Bacterial and Viral STIs Study Guide
Introduction:
STIs, or sextually transmitted infections occur when an infected person passes their body fluids on to a healthy person. This level of intimacy usually occurs during sex – thus the name! STIs are often caused by bacteria or viruses. This guide explores common infections caused by these pathogens, and resulting STD symptoms.
Bacterial STIs
Common STDs caused by bacteria are gonorrhea, syphilis, and chlamydia.
1. Gonorrhea
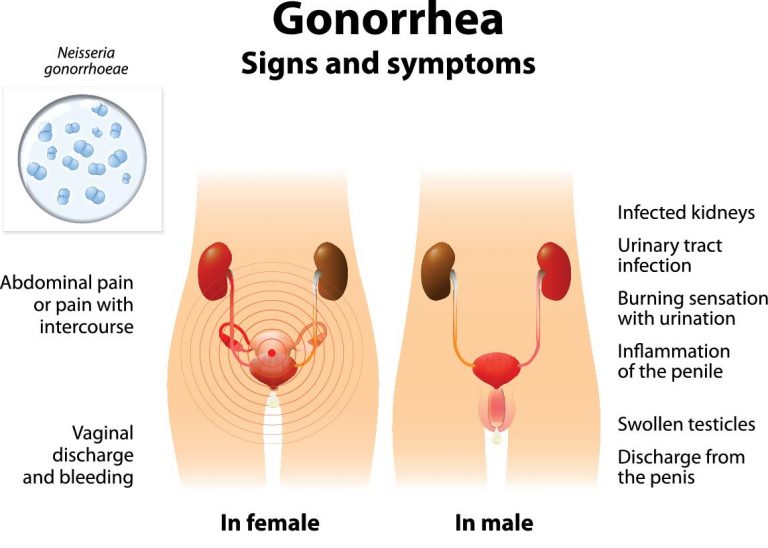
Gonorrhea, also known as ‘the claps’ , is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- It mostly infects the moist and warm areas of the body like the vagina, anus, urethra, eyes, throat and female reproductive tract, which includes the fallopian tubes, cervix, and uterus.
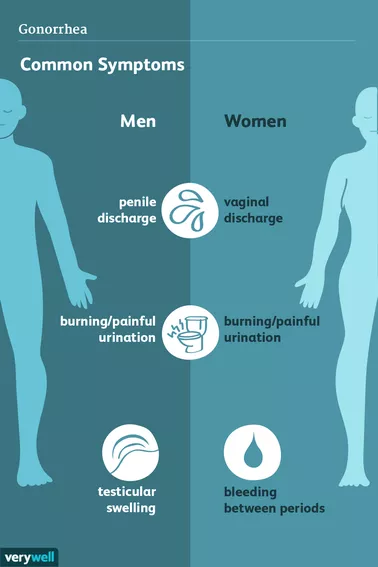
- Several people do not develop any symptoms, but some do have itching around the genitals, frequent urination, yellowish-white, brownish or greenish discharge from the vagina or penis, discomfort during sex and sore throat.
- Severe complications include Pelvic Inflammatory Disease( PID), infertility, infection of testicles, urethra or prostate gland when left untreated.
2. Syphilis
Syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum and spreads through direct contact with a syphilis sore on the infected person. It can also enter through mucous membranes and cuts on a healthy person. It usually spreads through vaginal, oral or anal sex with an infected partner.
Syphilis symptoms are sores, growths on genitals, vaginal discharges, sometimes painless ulcers, rash on the skin, bumps on the skin, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, redness, mouth ulcers, rash on soles and palms, inflammation in the rectum, weight loss and itching.
There are typically four stages in a syphilis infection:
- Primary: It starts as a painless sore (chancre) on the genitals or mouth, where the bacteria may have entered the body.
- Secondary: Upon healing, a rash develops across the body, and the person is highly contagious at this point
- Latent (Hidden): The latent stage is the hidden stage when it is undetected, and can range between a period of 5-20 years! Diagnosis of the disease at this stage is only possible through blood testing.
- Tertiary: The most severe of all stages, the infection may result in damage to the eyes, heart, brain or nerves. 15-30% of the untreated patients can suffer from the effects of the tertiary stage even decades after the primary infection.
Neurological diseases like meningitis, memory loss, mental illness, strokes, and others like heart diseases, blindness, deafness, neurosyphilis in the brain or spinal cord are dangerous outcomes of tertiary syphilis.
Treatment includes the use of antibiotics like penicillin, doxycycline, azithromycin, ceftriaxone, etc.
3. Chlamydia
-
Chlamydia is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and can infect men and women and is spread by unprotected and or anal or vaginal sex.
-
Symptoms in men typically start showing in one to three weeks after infection. They include yellow or green discharge from the penis, testicles, burning during urination, pain in the lower abdomen, anal pain, discharge, bleeding, sore throat, cough, or fever.
-
Symptoms in women include dyspareunia (pain during sex), bleeding between periods, vaginal discharge, cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), and PID with severe pelvic pain, fever, nausea, and infection of the Fallopian tubes.
-
Treatment includes antibiotics like azithromycin and doxycycline.
