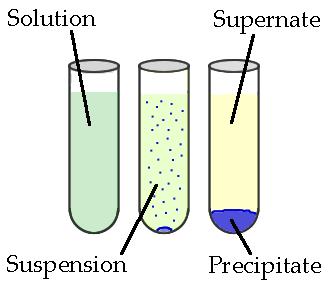
Precipitates And Solubility Rules Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
What is precipitation?
Precipitation is a chemical reaction that is known to occur within an aqueous solution when two ions bond together, forming an insoluble salt. For example, two solutions that contain different salts come in contact, resulting in the formation of an anion/cation pair. An insoluble salt is then formed, which then precipitates out of the solution. To properly make predictions regarding precipitation reactions, knowing all the solubility rules and net ionic equations is necessary, and this guide will help you learn just that!
WHAT IS SOLUBILITY?
Solubility of any gaseous, liquid, or solid substance is its ability to dissolve in the solvent and form a solution.
- What does solubility primarily depend on? It depends on the solvent used and the temperature alongside pressure.
- How is solubility measured? It is measured using the concentration of the given saturated solution. A solution can be considered a saturated solution when even after adding solute, the concentration of the solution does not increase anymore.
The degree of solubility usually depends, as mentioned before, on the substance, which could range from being infinitely soluble like ethanol in water or even poorly soluble like silver chloride in water. Under some specific situations, the equilibrium solubility can also be exceeded, resulting in a supersaturated solution.
However, remember, solubility never depends on the particle size; even really large particles can eventually dissolve!
FACTORS THAT AFFECT SOLUBILITY
- Temperature: The solubility of any solute depends on the temperature. For solids that dissolve in liquid, the solubility changes with changing temperature. However, with gasses, solubility decreases with an increase in temperature.
-
Pressure: Pressure has very little effect on the solubility of solids and liquids but has a drastic effect on the gaseous solutes. This is very much visible when you open a soda bottle and experience a hissing sound which happens because the content has been under pressure to ensure the soda stays carbonated.
-
Polarity: A solute would dissolve best in a solvent with a similar chemical structure. An example would be sugar which is a polar solute, and it dissolves exceptionally well in polar water; however, it remains insoluble in non-polar solvents like benzene.
SOLUBILITY RULES AND PRECIPITATION REACTIONS
- Alkali metal compounds are soluble.
- Ammonium (NH₄) is considered soluble.
- Nitrates, perchlorates, and chlorates are soluble.
- Most hydroxides are considered insoluble, exceptions would be alkali metal hydroxides, and Ba(OH)₂.Ca(OH)₂ are slightly soluble.
- Most bromides, iodides, and chlorides are soluble; exceptions are ones containing Ag⁺, Hg₂²⁺, Pb²⁺.
- Carbonates, sulfides, and phosphates are insoluble.
CONCLUSION
- Precipitation reaction occurs when cations and anions in an aqueous solution combine to form an insoluble ionic solid termed precipitate.
- To determine a precipitate, one must know the solubility rules.
- Solubility depends on temperature, pressure, and polarity.
FAQs
1. How do you know if a reaction is precipitating?
One must know the solubility rules to determine whether the reaction is precipitation or not.
2. How do you find the precipitate in a formula?
You can find precipitate in a formula by observing the solubility rules.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Precipitate And Solubility Rules! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Precipitation Reaction: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-chemistry/chapter/precipitation-reactions/.Accessed 10th March 2022.
- Precipitations Reactions: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Inorganic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_and_Websites_(Inorganic_Chemistry)/Descriptive_Chemistry/Main_Group_Reactions/Reactions_in_Aqueous_Solutions/Precipitation_Reactions#:~:text=If%20the%20rules%20state%20that,then%20no%20precipitation%20reaction%20occurs.Accessed 10th March 2022.