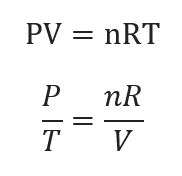Universal Gas Law Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
The general gas equation, often known as the universal gas law, describes a hypothetical ideal gas. Despite its flaws, this model approximates the behavior of many gases under a range of situations. Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron created the law in 1834 as an integration of empirical Boyle’s law, Charles’ law, Avogadro’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law.
UNIVERSAL GAS LAW FORMULA
The following is the empirical form of universal gas law:
PV=nRT
Where,P stands for pressure
The letter V stands for volume.
The number n denotes the amount of material.
And R is Constant for ideal gas.
Where R = 8.31 J/K. Mol.
UNIVERSAL GAS LAW APPLICATION
The volume of gases consumed or produced must be calculated using the universal gas law. In chemical equations, the ideal-gas equation is widely used to convert between volumes and molar quantities.
UNIVERSAL GAS LAW GRAPH
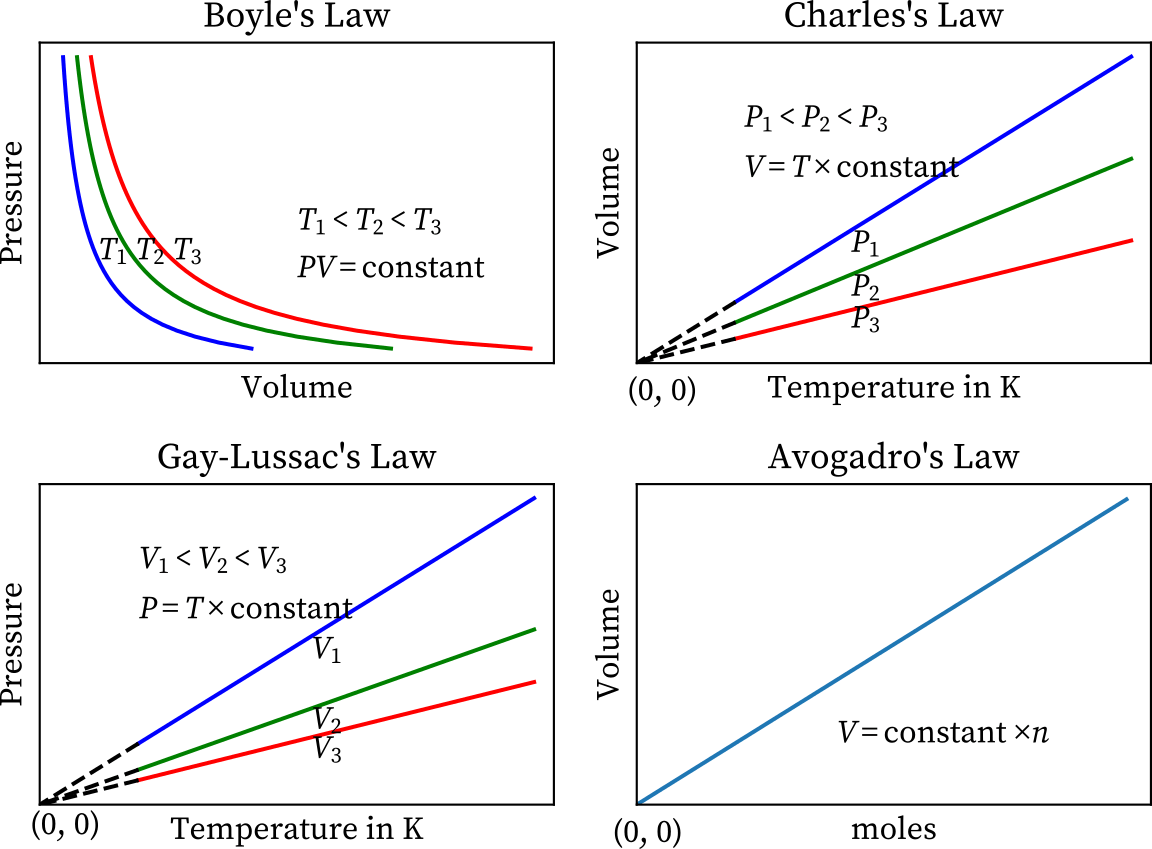
- P, V, T, and n are the four variables in the universal gas law.
- The ideal equation will be four-dimensional, which is impossible to depict on paper.
- Each of the parameters, on the other hand, can be plotted separately.
