CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Revision Notes
Chapter 1: The Solid State Revision Notes
- Solids are materials with a definite shape and volume.
- Rigidity, incompressibility, slow diffusion, and mechanical strength characterize them.
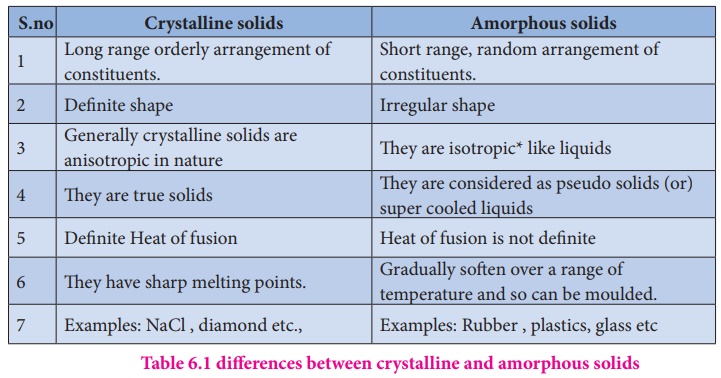
- Solids are categorized as crystalline solids amorphous solids.
Types of Crystalline Solids
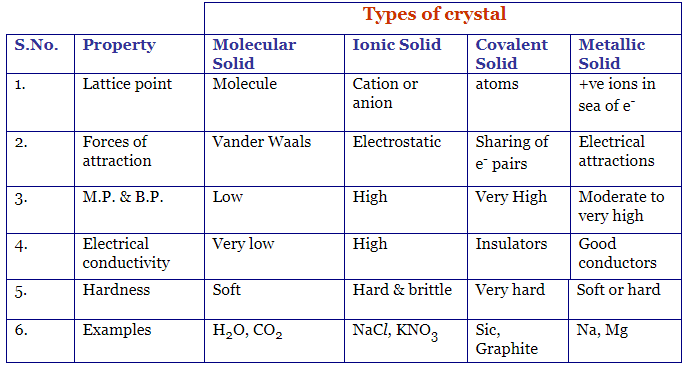
- Crystalline solids are of 4 types – ionic solids, covalent solids, molecular solids, metallic solids
Crystal Lattices
- The pattern formed by the points is known as the crystal lattice.
- These points are used to represent the positions of the repeating structural elements.
- A lattice is the best way to describe the periodic structure of an ideal crystal.
- The crystal lattice is a three-dimensional symmetrical structural arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules (constituent particles) as points inside a crystalline solid.
- It is a geometrical arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules of a crystalline solid as points in space.
- A single point represents each atom, molecule, or ion (constituent particle) in a crystal lattice.
- The term lattice site or lattice point refers to these points.
- In a crystal lattice, a straight line connects the lattice sites or points.
- We can get a three-dimensional view of the structure by connecting these straight lines.
- This three-dimensional arrangement is called Bravais Lattices.
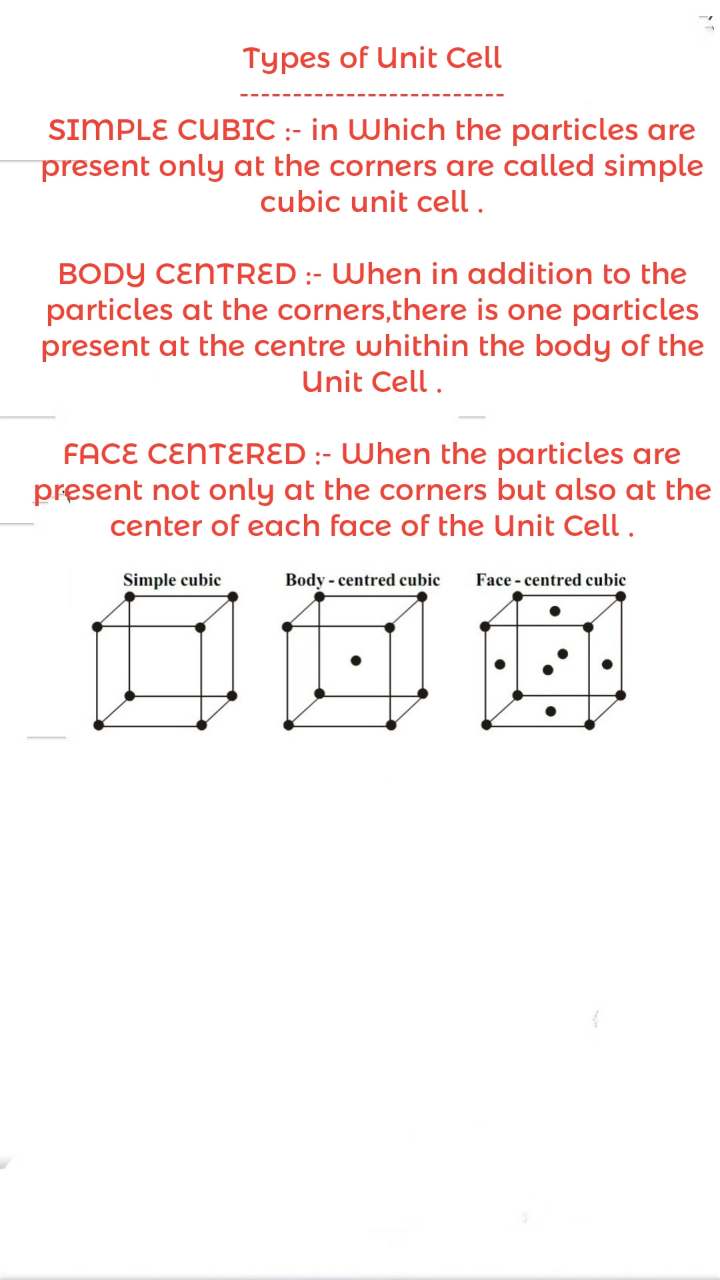
Unit Cell
- The tiniest of a crystal lattice is the unit cell.
