CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision Notes
Chapter 8: Cell Structure And Functions Revision Notes
-
A cell is an organism’s smallest living element (basic structural unit).
-
Robert Hooke discovered cells in cork for the first time in 1665 using a microscope.
-
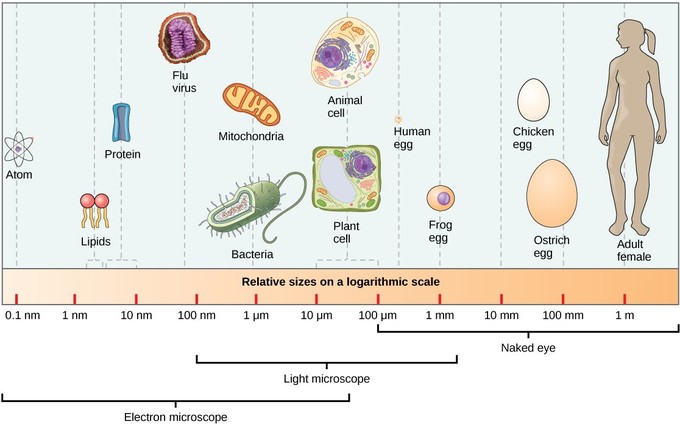
Cells come in a wide array of forms and sizes in different organisms (bacteria to ostrich eggs).
-
Some cells are sufficiently big to be seen without a microscope. An example is a hen’s egg.
-
Cell size is based on cell function (long nerve cells).
-
The cell numbers in an organism vary as well.
-
Some species have only one cell, whereas others have a great number.
-
In unicellular creatures (amoeba), a single cell performs all of the basic processes done by a variety of cells in multicellular organisms.
-
Organs are the different body parts that make up all creatures.
-
Organs are made up of groups of specialized cells called tissues.
-
Pseudopodia are used to move and feed on the amoeba.
PARTS OF THE CELL
The cell membrane, cytoplasm, which contains smaller components known as organelles, and the nucleus are the three primary components of the cell.
- CELL MEMBRANE:
The basic component of a cell is the cell membrane. The cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm and nucleus. Plant cells have a thick exterior layer called the cell wall.
- CYTOPLASM:
Between the cell membrane and the nucleus is a jelly-like substance called cytoplasm. The ensuing organelles can be found in the cytoplasm:
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Lysosomes
- Vacuole
- Golgi bodies
Protoplasm: It is the sum of the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
- NUCLEUS:
-
A nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Situated in the cell’s centre, it’s usually spherical and acts as the control centre.
-
Nucleolus: The nucleus has a tiny spherical body called the nucleolus.
-
Chromosomes: These are thread-like structures found in the cell nucleus. These contain genes and aid in inheritance from parents to offspring.
-
Prokaryotic cells lack a well-organized nucleus, i.e., the nuclear membrane.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
-
Plant cells differ from animal cells in that they have a cell wall that wraps around the cell membrane.
-
Only plant cells include coloured structures known as plastids. Chloroplasts are chlorophyll-containing green plastids (for photosynthesis).
-
In contrast to animal cells, which have a multitude of tiny vacuoles, plant cells have a large central vacuole.
Source: Chapter-8.pmd (ncert.nic.in)
]]>