CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Revision Notes Part 1
Chapter 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance Revision Notes Part 1
- DNA is the genetic material for most organisms, except for viruses which use RNA instead
- DNA helps in the synthesis of RNA, which in turn helps in protein synthesis, and these proteins control traits of individuals.
- DNA, RNA, and the genetic code are responsible for the transmission of genes from parents to progeny.
Molecular Basis of Life
- At the molecular level, all living organisms are made up of cells
- Some organisms are made up of a single cell, while others contain millions of cells that carry out particular or specialized functions in the organism as a whole
Nucleotides: DNA & RNA
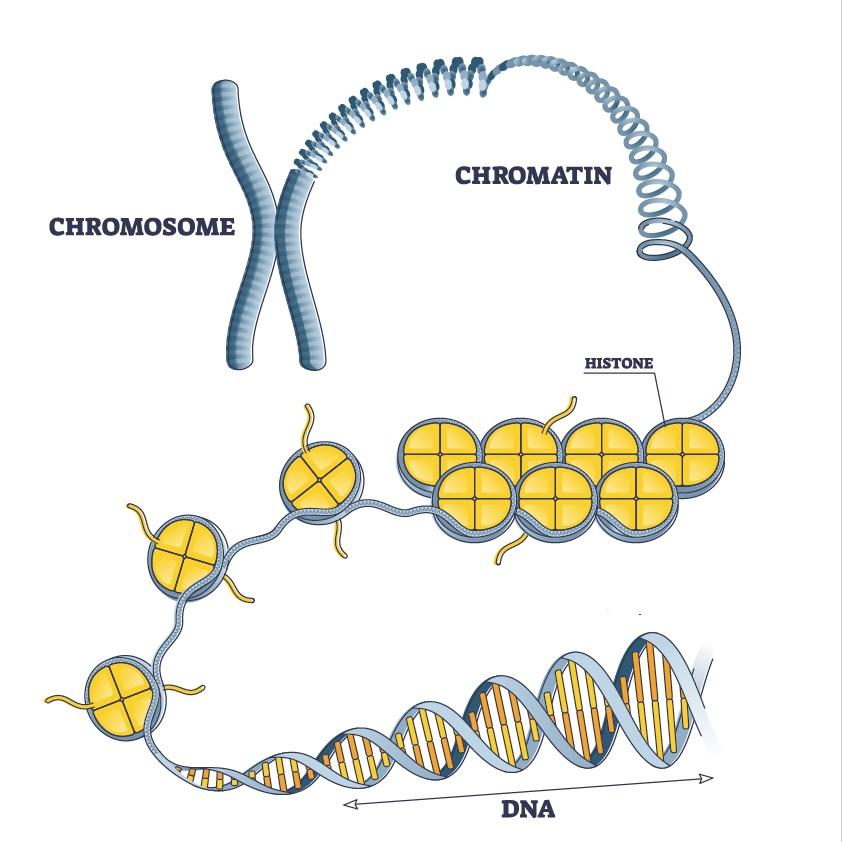
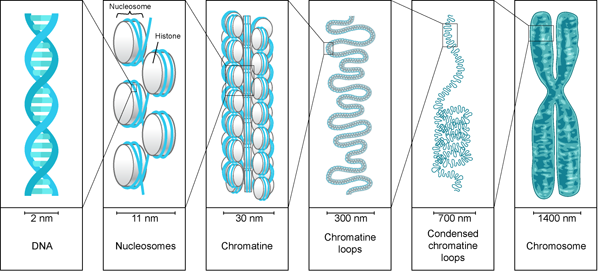
- The nucleolus of the cell contains chromatin which makes chromosomes. Chromosomes, in turn, consist of genes that are made up of twisted DNA strands.
- Living organisms have a fixed number of chromosomes. For example, human beings have 23 chromosome pairs, amounting to 46 total.
