Gas Displacement Study Guide
Introduction
Just out of curiosity, take a glass of water and blow air into it through a straw. You will notice that as you blow, air bubbles will form inside the water, and then these bubbles eventually rise to the surface of the water and burst. Why do these bubbles move upwards? The obvious answer to this is that because the air inside the bubble is lighter than water, it rises. This very same concept is used in laboratories by scientists whenever they have to measure the volume or pressure of the gas that is formed during a reaction. Let’s learn more about this in more detail.
GAS COLLECTION
Throughout chemical processes, gases can occasionally be created. We can learn more about the reaction that took place by collecting and measuring the amounts of gas created, and we can also utilize this as a reactant in another reaction if we collect and measure the volumes of gas produced.
The method for collecting a certain gas is determined by the following factors:
– Solubility- refers to a substance’s capacity to dissolve in water
– Density- refers to how “heavy” it is in comparison to air.
The following are three popular ways for collecting a gas sample:
1. Displacement of Water
2. Upwards Delivery
3. Downwards Delivery
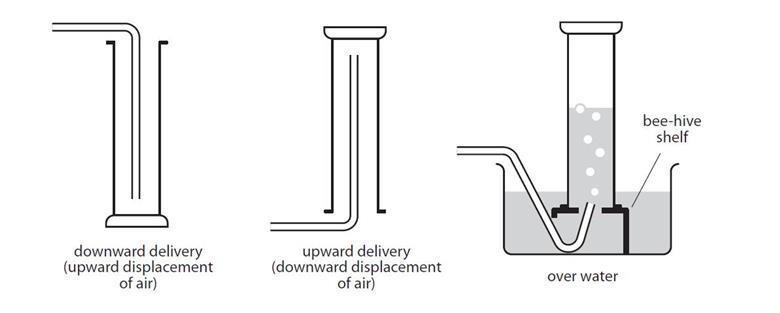
DISPLACEMENT OF WATER
- A jar is filled with water and hung upside-down in a pan of water in this procedure. Rubber tubing is attached to the reaction flask and supplied under the water bottle.
- The gas escapes through the tubing and displaces the water in the bottle as it is created in the reaction flask.
- The jar may be sealed with a cap once it has been filled with gas. The gas is not pure since it is gathered above water and is combined with vapor from the evaporation of the water.
- By eliminating the contribution of water vapor, Dalton’s law may be used to compute the quantity of the desired gas.
UPWARDS DELIVERY
- This approach is used to capture gases that are water soluble and have a lower density than air.
- Cl2, HCl, SO2 are among the gases that may be collected in this manner.
DOWNWARDS DELIVERY
- This approach is used to capture gases that are water soluble and have a higher density than air.
- One of the gases that may be collected in this manner is NH4.
SUMMARY
- The method for collecting a certain gas is determined by the solubility and density of the gas.
- Because gases have such low densities, determining their mass can be challenging.
- Collecting gas over water and measuring the level of displaced water is a typical approach to assess the amount of gas available; this is performed by inserting a tube into an inverted container, the opening of which would be submerged in a larger container of water.
FAQs:
1. Why is oxygen collected by the downward displacement of water?
Because oxygen is somewhat heavier than air, it is gathered by the downward displacement of water rather than by air. Air has a vapor density of 14.4, while oxygen has a vapor density of 16. It’s also water-soluble to a lesser extent. As a result, it does not collect in the air.
2. Which gas cannot be collected by displacement of water?
Gases that dissolve in water are unable to be collected over water. Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, methane, ethylene, and chlorine are among the examples.
3. What are the methods of collecting gases?
- A gas that is denser than air can be collected by delivering it downward.
- Carbon dioxide, chlorine, and other gases can be collected using this approach.
- The delivery tube is simply pointed downwards into a test tube (downward delivery) or upwards into an upside-down volumetric flask (upward delivery).
- Whether the gas is denser than air (employ downward delivery) or lighter than air (utilize upward delivery) determines the method adopted.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Gas Displacement! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
SOURCES:
- Collecting Gases Over Water: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introchem/chapter/collecting-gases-over-water/ accessed 16 march 2022
- Gas Collection by Water Displacement: https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/gas-collection-by-water-displacement accessed 16 march 2022