CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Revision Notes
Chapter 16: Light Revision Notes
Light: Only when an object emits light or reflects light is when the object is visible to our eyes.
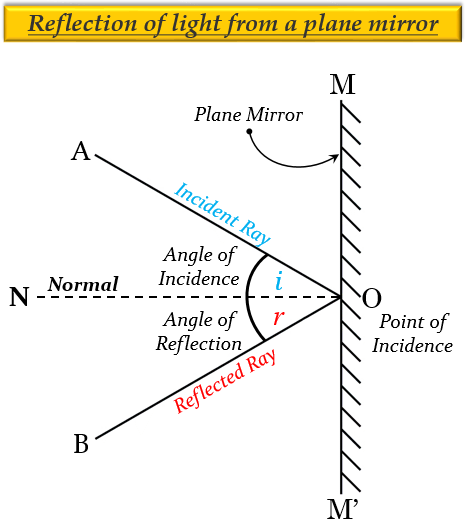
LAWS OF REFLECTION
1] The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
2] The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray lie in the same plane.
A plane mirror’s effect of reversing pictures from left to right is known as lateral inversion. Our left hand, for example, will appear to be right and vice versa.
TYPES OF REFLECTION
(i) Regular Reflection:
When a parallel light beam strikes a smooth and level surface, the reflected rays will be parallel, which is called regular reflection. A plane mirror’s reflection is an example of regular reflection and helps form images.
(ii) Diffused or Irregular Reflection:
When light strikes a rough or uneven surface, it is reflected in various directions due to irregularities.
- Multiple reflections occur when a reflected light beam is incident on another surface and reflected again.
- Periscopes make use of many reflections. Submarines, battle tanks, and personnel in bunkers use periscopes to see items that aren’t visible.
- Multiple reflections due to mirrors placed at specific angles to each other provide stunning patterns in a kaleidoscope.
- Sunlight, sometimes known as white light, comprises seven different colours.
THE HUMAN EYE
(i) Cornea: A transparent protrusion on the front surface of the eyeball that protects the eye while also aiding in light refraction.
(ii) Iris: Behind the cornea, a coloured diaphragm controls the quantity of light that enters the eye.
(iii) Pupil: Light enters the eye through a dark hole in the middle of the iris called the pupil.
(iv) Lens: The eye lens is a transparent, crystalline structure that lies behind the pupil and iris.
(v) Retina: The back of the eyeball’s surface where the lens concentrates light. It contains nerve cells.
(vi) Optic nerve: Collects sensory information from the nerve cells and transports it to the brain.
- Rods and Cones: Rod cells are sensitive to dim light, whereas cone cells are sensitive to colour and bright light.
- Blind spot: Lack of sensory cells where the retina and optic nerve meet leads to a blind spot as no vision is likely.
- Images formed remain for 1/16th of a second.
- Cataract (eye lens becomes cloudy) is treated by replacing with a new artificial lens.
- A normal eye can distinguish between items that are close by and those that are far away.
- Lack of vitamin A causes night blindness.
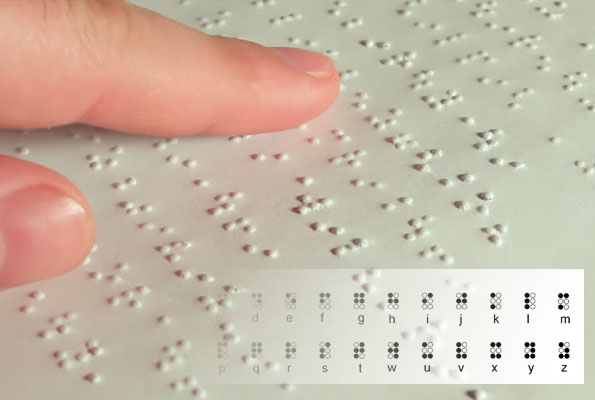
THE BRAILLE SYSTEM
- Eyesight could be lost due to disease or injury.
- Visually impaired people sharpen their other senses like touch and listening.
- The Braille system allows visually impaired people to read and write.
- The Braille code is embossed onto Braille sheets and depends upon recognition by touching.
Source: NCERT Book Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light (aglasem.com)
]]>