- In a crystal structure, it is the simplest repeating unit.
- The unit cell is repeated in different directions to create the entire lattice.
Types of Unit Cells
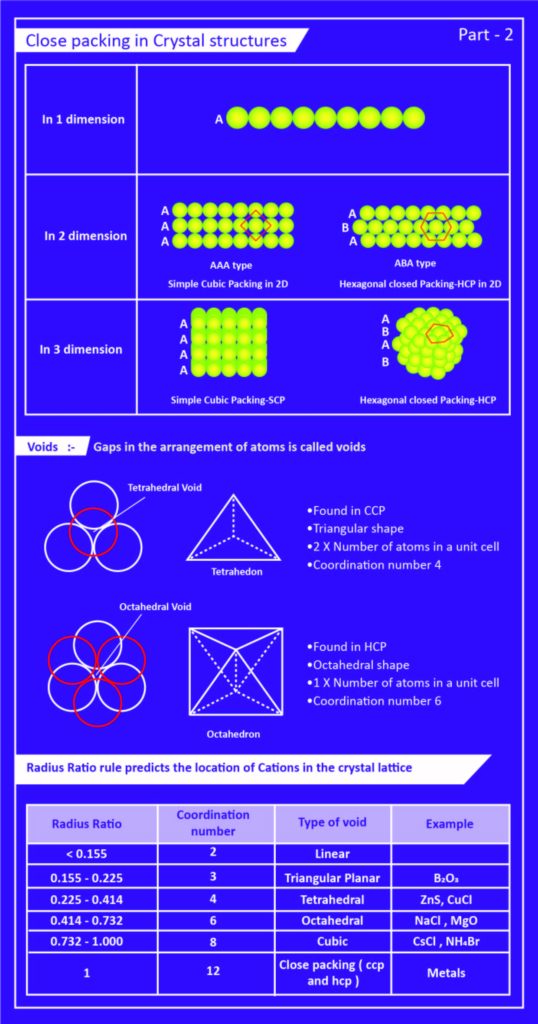
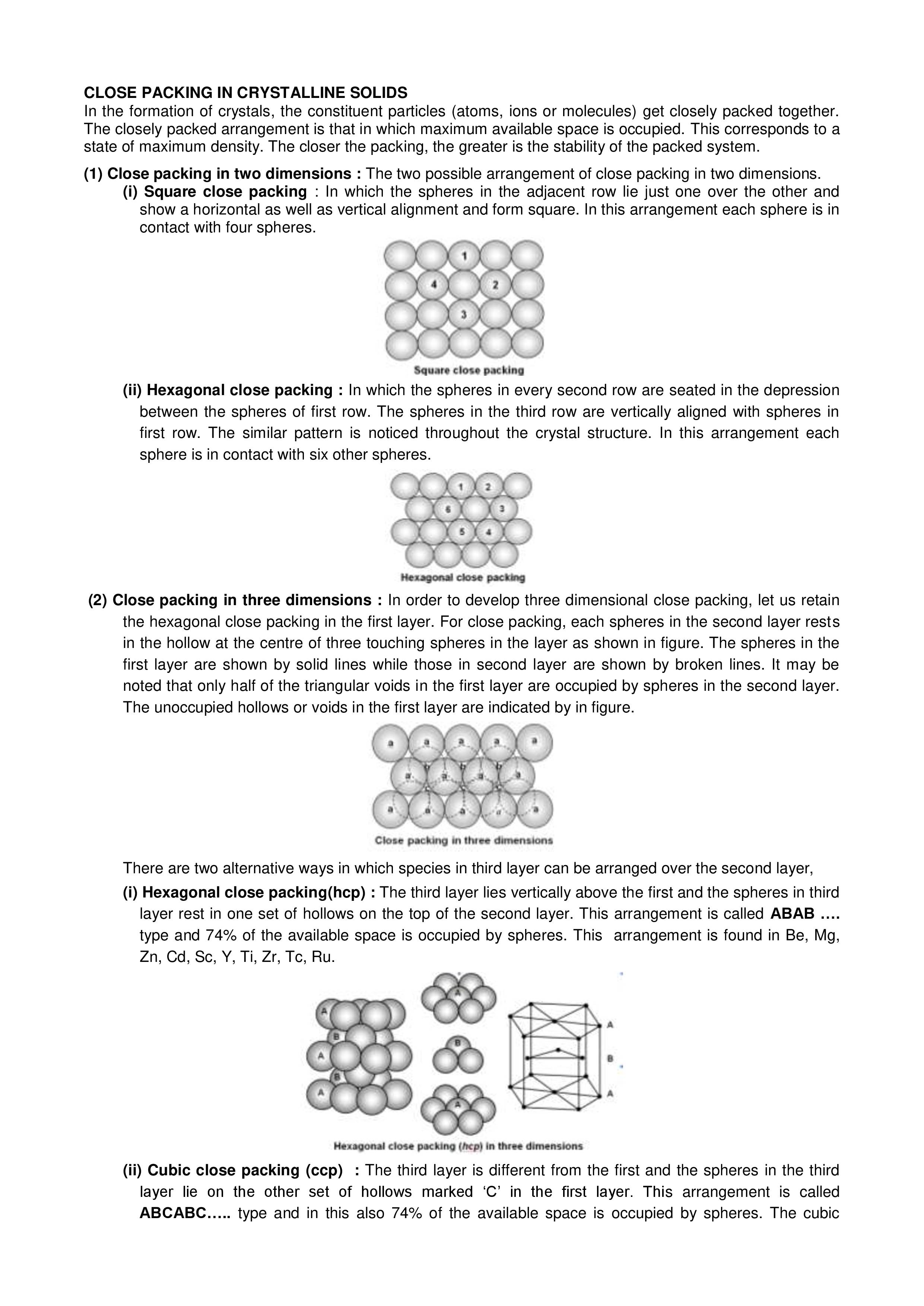
Close Packing
- The space efficient arrangement of the constituent particles in a crystal lattice is known as close packaging.
- To better comprehend this packing, we must assume that all particles (atoms, molecules, and ions) have the same spherical solid shape.
- As a result, the lattice’s unit cell is cubic in shape.
- There will always be some empty spaces in the cell when we stack the spheres.
- The arrangement of these spheres must be very efficient in order to minimize these empty spaces.
- To avoid empty spaces, the spheres should be arranged as close together as possible.
