CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Revision Notes Part 2
Chapter 8: Human Health and Diseases Revision Notes Part 2
Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which type of tumors can invade adjacent tissues and cause harm? _______
-
Plasmodium, the parasite that causes malaria, is spread from person to person by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito. __________
-
The HIV virus uses __________ to generate viral DNA in the host.
-
Which of these impacts the cardiovascular system? ___________
-
Ringworm is caused by _________.
Human Health and Disease
- A state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being is characterized as health.
- A pathogen is a disease-causing organism, such as bacteria, viruses, protozoans, fungus, or worms.
- A pathogen can enter our bodies in a variety of ways.
Pathogen-related Disease
Typhoid: caused by a bacteria, Salmonella typhi.
- One can contract this disease through contaminated food and water.
- Symptoms include high fever, headache, constipation, and loss of appetite.
- This disease can be diagnosed by performing a Widal test, and intestinal perforations can be seen In some extreme cases.
Pneumonia: a lung infection that causes the air sacs in one or both lungs to become inflamed.
- Cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and trouble breathing can occur when the air sacs fill with fluid or pus (purulent material).
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most prevalent cause of bacterial pneumonia.
- This form of pneumonia can develop independently or as a result of a cold or virus.
Ascariasis: a parasitic illness of the small intestine.
- Caused by the roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides.
- Roundworms are parasitic worms, and Roundworm infections are rather frequent.
- The most prevalent roundworm infection is ascariasis.
Ringworm: A fungus causes ringworm, which is a common skin illness.
- Because it can create a circular rash (formed like a ring) that is generally red and itchy, it’s nicknamed “ringworm.”
- Ringworms may affect anyone.
Malaria: Malaria is an infectious illness spread by mosquitoes that affect people and other animals.
-
Malaria is characterized by fever, exhaustion, vomiting, and headaches.
-
In extreme cases, it can cause yellow skin, convulsions, coma in extreme cases, or death.
-
Lifecycle of Plasmodium
- Plasmodium is spread from person to person by female Anopheles mosquito bites.
- Sporozoites, which are formed by female anopheles saliva after they bite, are the infectious form.
- Before attacking RBCs, it replicates in liver cells, leading RBCs to explode.
- Haemozoin, a harmful toxin, is secreted.
- The infected person’s gametocyte is transferred to the mosquito whenever a mosquito bites an infected person.
- Macro and micro gametocytes get fertilized, converted, and sporogenesis happens in the mosquito’s stomach, culminating in the formation of sporozoites.
- The cycle is restarted when sporozoites reach a mosquito’s salivary gland.
- Plasmodium sp. needs both humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes to finish its life cycle.
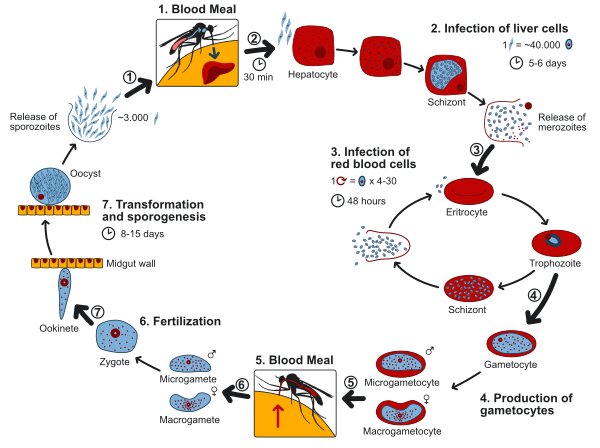
Source: Plasmodium lifecycle
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
- Caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
- The virus uses the reverse transcriptase enzyme to generate viral DNA in the host.
- The viral DNA is integrated into the host genome, resulting in numerous copies of the virus.
- The virus targets helper T-cells, where it replicates and multiplies, resulting in a significant reduction in T lymphocyte numbers.
- After the virus targets T-helper cells, the infected person develops immunodeficiency.
- AIDS patients are vulnerable to infections such as mycobacterium, toxoplasma, fungal, and viral infections.
- The ELISA test is a commonly used AIDS diagnostic test.
- AIDS can be passed down from mother to fetus through the placenta, contaminated blood transfusions, or using an infected syringe.