- The diagram below depicts four major relationships or gas laws.
- When one of the four parameters is held constant, the Universal gas equation can be plotted in three dimensions.
- So, with constant n, we have PV/T=k, which is the combined gas equation.
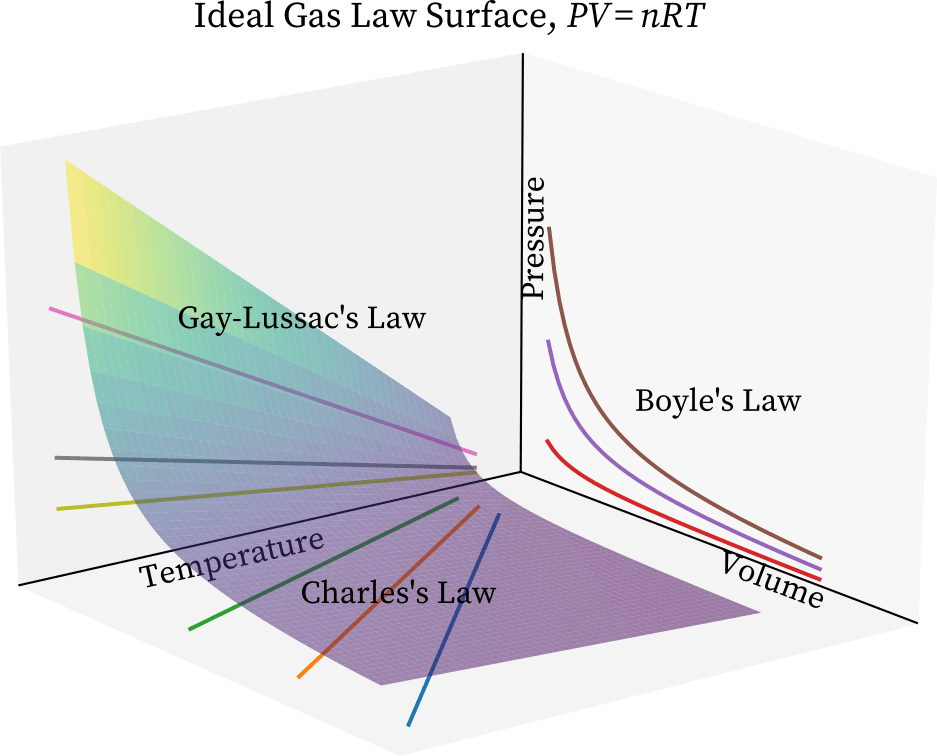
- The surface of this equation is depicted in the diagram below.
-
Boyle’s law governs the projection of the surface on the pressure-volume plane, as shown in the graph above.
-
We get PV = k by making variable temperature T constant in the combined gas equation while projecting.
-
Similarly, we get Charles’ law, T = k V, when we project on the temperature-volume plane, and Gay-Lussac’s law, P = kT, when we project on the temperature-pressure plane.
SUMMARY
- The general gas law is another name for the universal gas law.
- As the name implies, the law only applies to ideal gases and not to real gases.
- The pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas are all related to this law.
- Note that ideal gases are fictitious gases that do not exist in reality. Under certain conditions, such as low pressure and high temperature, many gases behave like ideal gases.
FAQ’s
Q. What does the universal gas law state?
The universal gas law is entirely obeyed by ideal gases. The volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas, directly proportional to temperature, and inversely proportional to pressure, according to this law. pV = nRT, in other words.
Q. Is the universal gas law considered a law?
Émile Clapeyron initially expressed it in 1834 as a combination of empirical Boyle’s law, Charles’ law, and Avogadro’s Law. The combined law form, often known as the Universal gas law, is the most basic full form.
Q. What is the equation of state from universal ideal gas law?
PV = nRT is the formula for the Universal gas equation. In this equation, P denotes the ideal gas’s pressure, V denotes the ideal gas’s volume, n is the total amount of ideal gas measured in moles, R denotes the universal gas constant, and T denotes the temperature.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Universal Gas Law! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
REFERENCE
- Ideal Gas Law: https://chemistrygod.com/ideal-gas-lawAccessed13th April 2022
- Ideal Gas Law: https://byjus.com/physics/ideal-gas-law-and-absolute-zero/#:~:text=The%20ideal%20gas%20law%20states,and%20the%20universal%20gas%20constant. Accessed13th April 2022
- Ideal Gas Law: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ideal_gas_law Accessed13th April 2022