4. Viral STDs
These are caused by viruses like the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis B, Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV), and Human Papilloma Virus(HPV).
A. HIV causes AIDS or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
- The virus attacks the defense system of the human body, mainly the CD4 cells.
- The level of CD4 cells drops below 200cells/mm3 of blood which is why these patients always have one or more opportunistic infections and do not survive for more than one year if left without treatment.
- It is spread by direct contact during unprotected sex, exchange of body fluids, or sharing injection drug equipment.
- HIV cannot be cured, but Antiretroviral Therapy or ART can help patients live long, healthy lives.
- Typical symptoms include weight loss, diarrhea, cough, swollen lymph nodes. Severe diseases like tuberculosis, bacterial infections, cryptococcal meningitis, cancers like Kaposi’s sarcoma, and lymphomas occur in the worst case patients.
- HIV can also be transmitted from mother to child during delivery or breastfeeding.
- Diagnosis of HIV is done by the rapid diagnostic test, which detects antibodies produced to fight the virus.
- Typically, the antibodies are produced 28 days after the initial infection.
- It is advised to repeat the test after this window period.
- Prevention of HIV infection includes Anti-retroviral drugs (ARVs) like Atazanavir, Darunavir, Fosamprenavir, Indinavir, Nelfinavir, Ritonavir, etc. given in combinations of three or more types.
- They suppress the replication of HIV in the body, thus allowing the host immune system to build up and fight opportunistic infections.
B. HPV or Human Papilloma Virus
- It causes warts and cancers in humans and is transmitted sexually or by skin-to-skin contact.
- Different types of cancers of the penis, vagina, vulva, anus, oropharynx, and cervix are caused by HPV.
- Common warts appear as rough bumps on the hands and fingers, which may or may not be painful. Plantar warts can appear on the heels of the feet, which are grainy and hard painful growths. Flat warts can appear on any part of the body and are slightly raised, flat-topped lesions.
- Warts are highly contagious and can spread either by direct contact with a wart or any surface contaminated with a wart.
- Complications include lesions on the tongue, tonsils, nose, and larynx. HPV vaccines like Gardasil 9 approved by the US FDA are recommended for men and women. Treatment for warts includes Imiquimod, Podofilox, Sinecate his, Tricholoacetic acid, etc.
C. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
- HSV causes Genital Herpes and an STI characterized by painful sores or blisters fluid-filled.
- There are two types of HSV, HSV-1 which mainly causes cold sores, and HSV-2, which mainly causes genital herpes.
- Blisters on the penis, buttocks, anal area, scrotum, vagina, etc., are the common symptoms of the infection.
- They may get ulcerated and ooze fluid. Treatments like antiviral drugs can only heal the sore and reduce their number but cannot cure the viral infection.
D. Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
- HBV causes a serious liver infection, leading to liver failure, liver cancer, or cirrhosis.
- Symptoms include dark urine, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, pain in the abdomen, weakness, joint pain, jaundice, etc.
- Treatment includes drugs like Adefovir dipivoxil, Entecavir, Interferon alfa, Lamivudine, pegylated interferon, Telbivudine, etc.
Conclusion:
- Education and counseling will help decrease the spread of STI’s to a great extent by following guidelines such as having protected sex, avoiding intercourse with multiple partners, and disuse of recreational injecting drugs.
- Vaccines like the HPV vaccine, Hepatitis B vaccine can be taken to prevent such STIs.
FAQs:
1. What is the difference between bacterial and viral STIs?
Viral STI’s are caused by viruses like HIV, HPV, HBV, and HSV, while bacterial STIs are caused by bacteria like Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Treponema pallidum, and Chlamydia trachomatis.
2. What is a viral STI?
It is a Sexually Transmitted infection caused by a virus such as HIV, which causes AIDS.
3. What is the most common STI? Is it viral or bacterial?
Human Papilloma Virus or HPV is the most common virus which causes sexually transmitted infections.
4. What are the three major differences between viral and bacterial STIs?
Bacteria cause bacterial STIs, can be treated with antibiotics like Penicillin, azithromycin, etc. and can be cured while viral STI’s are caused by viruses like HIV, HPV, HSV, can be treated with antiviral drugs like Imiquimod, Entecavir, Ritonavir, Indinavir, etc. and cannot be cured.
5. What is the most common bacterial STI?
Chlamydia is the most common bacterial STI.
6. Is syphilis bacterial, viral, or parasitic?
It is a bacterial STI.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Bacterial and Viral STIs! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun!😎
Sources:
- Viral STIs. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.74/primary/lesson/viral-sexually-transmitted-infections-bio/. Accessed on 1 Dec 2021
- Bacterial STIs. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.73/primary/lesson/bacterial-sexually-transmitted-infections-bio/. Accessed on 1 Dec 2021
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sexually-transmitted-infections-(stis) Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.
- Diseases & Related Conditions. https://www.cdc.gov/std/general/default.htm. Accessed on 1 Dec 2021.
- Understanding Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs.). https://www.webmd.com/sex-relationships/understanding-stds-basics. Accessed on 1 Dec 2021