Fluid Pressure Study Guide
What is Fluid Pressure?
Fluid pressure is the pressure that a fluid exerts at any point within it. The product of the difference in height, density, and free-fall acceleration determines the difference in pressure between the two levels.
Furthermore, hydraulic systems and variations in the fluid’s velocity might cause the fluid pressure to be amplified. The manometer is the device used to measure fluid pressure.
Fluid Pressure Formula
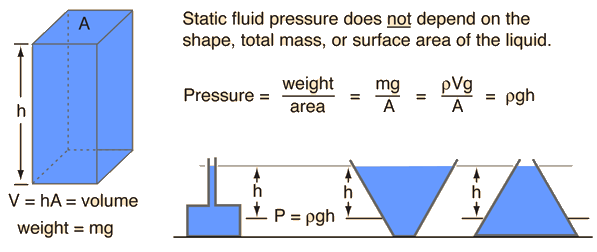
Fluid Pressure Formula
Pfluid = P ρgh
where
P = reference point’s pressure
Pfluid = fluid pressure absorbed at the point
Ρ = fluid density
g = accelerated gravity
h = Altitude from a reference point
Divide the mass of the liquid under consideration by the volume of the liquid under consideration to determine Liquid density.
ρ = m / v
m = Liquid mass
v = Considered liquid volume
At liquid atmospheric pressure, the system’s total pressure is:
Liquid = Po + ρgh
Where
Po = Atmospheric pressure
How do we Measure Fluid Pressure?
Liquid pressure is measured using a manometer in relation to an external source, which is often thought of as the earth’s atmosphere.
• Here, a liquid like mercury is used to monitor pressure while the gas whose pressure has to be computed is placed at the opposite end of the U-tube.• The end that is filled with gas is sealed, while the other end is left open.• However, both the gas pressure and the atmospheric pressure have an impact on the liquid.• When the liquid is level in both tubes, the air pressure within is said to be equal to the air pressure outside.• When the liquid rises over the straight level, it is also said to be lighter than the outside air’s pressure.• When the liquid is below the straight level, it is claimed that the air in the tube has a heavier pressure than the air outside.
Conditions for the Consideration of Fluid
We analyze fluid pressure in two scenarios:
• open circumstances or open channel flow• closed conduit or in a closed state
Hydrostatic pressure, which is sometimes called static fluid pressure, is the pressure of the fluid that is shown above. Since the pressure caused by moving fluid may not seem like much, it is only taken into account here in relation to the depth of the fluid. The static pressure of a liquid has nothing to do with its volume, mass, total surface area, or the type of container it is in.
Pascal’s Principle
As stated by Pascal’s Law,
“A restricted liquid’s external static pressure is “spread or transmitted uniformly throughout the liquid in all directions.”
Any surface in contact with the fluid is at right angles to the static pressure’s action. Pascal discovered that for a static fluid, the pressure at a location would be the same for all planes going through the fluid. Pascal’s principle or the fluid-pressure transmission principle are other names for Pascal’s law. French mathematician Blaise Pasca introduced the concept of Pascal law in 1653.
Conditions for Considering Hydraulic Pressure
Two scenarios that need to be considered are considered.
-
Open channel or open channel flow
-
Closed channel or channel affected
Effect of Gravity on Fluid Pressure
Gravity’s influence on fluid pressure is that it causes the fluid body to move in the opposite direction of its net acceleration. It also depicts the fluid pressure variation as a function of depth.
Summary
- The pressure inside a fluid caused by the fluid’s weight is referred to as fluid pressure.
- The pressure that a fluid exerts at any point within it. The product of the difference in height, density, and free-fall acceleration determines the difference in pressure between the two levels.
- Furthermore, hydraulic systems and variations in the fluid’s velocity might cause the fluid pressure to be amplified. The manometer is the device used to measure fluid pressure.
FAQ’s
Q. What are the factors affecting fluid pressure?
Fluid pressure is influenced by two things. They are the fluid’s depth as well as its density. At greater depths, a fluid exerts more pressure. As you get deeper into a fluid, all of the fluid above it presses down on you.
Q. What are the methods for calculating fluid pressure?
Use the formula pgh = fluid pressure to compute fluid pressure, where p is the density of the liquid, g is the acceleration of gravity, and h is the fluid’s height. To solve the equation, multiply the variables and obtain the product of the three.
Q. Why does fluid flow?
The density differential between liquid and solid (shrinkage flow) or the impact of gravity on density gradients within the fluid phase itself can generate fluid flow during solidification.
Q. Where can we use fluid pressure?
In automotive brakes, the liquid pressure is applied. When a vehicle’s brakes are deployed, the car comes to a halt due to liquid pressure. ii. Injection syringes are filled at atmospheric pressure.
Q. Explain how fluid pressure works?
Fluid particles move in all directions at random all of the time. The particles continue to collide with each other and anything else in their path as they advance. These impacts create pressure, which is distributed evenly in all directions.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Fluid Pressure! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun😎
]]>