Bases – Naming and Formulas Study Guide
INTRODUCTION:
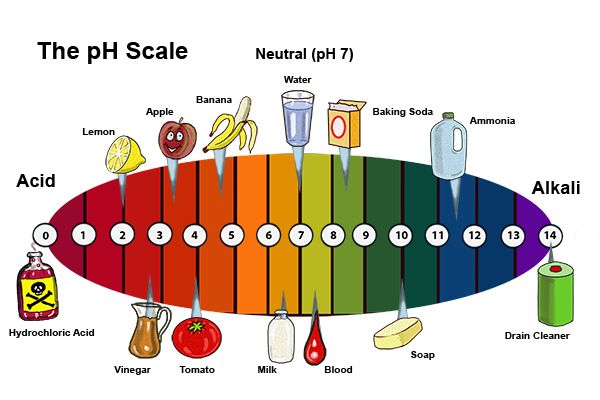
What is a base in chemistry? Basic compounds take protons, give away electrons, or release hydroxide ions in the aqueous phase. They neutralize acids by forming salts and water when they react with hydrogen ions. “Alkali” is a term for a base that dissolves in water. Bases play an important role in our day-to-day lives. Baking soda is a weak base common in our households, whereas drain cleaners are examples of strong bases.
WHAT IS A BASE?
- The base is an ionic compound that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
- Bases are bitter and are slippery.
- They have a pH greater than 7.
NOMENCLATURE OF BASES:
- Hydroxide, a polyatomic ion (covalently bonded set of two or more atoms), is found in the most strong bases. As a result, strong bases are called according to the naming conventions for ionic compounds.
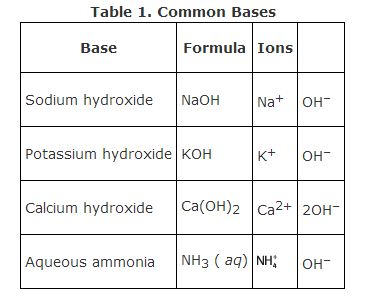
- For instance, sodium hydroxide is NaOH, potassium hydroxide is KOH, and calcium hydroxide is Ca(OH)₂.
- The ionic nomenclature scheme is also used to designate weak bases constituted of ionic compounds.
- Ammonium hydroxide, for instance, is NH₄OH.
- Because of their covalent connections, weak bases are frequently referred to as molecular or organic compounds. As a result, they are given names that fulfill the guidelines for naming molecular or chemical compounds.
EXAMPLES OF EVERYDAY BASES
ARRHENIUS BASES
They produce hydroxide ions, which raise the hydroxide content in the water. Arrhenius bases can be found in a variety of items, including:
- Cleaner for drains
- Detergent for laundry
- Grease lubricant
- Alkaline batteries
- Soaps and bath items
- Baking soda
BRØNSTED-LOWRY BASES
Bronsted-Lowry bases are bases that receive protons from other molecules. Bronsted-Lowry bases can be found in the following goods:
- Alkaline batteries with ammonia
- Mouthwash
- Pain relievers that are applied to the skin
- Chewing gum
- Upholstery for furniture
LEWIS BASES
Lewis bases are electron-pair givers, whereas Lewis’s acids are electron-accepting compounds. Here are some examples of bases.
- Alcohol
- Hair color
- Tobacco smoke
- Pesticides
- Plaster
- Epsom salts
CONCLUSION:
- The base is an ionic compound that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
- All the bases have hydroxide (OH‐) ions as anions, so their names end with hydroxide. The cations are simply the name of the other compound involved.
- Bases are bitter and are slippery. They have a pH greater than 7.
- Here are a few bases of your daily life. Laundry detergents, drain detergent, bathing soap, baking soda, toothpaste, mouth wash, oven cleaner.
FAQs:
1. How do you name and write chemical formulas of bases?
There is no particular system for naming a base. They all have hydroxide (OH‐) ions as anions, so their names end with hydroxide. The cations are simply the name of the other compound involved.
E.g., Sodium Hydroxide – NaOHAmmonium Hydroxide – NH₄OHMagnesium Hydroxide – Mg(OH)₂
2. What are 10 common household bases?
There are so many household bases. A few of them are:
- Baking soda
- Washing detergent
- Mouth wash
- Bathing soap
- Chewing gum
- Toothpaste
- Oven cleaner
- Drain cleaner
- Bleach
- Cement
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Base naming and formulas! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- 10 common household bases https://www.toppr.com/ask/question/what-are-10-common-household-bases/, Accessed on 15th Feb 2022.
- Bases naming and formula https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/bases-naming-and-formulas/lesson/Names-and-Formulas-of-Bases-CHEM/. Accessed on 15th Feb 2022.