- DNA is responsible for the transfer of traits from one generation to another
- DNA functions:
- genetic material passed from parent to offspring
- provides all of the required information to direct and regulate the construction of the proteins necessary for a cell to perform all of its functions
- RNA is essential for various biological roles like coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes
- RNA is the genetic material in viruses
- RNA functions:
- convert the information stored in DNA into proteins
DNA and RNA Structure
- DNA and RNA molecules are polymers formed by single units called nucleotides (called ribonucleotides for RNA)
- DNA is double stranded, whereas RNA is single stranded
- Nucleotide components:
- Pentose Sugar
- Nitrogenous Bases
- Phosphate Group
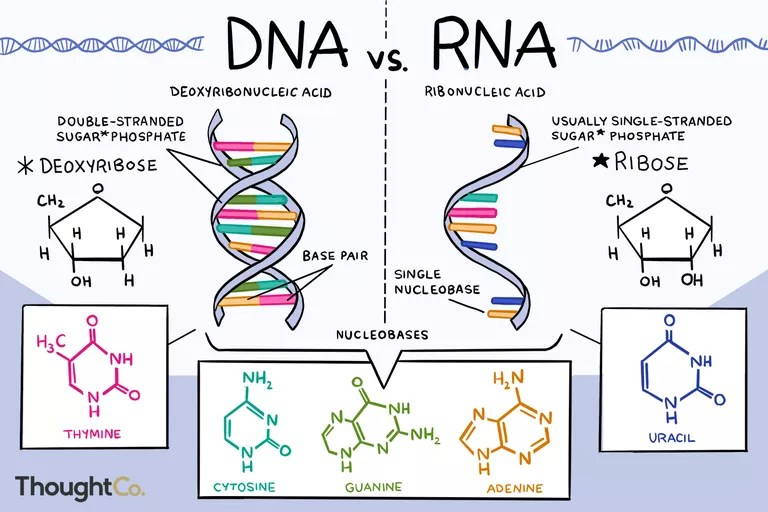
- Multiple nucleotides joined together form polynucleotides
- The structure of polynucleotide chain is as follows:
- adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), or thymine (T) and a phosphate group together make the polynucleotide chain.
- The phosphate groups are connected by phosphodiester bonds to the subsequent nucleotide’s sugar molecule, thus forming the polynucleotide chain.
DNA: Double Helix Structure
- made up of two polynucleotide chains
- backbone = sugar + phosphate
- interior parts made of nitrogenous bases
- complementary base pairing – only certain bases will pair with the another
- Maintains a uniform distance between these pairs – pairing occurs between one purine and one pyrimidine
DNA Structure and Packaging
- Cells make histone proteins that bind the DNA to counterbalance negative charge of the double helix
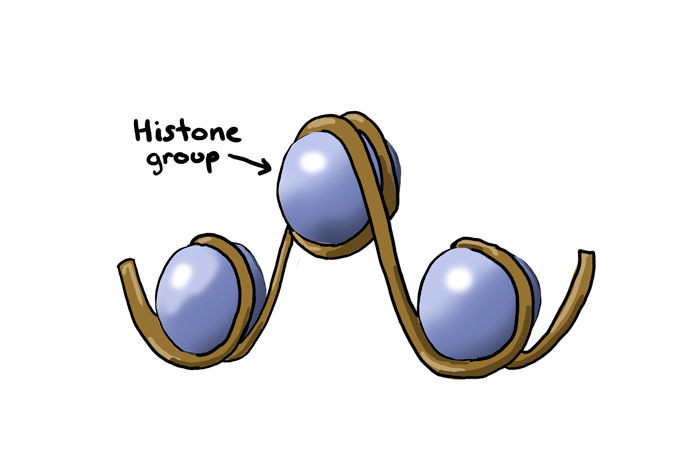
- DNA Packaging is the process of folding the DNA molecule into chromatin to fit into the nucleus of a cell
- required because DNA is around 3 meters in length, and it needs to be packed into the small nucleus
- DNA strands are helically coiled (right-handed coil)
- Pitch of each helix is 3.32 nm (10 nucleotides per turn)
- A typical strand of DNA is 2.2 meters long
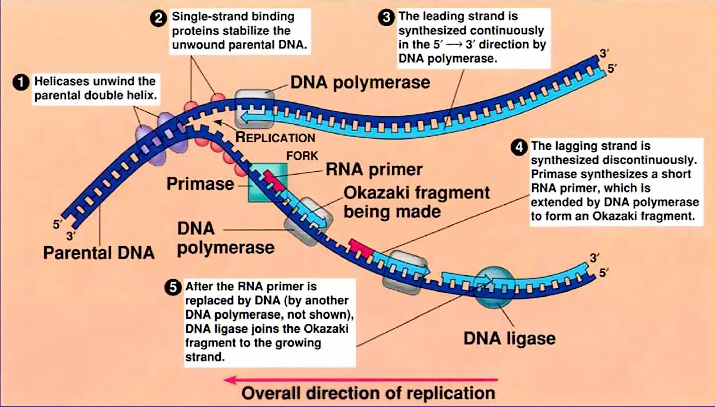
DNA Replication
- Replication results in multiple copies of a DNA strand, that takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination
- Primary enzyme involved in the process: DNA Polymerase
- DNA replication occurs after the unwinding of the double strand by helicase
Check out our DNA Replication Simulation in 3D!
Multiple Choice Questions
-
DNA Polymerase synthesises the new DNA strand in which direction?
-
Packaging of the DNA is important because ____________________
-
TRUE or FALSE: Chromosomes are made up of wound up RNA and DNA.
-
The different stages of DNA replication are ______, _________, and ________.
-
The negative charge of the DNA double helix is neutralized by ______ proteins.
