Digestive System Study Guide
Introduction
The human body needs the energy to carry out various tasks throughout the day, and this energy is obtained from food through digestion. The digestive system is a collection of different organs in the human body which work together to ensure that the body properly digests food. Let’s take a closer look at how this process is completed.
What is Digestion?
Digestion refers to turning solid food molecules into soluble food molecules that the blood can soak up. In simpler terms, it is a series of activities that begin from eating food and removing waste products.
What is the Digestive System?
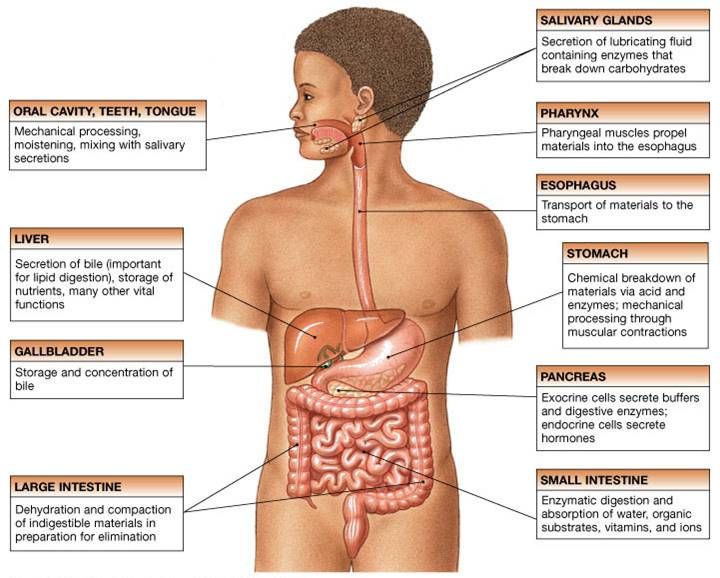
Digestive system definition refers to the combination of various body parts which work together as a unit to complete the process of digestion. The mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, esophagus, pharynx, stomach, pancreas, liver, gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine, and anus are the organs that make up the human digestive system. Each of these parts performs its functions in multiple ways, making digestion possible.
The Digestive System Functions
The digestive system functions include ingestion, propulsion, mechanical breakdown, chemical digestion, absorption, and elimination. These functions are based on the nature of work carried out by each organ and are as follows:
Mouth: Mouth is that part of the body where digestion begins. It consists of teeth, tongue, salivary glands, and other internal organs. It produces a lubricating material known as mucus with the help of a membrane called the oral mucosa. Mucus is a lubricant that helps to soften food molecules when food is being chewed.
Salivary glands: Salivary glands produce many kinds of liquids necessary to keep other parts like teeth and tongue healthy, but the main substance produced is saliva. Saliva is similar to mucus, but it initiates the digestion or breaking down of starchy substances and fats while softening food molecules.
Pharynx: The pharynx is divided into three parts, out of which two are a part of the digestive system. These parts are known as the oropharynx and laryngopharynx. The pharynx is responsible for transporting food from the mouth to the esophagus.
Esophagus: It is also described as a food pipe at times. The esophagus connects the mouth and the stomach through the pharynx, and the main function is to deliver food molecules to the stomach.
Stomach: The stomach is one of the most important organs in the human digestive system. It produces gastric acid, which along with other chemicals, turns food into a more soluble liquid known as chyme. Chyme enters the small intestine after more chemicals are mixed into it, and this process continues.
Liver: This organ has many functions, such as producing glucose and maintaining sugar levels in the blood, but its main function during digestion is breaking down carbohydrates. It also produces bile juice which is supposed to break down fats and produce fatty acids.
Gallbladder: The gallbladder is tasked with storing bile produced by the liver.
Pancreas: Pancreas helps in digestion, but its main aim is to control the sugar level in the bloodstream.
Small Intestine: It is a major part of the human digestive system. It extends up to 6 meters and is longer than the large intestine. Chyme produced by the stomach enters the small intestine, and the small intestine soaks up all the nutritional elements in the food. A major part of the process is completed within the small intestine.
Large Intestine: Digestion is almost complete before it reaches the large intestine. It is responsible for absorbing any remaining nutrients, water, and salts and producing and pushing feces towards the rectum for excretion. This is how the digestion process is completed.
Conclusion
- This process of digestion takes a few hours to complete.
- Most of the food is digested within the initial 10 hours or when the process begins.
- Defecation or excretion of human waste from the body takes up to 30 to 40 hours.
FAQs:
1. What are the 7 steps of digestion?
Ans. The 7 digestion steps are ingestion, propulsion, mechanical breakdown, chemical digestion, absorption, and elimination.
2. What is the digestive system and its function?
Ans. The digestive system is the combination of various body parts which work together as a unit to complete the process of digestion. Its function is to break down food molecules and absorb nutrients.
3. What are the 12 digestive systems?
Ans. Mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, esophagus, pharynx, stomach, pancreas, liver, gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine, and anus are the 12 parts of the digestive system.
4. What are the 5 main functions of the digestive system?
Ans. Intake of food, Secretion of enzymes, mixing of food, digestion of food, absorption of nutrients, and removal of wastes are the 5 main functions of the digestive system.
5. What are the 6 major functions of the digestive system?
Ingestion, propulsion, mechanical breakdown, chemical digestion, absorption, and elimination are the 6 major functions of the digestive system.
6. What are the two types of digestion?
The two types of digestion are mechanical and chemical digestion.
7. What are the five stages of the digestive system, and what does each one do?
I) Mouth – Ingestion of food II) Esophagus – passage of food III) Stomach – Digestion of foodIV) Small Intestine – Absorbing nutritional elements V) Large Intestine – Soaking up salts and removal of waste products.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about the Digestive System! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Digestive System. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7041-the-structure-and-function-of-the-digestive-system. Accessed 27 Nov, 2021.
- Digestive System. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/13.35/primary/lesson/digestion-bio/. Accessed 27 Nov, 2021.
- Digestive system. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/digestive-system. Accessed 27 Nov, 2021.