CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Revision Notes
Chapter 9: Heredity and Evolution Revision Notes
Sexual reproduction
- The form of reproduction in which two individuals, one male and one female, reproduce together.
- They create sex cells, also known as gametes, which fuse together to form a new creature.
Genes
- The functional unit of heredity is the gene.
- In living creatures, each gene regulates one or more specific characteristics.
HEREDITY
- Heredity is the process through which an organism’s characteristics are passed down from generation to generation.
- Genes, which define the characteristics of an organism, carry out this process.
The work of Mendel
- Gregor Johann Mendel, sometimes regarded as the “Father of Genetics,” was an Austrian monk who studied pea plants to better understand heredity.
- His research created the groundwork for current genetics.
- The Law of Dominance, The Law of Segregation, and The Law of Independent Assortment were his three primary rules of inheritance.
Dominant traits
- Dominant qualities are traits that manifest themselves in an organism in every possible combination and are visible.
- The tall trait in pea plants tended to express more than the short trait in Mendel’s experiment.
- As a result, the plant’s tall characteristic is considered to be dominant over its short trait.
Recessive traits
- Recessive traits are those that are not expressed in the presence of a dominant allele.
- So, if a dominant allele occurs, a recessive character/trait is present in an organism but cannot be detected.
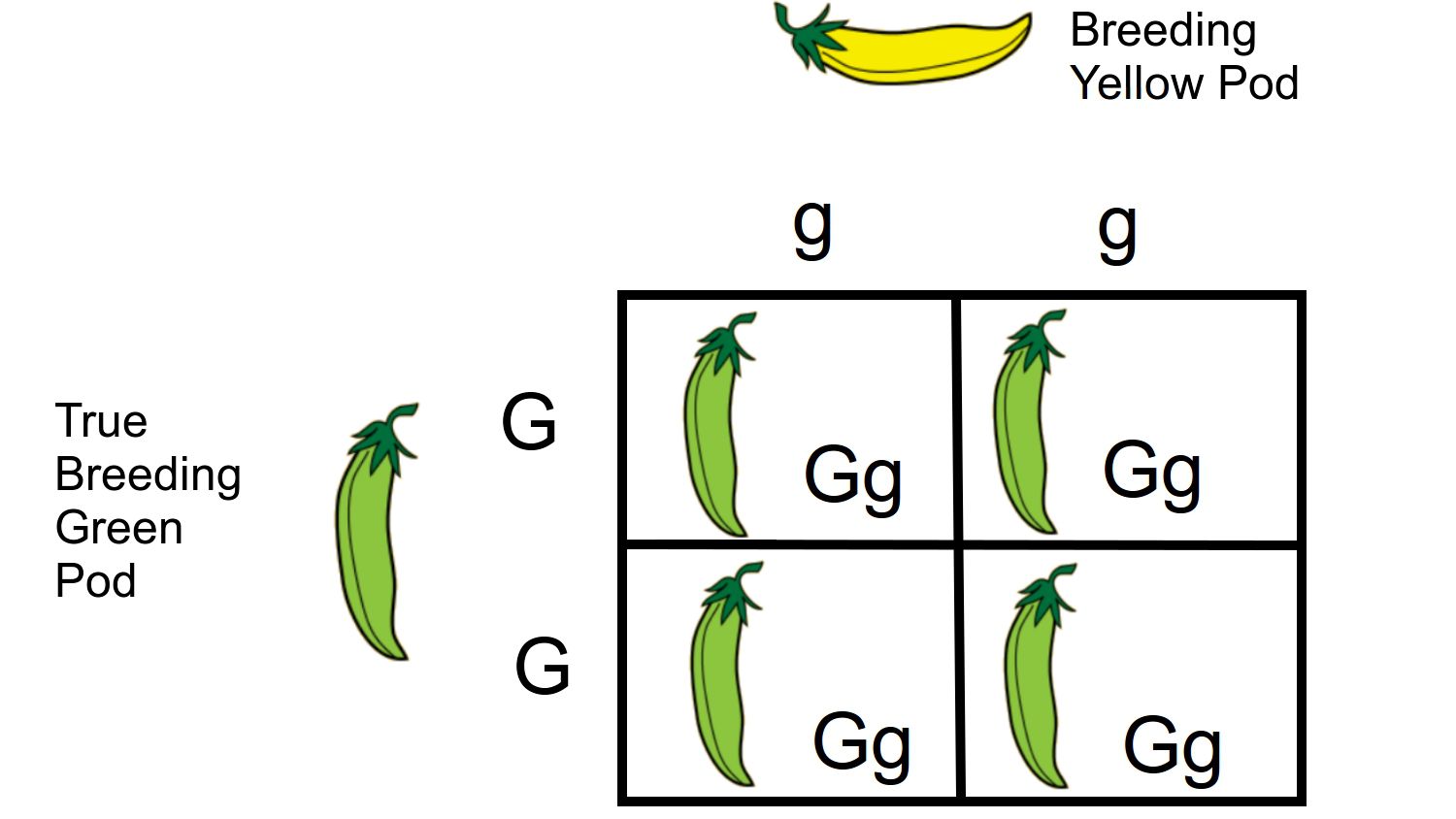
Monohybrid cross
- Monohybrid crosses occur when just one character is taken into account when crossing two organisms.