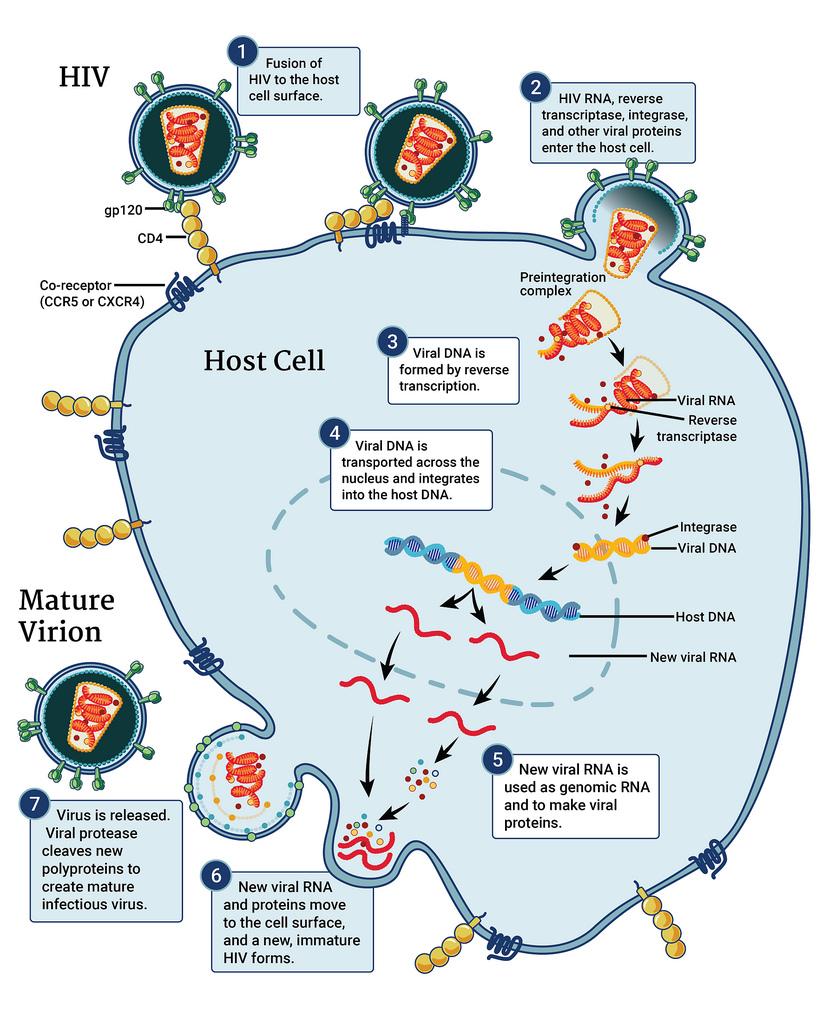
Source: HIV
Cancer
- Cancer is caused by unregulated cell division, which results in tumor development.
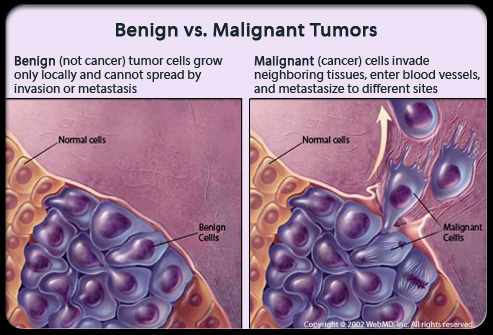
- Cancerous cells cannot stop future cell proliferation when they touch other cells.
- Non-invading benign tumors stay in their original position and do not spread.
- Malignant tumors can invade adjacent tissues and cause harm.
- Metastasis is a feature of malignant tumors in which sloughed-off cells travel to distant areas and establish tumors in various sections of the body.
- Cancer is caused by DNA damage or genetic mutations that result in improper cell cycle control.
- Under some conditions, cancer can also be triggered by the activation of proto-oncogenes found in normal cells.
- Ionizing radiation (e.g., X-rays, gamma rays), non-ionizing radiation (UV rays), chemical agents (e.g., tobacco), viral oncogenes of oncogenic viruses are all examples of carcinogens.
- A CT scan, MRI, X-ray, PET scan, or histological investigations of tissue and blood can all be used to identify cancer.
- Molecular biology approaches can also diagnose cancer by identifying inherited cancer-prone genes.
- Surgery, transplantation, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy are all options for cancer treatment.
- 𝛂 -interferon acts as a biological response modifier, activating the immune system and causing it to attack the tumor.
Alcohol and Drug Abuse
Commonly misused drugs include opioids, cannabinoids, and coca alkaloids.
- Opioids bind to opioid receptors in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
- Diacetylmorphine is sometimes known as smack or heroin.
- It’s made from the latex of the Papaver somniferum poppy plant, and the acetylation of morphine produces it.
- Cannabinoids interact with the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, and they have an impact on the cardiovascular system.
- Cannabis, hashish, charas, ganja, and other cannabinoids are extracted from the plant’s flower tops, leaves, and resins, Cannabis sativa.
- Cocaine, also known as coca alkaloid, is derived from the Erythroxylum coca plant.
- Cocaine works by interfering with dopamine transport, a neurotransmitter.
- Cannabinoids are also used by athletes to improve their performance, muscle relaxation, and anxiety reduction.
- Morphine is a sedative and a pain reliever.
- Depression, sleeplessness, and other mental illnesses are treated with barbiturates, amphetamines, and benzodiazepines, among other drugs.
- Tobacco’s nicotine (alkaloid) promotes the adrenal gland’s secretion of adrenalin and nor-adrenalin hormones. It raises blood pressure and heart rate.
- Smoking causes oxygen deficit by raising carbon monoxide levels in the blood, lowering the concentration of oxygen bound to hemoglobin.
- Excessive drug and alcohol use harms the nervous system and leads to liver cirrhosis.
