Plasma Membrane Study Guide
Introduction
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is the membrane found in all cells that separate the inside from the outside parts of the cell. In-plant and bacterial cells, a cell wall is linked to the plasma membrane on the exterior. The plasma membrane is made up of a semipermeable lipid bilayer. It helps in transporting materials and chemicals into and out of the cell.
What is a Plasma membrane?
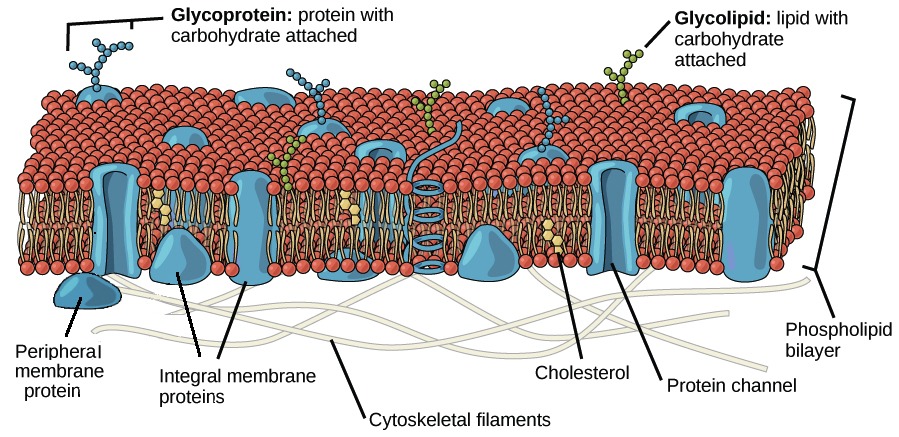
The plasma membrane is composed of membrane proteins and a lipid bilayer of phospholipids and maintains fluidity at different temperatures. This also comprises integral proteins that pass through the membrane and operate as membrane transporters. The peripheral proteins in the plasma membrane cling to it and perform the same role as the enzymes that make up the cell.
Functions of Plasma membrane
This membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer that consists of proteins. It provides a durable barrier between two aqueous compartments in the plasma membrane, one on the exterior and one on the interior of a cell. The proteins perform functions like cell-cell identification and targeted chemical transport. The plasma membrane or the cell membrane protects the cell while maintaining a consistent environment. It is in charge of carrying out several duties. In order to allow proteins in and waste materials out of the cell, it must be flexible.
Furthermore, it anchors the cytoskeleton to provide a cell shape and connects with the extracellular matrix and other cells to help form a tissue. The plasma membrane is in charge of interacting with other cells, such as glycoproteins or lipid proteins. The membrane also aids proteins in monitoring and maintaining the chemical climate of the cell and the movement of molecules across the membrane.
Plasma Membrane – Components
It is made up of the following elements:
- Phospholipids – the ultimate membrane fabric
- Membrane proteins – present on the outer, inner surface and also embedded in the phospholipid bilayer
- Cholesterol – folded between the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid membrane
- Carbohydrates – glycolipids, and glycoproteins are formed when lipids or proteins are found to be connected to the extracellular side of the membrane.
Plasma Membrane Structure
- The plasma membrane is a fluid network containing proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates.
- It is impenetrable to ions and water-soluble compounds, and only carriers, transmembrane channels, and pumps may pass through it.
- Transmembrane proteins provide nutrients to the cell, control internal ion concentrations, and provide a transmembrane electrical potential.
- Depending on where the membrane is located in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80% of the membrane, with proteins accounting for the remaining.
- The phospholipids are arranged in two layers (bilayer) stacked on top of each other.
- Phospholipids are lipids that include a phosphate group.
- The phospholipids feature a polar head and two tails, with the head being water-loving or hydrophilic. The head thus faces the outside and inside of the cell, where water is present.
- On the other hand, the tails are nonpolar and hydrophobic. These face inward and do not interact with water.
- The fluid mosaic model is used to describe the plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Conclusion:
- The plasma membrane of every cell consists of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins and cholesterol molecules.
- Cholesterol makes the cell membrane flexible and reduces its permeability to water.
- Recognition proteins help in identifying a cell.
- Receptor proteins receive information from outside the cell.
- Transport proteins carry substances into and out of the cell.
FAQs:
1. What are the 4 functions of the plasma membrane?
The functions of plasma membrane are:
- Providing a selectively permeable barrier
- Solute transport
- Macromolecule transport
- Reacting to external cues
- Intercellular communication
- Energy transfer
2. What is plasma membrane made of?
Glycerophospholipids, molecules consisting of glycerol, a phosphate group, and two fatty acid chains, make up the plasma membrane.
3. What is plasma membrane important?
A plasma membrane is required for cellular equilibrium in animal and plant cells.
4. Why is plasma membrane called so?
The term plasma membrane is derived from the German word “Plasmamembran”. It is a phrase developed by Karl Wilhelm Nägeli (1817–1891) to describe the hard film that develops when an injured cell’s proteinaceous sap comes into contact with water.
5. What is plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is the membrane that divides the inside of the cell from the outside world. It is found in all cells. The plasma membrane controls the transfer of materials into and out of the cell.
6. What is the difference between the plasma membrane and cell membrane?
The plasma membrane is also called the cell membrane.
7. What is the permeability of the plasma membrane?
The rate of passive diffusion of molecules through a membrane is defined as its permeability, and these molecules are referred to as permeant molecules. Permeability is primarily determined by the molecule’s electric charge and polarity, and to a lesser extent, by its molar mass.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Plasma Membrane! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun VR classrooms – we promise it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Structure of plasma membrane https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9898/ Accessed 20 Dec, 2021
- Plasma membranes https://www.nature.com/articles/s41589-020-0529-6 Accessed 20 Dec, 2021
- Plasma membrane https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/plasma-membrane Accessed 20 Dec, 2021
- Membrane https://www.britannica.com/science/membrane-biology Accessed 20 Dec, 2021
- Cell membrane https://www.ck12.org/biology/cell-membrane/ Accessed 20 Dec, 2021
- Plasma Membrane https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-biology-course-and-exam-description-0.pdf?course=ap-biology Accessed 20 Dec, 2021.