- Monohybrid ratio refers to the character ratio that results from this cross at the F2 generation.
- For example, if a tall plant (TT) is crossed with a dwarf plant (tt), the F2 generation yields three tall:one short plant.
- As a result, the monohybrid ratio is 3:1.
- The plant’s height is taken into account one at a time.
Dihybrid cross
- A dihybrid cross occurs when two characteristics are taken into account while crossing two organisms.
- The dihybrid ratio refers to the character ratio that results from this cross at the F2 generation.
- For example, if a round and green pea plant is crossed with a wrinkled and yellow pea plant, the first generation plants will all have round and green pea.
- When we cross the same for an F2 generation, we get four different character combinations in the ratio 9:3:3:1.
- As a result, the dihybrid ratio is 9:3:3:1.
Inheritance
- In biology, heredity is the process of passing down qualities from one generation to the next.
Mendel’s Laws
- According to the Law of Dominance, a gene contains two opposing alleles, one of which is always expressed in the organism.
- It’s known as the dominant gene, and it may be expressed in any combination.
- The Law of Segregation states that characteristics are entirely separated throughout the creation of gametes, with no allele mixing.
- The Law of Independent Assortment states that during gamete production, characteristics can segregate independently of various features.
Sex Determination
- Sex determination is the process of determining an individual’s sex based on the genetic material’s makeup.
- Various variables influence the sex of an embryo in different species.
- The presence or absence of the Y chromosome determines a person’s gender in humans.
- XX is a girl, while XY is a man.
- The X chromosome is always present in an ovum.
- When an ovum fuses with Y-containing sperm, a boy is born, and when an ovum fuses with X-containing sperm, a girl is born.
Traits
- Traits are distinguishing characteristics of an organism that are exhibited in a visible physical form or in a physiological element of the organism.
Speciation
- Drift in the genetic code
- Natural selection may have a big influence on which characteristics survive in a population. Random variations in gene variants, on the other hand, have been seen on several occasions.
- Genetic drift is the term for this phenomena. In a small population, genetic drift is defined as a change in the frequency of an existing allele.
- Genetic drift can lead to the extinction of a gene variant from the population, reducing genetic variety.
Acquired Characteristics
- Acquired characteristics refer to the qualities that an organism acquires throughout the course of its existence.
- These traits might be passed on to the following generation or not.
Inherited characteristics
- Inherited characteristics are qualities that are passed down from one generation to the next.
- These qualities are always passed on to the next generation, although they may or may not be displayed depending on dominance or recessiveness.
- Height, skin colour, and eye colour are all examples.
Variations in genetics
- Genetic variants are discrepancies in DNA sequences among organisms that result in a diversified gene pool. Different physical characteristics or metabolic processes result from these changes.
- Natural selection is a process that occurs in nature.
- It’s the process of selecting a beneficial characteristic in a population of a species.
- All current species are under equal strain from changing ecological circumstances.
- Species/organisms that are more suited to changing conditions live and reproduce, i.e. they are selected by nature, whereas those that are unable to adapt perish, i.e. they are rejected by nature.
Gene Flow
- The transmission of genes from one group to the next is known as gene flow.
Population
- A population is a collection of animals, plants, or any living entity capable of reproducing and producing fruitful, viable offspring.
FOSSILS AND EVOULTION
Evolution
- Evolution is the gradual change in a population’s heritable features over numerous generations. These changes may result in the emergence of new species, or species may evolve to become more adapted to their surroundings.
Fossils are proof of evolution.
- The hypothesis of evolution is backed up by a plethora of data.
- Fossils are the largest of them all.
- The preserved remnants of ancient creatures or plants that died millions of years ago are known as fossils.
- The fossils help us comprehend the anatomy and even physiology of ancient species, as well as how evolution operated and led to the genesis of modern animals.
Human development
- Humans are classified as members of the ape family.
- Humans and chimps and other primates share a tight genetic link today.
- While the exact mechanism by which humans evolved from primates remains a mystery, a bigger picture of human development has emerged.
- Dryopithecus, Ramapithecus, Australopithecus, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens neanderthalensis, Cro-magnon man, and lastly us, the Homo sapiens, are some of our predecessors.
- Human evolution may be traced all the way back to Africa. Then they spread out around the globe.