CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Revision Notes
Chapter 8: Cell: The Unit of Life Revision Notes
Multiple Choice Questions
-
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesized within the _______________
-
The structures that are formed by stacking of organized flattened membranous sacs in the chloroplasts are called ________________
-
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is mainly regulated by _______________
-
Which one of these is not a constituent of cell membrane? ___________
-
Peptide synthesis inside a cell takes place within the ______________
- The term cell was obtained from the Latin word “cellula,” which means a hollow space.
- It was discovered in 1665 by a British Scientist named Robert Hooke.
- He observed a piece of cork under a microscope and found compartments that looked like honeycombs which he called cells.
- The study of cells is called cytology.
What is the basic unit of life?
- All living organisms are made of cells. It can be a single cell for unicellular organisms or many cells for multicellular organisms.
- A cell is composed of a cell membrane surrounding various organelles such as a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, etc.
- Some cells are very specific and have certain functions and characteristics.
Why are cells called the building blocks of an organism?
- All cells are broadly grouped as prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cells neither possess a membrane-bound nucleus nor any membrane-bound organelles.
- Prokaryotic cells include different forms of Bacteria and Archaea.
- Eukaryotic cells include a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound cell organelles.
- Examples of eukaryotic cells are animal cells, plant cells, fungi, protists, etc.
- Cells make up tissues which then form organs.
- Many organs together make up an organ system like the digestive, nervous, reproductive, etc.
- Many systems put together make up an organism.
The basic function of a cell
- Any individual cell can synthesize the nutrients and energy needed to survive.
- It can replicate and produce more cells and thus have its progeny.
- There are a variety of chemical reactions which take place within a cell.
- Multicellular organisms have differentiated cells that perform different functions such as digestion, respiration, photosynthesis, reproduction, etc.
- A cell is designed to metabolize its food and expel its waste products.
- There is a cooperation between different cells as various reactions occur to sustain the living organism.
Structure of a cell
- The cell is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- The nucleus is at the center of the cell and is circular or oval-shaped.
- The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus, called the cytoplasmic solution or the cytosol.
- It contains the cell organelles.
- The cell membrane or the plasma membrane acts as the barrier between other cells and intra and extracellular fluids.
- It also holds adjacent cells within a tissue.
- A cell membrane is composed of a double layer of lipids and phospholipids with proteins within them.
- The proteins help to move other molecules across the membrane.
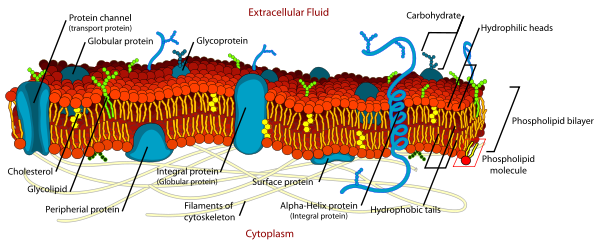
Source: Cell membrane parts
- The membrane is divided into a bimolecular layer of polar and nonpolar parts.
- The nonpolar part is inward and away from the water, and the polar parts are situated outwards towards the extracellular fluid.
- The phospholipid molecules are not attached chemically and are therefore free to move independently.
- It makes the bilayer flexibly fluid.
- It can be envisioned as a double layer of pins where the pinheads are outside and the needle parts point to the inside.
- It is called the fluid mosaic model of a cell membrane.
- The cholesterol molecules present in the membrane help transport particles to various cell organelles by forming vesicles.
There are two types of proteins in the cell membrane, which are:
- Peripheral membrane proteins are present on the surface of the membrane, which associates with other cytoskeletal elements and thus affects the motility and shape of the cell.
- Integral membrane proteins are present throughout the width of the membrane and cross through the polar and nonpolar parts of the cell membrane.
- A layer of monosaccharides is present on the surface of the membrane and is connected to the proteins and the membrane lipids.
- It is called the “glycocalyx” and is crucial for recognizing cells intracellularly.
- Membrane junctions are integrins which are proteins within membranes, and they connect to specific proteins on the other cells placed adjacently or to proteins present extracellularly.
- They differentiate between cells of different tissues.
Cell organelles
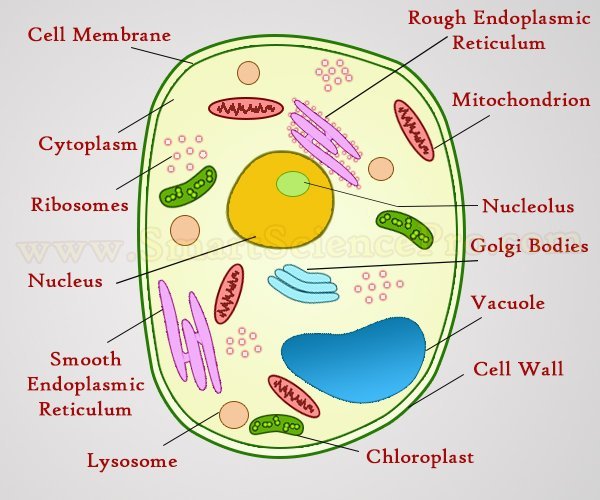
Source: Cell organelles
- Nucleus is the largest membrane-bound organelle and contains genetic material such as DNA and RNA.
- The nucleolus is a filamentous part containing RNA and protein constituents of the ribosomes, and it is present inside the nucleus.
- The endoplasmic reticulum(ER) is a network of membranes that packs proteins for the Golgi apparatus.
- Golgi apparatus is a sack that sorts proteins into vesicles.
- Ribosomes consist of proteins and RNA and are sites of the synthesis of proteins.
- Mitochondria are sites of energy synthesis and other chemical processes.
- Endosomes direct vesicles by either fusing with them or pinching them.
- Lysosomes digest cell debris and pathogenic bacteria and help the immune system.
- Peroxisomes help in chemical reactions by removing the hydrogen from many molecules like hydrogen peroxide.
