Blocks in periodic table Study Guide
INTRODUCTION:
In this era of technological development, you must have encountered the feature of fingerprint biometric identification. What is so special about the fingertips that we could use them as proof of identification? What makes your fingerprint different from another person? It must come as no surprise that every person on this planet has a unique fingerprint that doesn’t match anyone else’s.
Every fingerprint has its unique feature, whether texture or the design of the thin lines that you can see in the image below. Similarly, elements in the periodic table blocks (tabular display of the chemical elements) possess unique properties that do not match with the properties and characteristics of any other elements. Let’s know more about them!
TRENDS OF THE BLOCKS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE:
The elements of the periodic table can be compared to different styles of music. Every set of elements has its features, yet distinct sets of elements share some electron arrangement traits. In the periodic table, we can recognize electrical composition and reactivity patterns that help us better understand the behaviour of specific elements.
PERIODS:
Periods are the seven horizontal rows of the periodic table. The number of electrons capable of inhabiting the sublevels that fill throughout each period determines the length of each period.
BLOCKS:
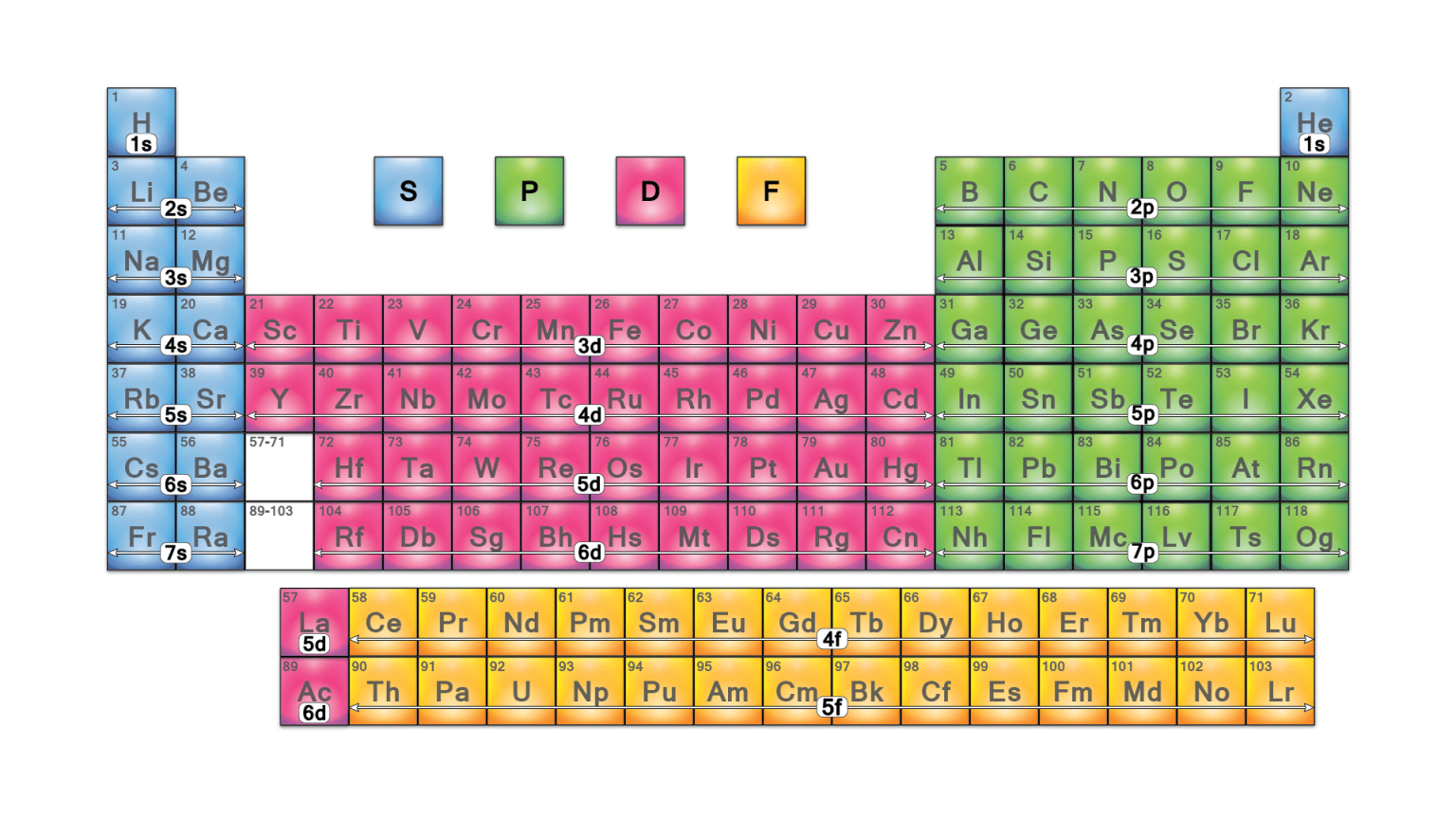
A periodic table block is a group of elements linked by the atomic orbitals whose valence electrons or vacant positions reside. The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block are designated after their respective orbitals.
S-BLOCK
Except for helium, the s-block elements are all on the periodic table’s left side. All the s-block elements are metals, excluding helium (and potentially hydrogen). Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals make up the s-block. Metallic character increases down the group.
P-BLOCK
The p-block elements are found on the periodic table’s right side. They are the table’s final six-element groups (except for helium). P-block metals have metal characteristics such as they are shiny and are good conductors of heat and electricity.
D-BLOCK
Transition metals (an element having a partially filled d subshell on its atom or the ability to produce cations with an unfilled d subshell) make up the d-block (groups 3-12). The characteristics of d-block elements are similar to those of highly reactive electropositive s-block elements and more electronegative p-block elements. For this reason, they are referred to as “transition” metals. They exhibit typical metallic properties, catalytic properties and paramagnetic behaviour.
F-BLOCK
Lanthanides and actinides are f-block elements or inner transition metals. The two rows of elements underneath the periodic table’s main structure consist of f-block elements. All the lanthanoids are silvery white soft metals and tarnish rapidly in air and are used for the production of alloy steels for plates and pipes. The actinoids are radioactive elements, and silvery in appearance.
CONCLUSION:
- Periodic table blocks indicate the filling of an electron sublevel.
- On the periodic table, groups are the vertical columns.
- The periodic table’s horizontal rows are known as periods.
FAQs:
1. What are the horizontal rows of the periodic table called?
Periods are the horizontal rows of the periodic table.
2. Which sublevel is being filled in period 1?
Only the first sublevel is being filled in the first period. The first period comprises only two elements because all orbitals can carry two electrons.
3. How does the electron configuration of an element give information about the period it is in?
The periodic table represents the number of circles in an element’s electronic structure as the period number that the element belongs to.
4. What are the 4 blocks in the periodic table?
The elements in the periodic table are divided into blocks based on their valence electron orbitals. S-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block are the four blocks.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Blocks in periodic table! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- Blocks of the Periodic Table. https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/blocks-of-the-periodic-table/lesson/Blocks-of-the-Periodic-Table-CHEM/. Accessed 27 Jan 2022.
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes for Chapter 8 – The d and f Block Elements. https://www.vedantu.com/revision-notes/cbse-class-12-chemistry-notes-chapter-8-the-d-and-f-block-elements. Accessed 27 Jan 2022.