CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Revision Notes
Chapter 13: Why Do We Fall Ill? Revision Notes
Health is defined as a condition of complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
- The immune system is the component of the body that protects you from diseases, external invaders, and other poisons.
Skin and Mucous Membranes
- The first line of protection is the skin and mucous membranes. W
- hile the skin protects the body from the outside, the mucous membrane protects the body from the inside.
WBC
- Leucocytes or Leukocytes are white blood cells. They are vital components of our immune system, and they may be found in the blood and lymph.
- They work by fighting and killing bacteria and keeping our bodies clear of diseases and pathogens.
- There are many various varieties of and they are also classed according to their region.
- Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils, and eosinophils are the several kinds of white blood cells present in the blood.
- These blood cells have a specific purpose.
NK Cells and Macrophages
- Macrophages are immune system cells that are huge and specialised.
- Infections or the growth of damaged or dead cells cause these cells to be formed. They assault cancer cells by destroying and ingesting them.
- Natural Killer Cells connect to the enemy cell and breakdown the cell’s membrane, rendering it useless.
Dendritic Cells
- Dendritic cells build the memory and transport pathogen information to the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
The Inflammatory Reaction
- When the body is wounded or infected by a disease, it produces an inflammatory reaction. Inflammation aids in the localisation of the problem and its prevention.
DISEASES
- Disease is a physical or mental ailment that affects the body.
- An external or internal element may be the cause of a disease.
- There are two sorts of diseases:
- Acute Diseases
- Acute illnesses are ones that last only a few days or weeks. These disorders are generally caused by an external factor and can be lethal.
- Chronic Diseases
- Chronic illnesses are ones that endure over an extended period of time. They might be caused by any external or internal trigger and require a long time to recover.
Symptoms and Signs of Diseases
- When the body becomes unwell, it exhibits distinct symptoms and indicators. These symptoms and indicators aid in the diagnosis and identification of the condition.
- A symptom is felt by the individual who is afflicted, whereas signs are visible to others.
- As a result, a symptom is subjective, but a sign is objective.
ORIGIN OF DISEASES
Different types of Causes of Disease
- Pathogens such as viruses and bacteria can cause disease. Internal causes, such as genetic mutation, can also cause illness.
Infectious Diseases
- Infectious illnesses are diseases that are caused by infections that can spread to other people in the community.
Non-infectious Diseases
- Non-infectious illnesses are those that do not transfer from one person to another. The majority of the time, these disorders are not caused by a pathogen.
Pathogens
- Pathogens are foreign agents that infect other organisms and cause illness. This pathogen encompasses bacteria, viruses, fungus, and protozoa, which are all hazardous germs or microorganisms.
Vector
- Vectors are creatures that transmit an infection from one host to another. Mosquitoes, rats, and mice are among the most prevalent vectors of infectious illnesses.
Bacteria
- Bacteria are microscopic creatures that may be found in practically every environment.
- Not all bacteria are pathogens’ enemies.
- Humans can benefit from some microorganisms as well.
- Bacteria are useful for digesting, antibiotic extraction, nitrogen fixation, and other processes.
Virus
- A virus is a harmful microbe that exists in nature.
- They lack the molecular machinery to reproduce in the absence of a host.
- As a result, they enter the host cell and proliferate, destroying the host cell in the process. Colds, influenza, dengue fever, AIDS, and other viruses are some of the most prevalent illnesses carried by viruses.
Fungi
- Fungi are eukaryotic creatures that rely on saprophytic nourishment.
- They might be single-cell organisms or multicellular organisms.
- Fungal illnesses include ringworm, nail infections, and other common skin infections.
Parasites
- A parasite is a creature that lives inside another organism, known as the host, and frequently causes harm to it.
- Its survival is reliant on its host; it must be present in the host to survive, develop, and proliferate.
Infections
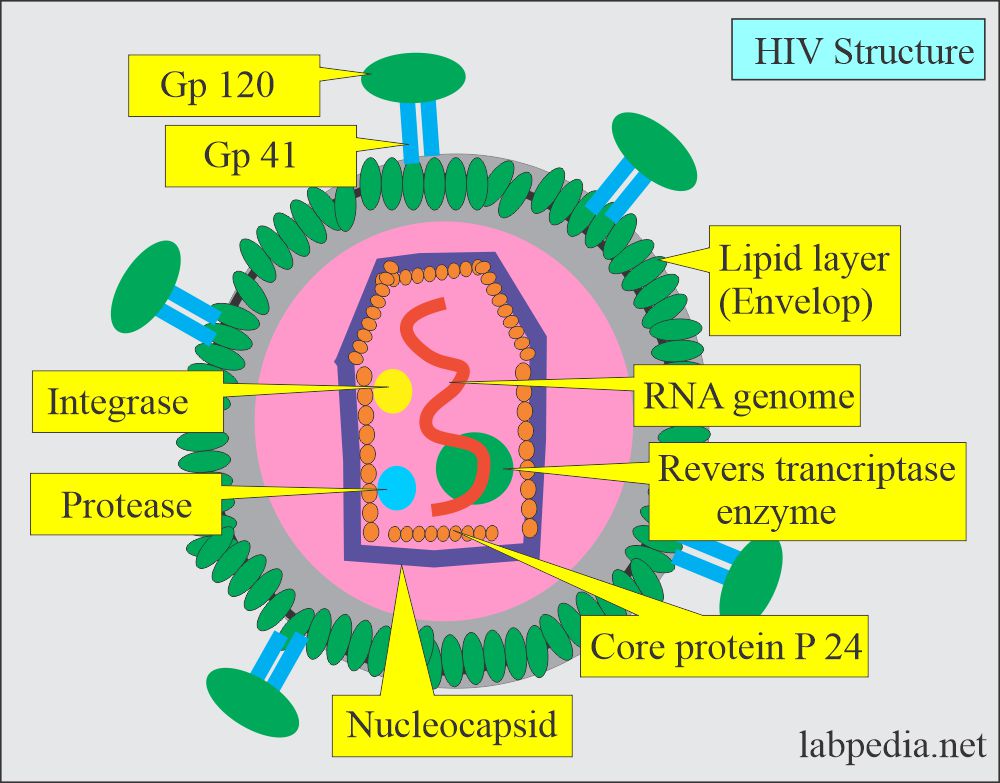
AIDS
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is an acronym for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
- The Human Immunodeficiency Virus is to blame.
- The patient’s immune system is methodically destroyed by AIDS, leaving them vulnerable to the simplest of infections.
PREVENTION OF DISEASES
Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are antimicrobial medications derived from other species, such as fungi and bacteria, that are used to treat illnesses caused by pathogens or dangerous germs.
- These antibiotics work in the following ways:
- Membrane Changes in Cells
- Antimetabolite Activity Inhibition
- Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibition
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibition
- Protein Synthesis
Preventative Actions
To avoid infection from many diseases, preventative steps can be implemented. The most typical measure is to maintain a clean environment.
Immunization
- The process of making a person immune or resistant to an infectious illness is known as immunization.
- Vaccines are the most prevalent kind of immunisation.