Longitudinal Waves Study Guide
What Is Longitudinal Wave?
Longitudinal waves form when the substance is moved in almost the same way as the wave propagates. Longitudinal and transverse waves are 2 types of mechanical waves. Examples of longitudinal waves include sound waves, seismic P-waves, and ultrasonic waves. Electromagnetic waves and ocean waves are examples of shear waves. Refraction and compression form longitudinal waves.
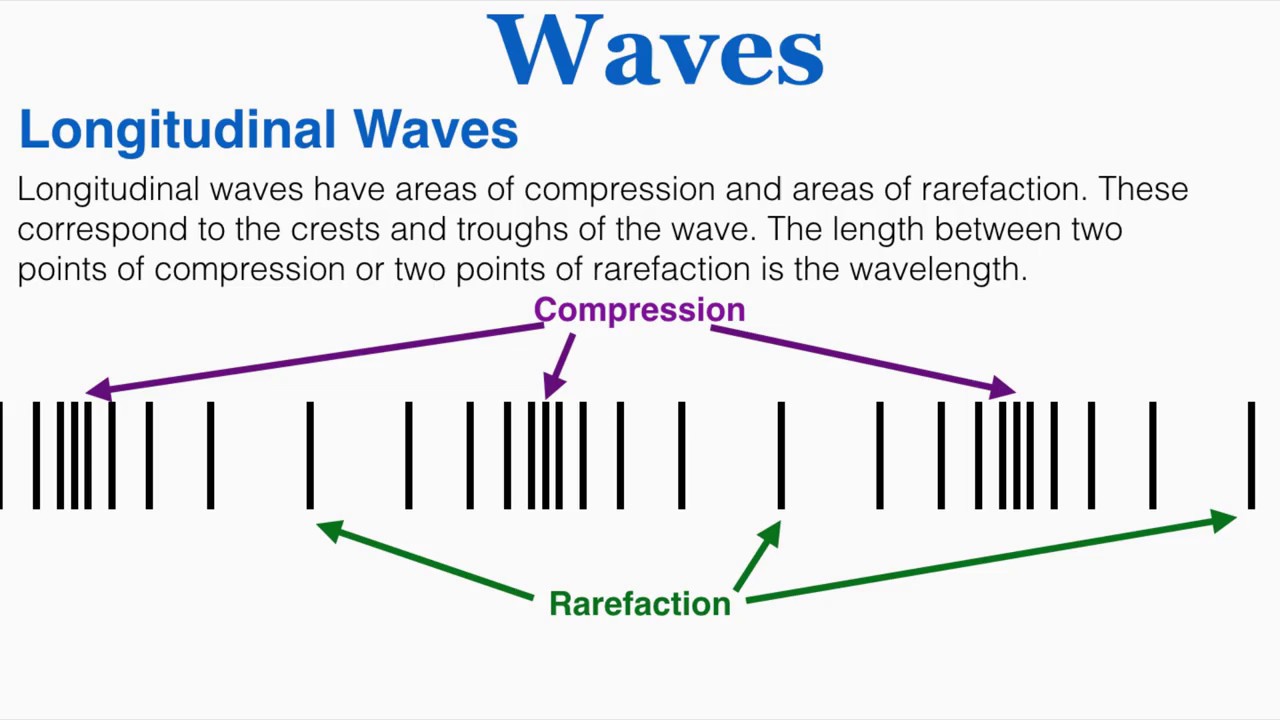
Sound propagates in the medium in the form of compressions and rarefactions. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the displacement of the medium is parallel to or opposite from the direction the wave travels, and the medium vibration is parallel to the direction the wave travels.
Each particle of matter vibrates about its normal rest position and along the axis of propagation in a longitudinal wave. All particles involved in the wave motion behave similarly, with the exception that there is a gradual change in the vibration’s phase, which means that each particle completes its cycle of reaction at a different time. The result of the combined motions is the advancement of alternating compression and rarefaction areas in the propagation direction.
Longitudinal Wave Formula
Y(x,t) = y0cos[ω (t – x / c)]
- Where y is the displacement of the point on the propagating sound wave and x is the distance traveled from the source of the wave.
- t is the elapsed time.
- The amplitude of the vibration is given by y0.
- The velocity of the wave is given by c.
- ω is the angular frequency (in degrees) of the wave.
- Time = quantity x / c (waves take to travel distance x).
- The formula for wave frequency (f) is f = ω2π
Sound Waves
A sound wave is created when energy moves through a medium, such as air, water, or any other liquid or solid material, creating a pattern of disruption that propagates away from the sound source. Sound waves are longitudinal waves.
Pressure Waves
Pressure waves are produced when an object vibrates, such as a ringing phone, and these waves are the result of sound waves. The surrounding medium’s particles are disturbed by the pressure wave, and those particles disturb the particles next to them, and so on.
LONGITUDINAL WAVE DIAGRAM
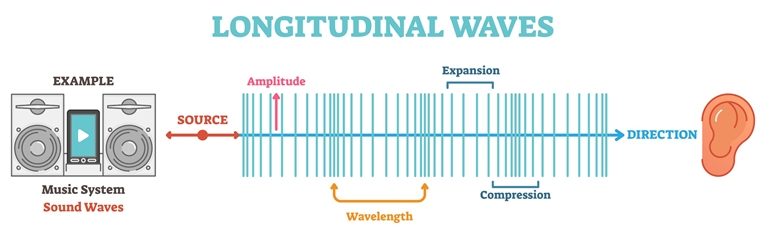
Characteristics of Longitudinal Waves
- Wavelength is the distance between two adjacent peaks or any two identical locations.
- The distance between the wave’s midpoint and its peak or between the wave’s midpoint and its dip.
- The number of full waves that pass by a specific place each second is known as frequency. Hertz is the unit of frequency measurement (Hz).
- Compression refers to the part of the longitudinal wave particles that are closest to each other.
- For longitudinal waves, the particles become thinner when they are farthest apart.
Difference Between Longitudinal And Transverse Wave
LONGITUDINAL WAVE
- The medium moves in the same direction as the shaft.
- There is only one action dimension.
- Waves cannot be polarized or aligned.
TRANSVERSE WAVE
- The medium is traveling in the opposite direction of the wave.
- It has two-dimensional effects.
- The wave might be aligned or polarized.
SUMMARY
- Longitudinal and transverse waves are 2 types of mechanical waves.
- Examples of longitudinal waves include sound waves, seismic P-waves, and ultrasonic waves.
- Refraction and compression form longitudinal waves.
FAQ’s
Q. What can a longitudinal wave pass through?
Through a gas, a longitudinal wave can travel.
Q. Do longitudinal waves need air?
Yes, longitudinal waves need air.
Q. What is the distance between waves?
The wave height is the vertical distance between the crest and the trough. The wavelength is the horizontal distance between two adjacent crests or troughs.
Q. What is the velocity of a longitudinal wave?
Longitudinal waves, such as sound, travel through a medium at different speeds depending on their density and elasticity. In the air, sound travels at 0.33 kilometers per second (0.2 miles per second), 1.5 kilometers per second in water, and 5 kilometers per second in steel.
Q. Are electromagnetic waves longitudinal or transverse?
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves.
Q. Why is a sound wave called a longitudinal wave?
Because the particles of the medium through which the sound is transmitted vibrate parallel to the direction in which the sound wave moves, sound waves in air (and any fluid media) are longitudinal waves.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Longitudinal Waves! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! We promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
]]>