One Dimension
- The spheres (i.e. the atoms) are arranged in a row in this arrangement.
- All of the spheres are tightly packed and in close proximity to one another.
- As a result, one sphere is in contact with the other sphere on both sides.
- So there are two spheres or particles in close proximity to each other.
- As a result, the one-dimensional structure’s coordination number is 2.
Two and Three Dimension
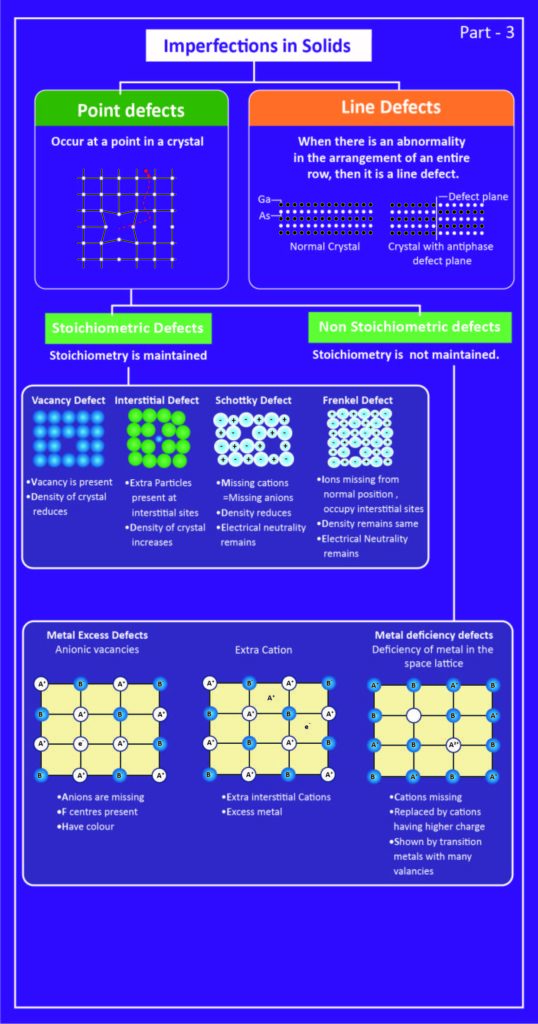
Imperfections in Solids
- Any irregularities in the pattern of crystal arrangement in a solid lattice leads to imperfection in the solid.
- These defects occur when crystallization happens very fast.
- This is mainly due to the limited amount of time for particles to arrange themselves in a regular pattern.