CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 Revision Notes
Chapter 1: The Living World Revision Notes
Multiple Choice Questions
-
The biologically cohesive unit of taxa is __________
-
Metabolism refers to __________
-
The term phylum was coined by _________
-
Which of these shows maximum diversity? ___________
-
** **Binomial nomenclature was given by _____________
- The living world comprises all living beings from billions of years of evolution.
- The living world is also known as the biosphere, and it is the sum of all living ecosystems on the planet.
- Every organism that respires, grows, functions independently, and needs specific living conditions to sustain are included in the living world.
- The living world is made of infinite living beings like humans, animals, microorganisms, and plants.
- The basic characteristics of all living beings have been the same for millions of years.
- All living beings consist of organic and inorganic matter.
Characteristics of the living world
All living beings show some basic characteristics.
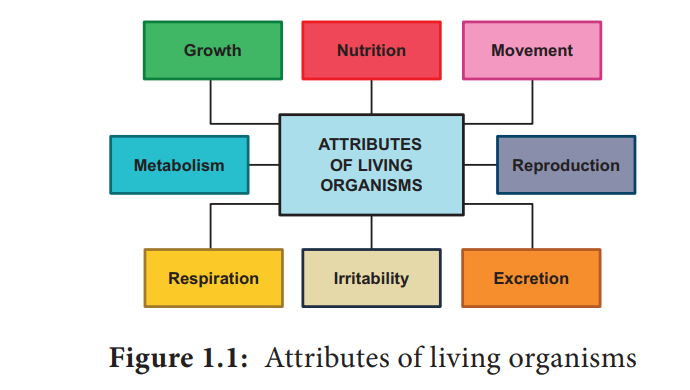
Source: Characteristics of the living world
- Growth– All beings of** the living world grow (in size and mass).
- Growth is an internal process and happens with the formation of new cells.
- Some organisms like plants have infinite growth and keep growing throughout their lives.
- Other organisms like animals and humans have finite growth, and their growth stops after a certain time.
- Reproduction– All beings of the living world reproduce, and reproduction is an essential process that helps them continue their species’ lineage.
- Reproduction is of two types- asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
- Metabolism– Metabolism is a set of all the life-sustaining chemical reactions that take place in the interior of the cells of living beings.
- Microbes, fungi, plants, and animals all need metabolism to sustain.
- Metabolism is of two types- anabolism and catabolism.
- Anabolism is when simpler molecules combine to form a complex compound. e.g., photosynthesis.
- Catabolism is a process when complex molecules break down to form simpler molecules. e.g., digestion and respiration.
- External Stimuli Response– All living beings tend to respond to external stimuli.
- These external stimuli could be heat, light, chemicals, pollutants, water, food, etc..
- The response to external stimuli is a proof of the consciousness of the living beings in the living world.
- Mortality– Every living creature in this living world goes through a complete cycle that involves birth, growth, maturity, and death.
- Nutrition– Every living being’s most basic sustainability requirement is food, which provides them with nutrition.
- Every being derives its nutrition from different sources. Without nutrition, all their basic functions will hamper, and they will not survive.
Diversity
- There are millions of living organisms on this planet. They are collectively referred to as biodiversity.
- Different organisms have different names in different languages.
- In order to avoid confusion, a common nomenclature is given to each species.
- It is a binomial nomenclature, i.e., each name consists of two parts.
- The first part is the** generic name** followed by the specific epithet.
- These biological names are in Latin and printed in italics.
- If handwritten, both the names are separately underlined.
- The first word denoting the genus starts with a capital letter, while the specific epithet starts with a small letter.
- The scientific name of mango is written as Mangifera indica.
- In this name Mangifera represents the genus while indica, is a particular species, or a specific epithet.
- To make studying of living organisms easier, the organisms are grouped based on easily observable characteristics; this is called classification.
- The scientific name for these groups is taxa.
- Hence, based on characteristics, all living organisms can be classified into different taxa. This process of classification is taxonomy.
- The study of relationships between different organisms is known as systematics.
Taxonomy Categories
- Classification involves hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a rank or category.
- Since the category is a part of overall taxonomic arrangement, it is called the taxonomic category and all categories together constitute the taxonomic hierarchy.
- Species: a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities.
- Genus: a group of related species which has more characters in common in comparison to species of other genera
- Family: a group of related genera with still less number of similarities as compared to genus and species. Families are characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species.
- Order: this and higher taxonomic categories are identified based on the aggregates of characters. Order is the assemblage of families which exhibit a few similar characters.
- Class: includes related orders.
- Phylum: classes comprising animals like fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds along with mammals constitute this category. In the case of plants this category is called division.**
- Kingdom: All animals belonging to various phyla are assigned to the highest category called Kingdom Animalia. The Kingdom Plantae, on the other hand, is distinct, and comprises all plants from various divisions.
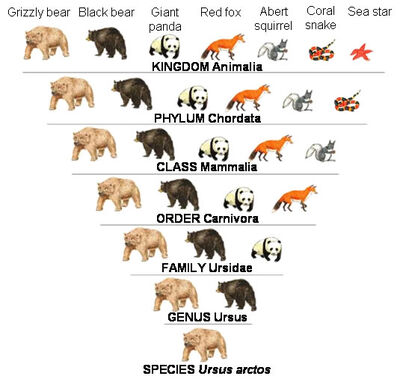
Source: Nomenclature
Taxonomical Aids
- Herbarium: a store house of collected plant specimens that are dried, pressed and preserved on sheets.
- Botanical Gardens: specialized gardens with collections of living plants for reference. Plant species in these gardens are grown for identification purposes and each plant is labeled indicating its botanical/scientific name and its family.
- Museums: have collections of preserved plant and animal specimens for study and reference. Specimens are preserved in the containers or jars in preservative solutions and also as dry specimens.
- Zoological Parks: places where wild animals are kept in protected environments under human care and which enable us to learn about their food habits and behavior.
