DNA and RNA Study Guide
INTRODUCTION
Have you ever wondered why an elephant invariably gives birth to an elephant baby and never to a different animal? Or why does a mango seed only grow into a mango plant and not some other? It occurs as a result of Inheritance (the process through which traits are passed down from one generation to the next). But who relays this information from the parent to the offspring? For transmitting any message, we need a messenger. In this case, the genetic materials, DNA, and RNA act as messengers to carry the information from one generation to another. Let’s learn more about these genetic materials in more detail.
TYPES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are the two primary forms of nucleic acids. DNA is the genetic substance present in all living species, from single-celled bacteria to multicellular animals.RNA, the other form of nucleic acid, is used mostly in protein production. In eukaryotes, DNA molecules never exit the nucleus and instead interact with the remainder of the cell through an intermediate. The messenger RNA serves as an intermediate in this process (mRNA).
NUCLEOTIDES
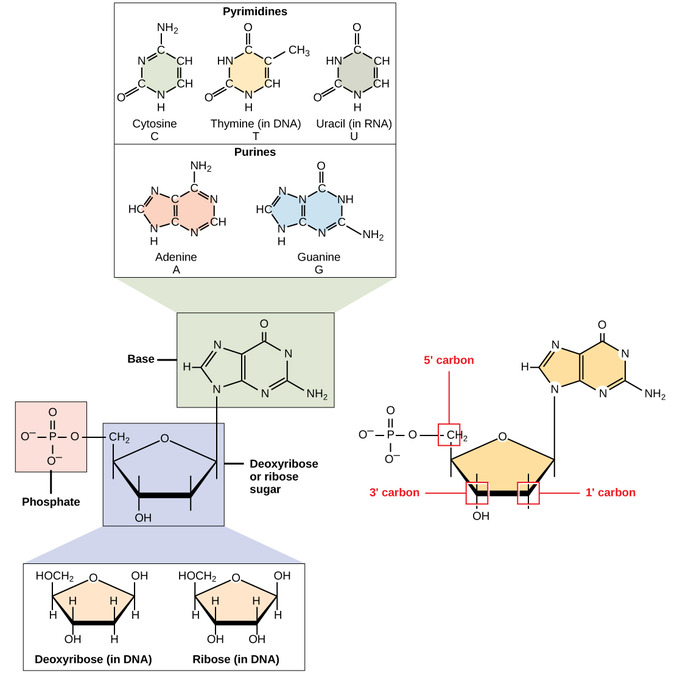
Nucleotides are monomers that makeup DNA and RNA. The nucleotides unite to produce a polynucleotide, such as DNA or RNA. Each nucleotide consists of three parts:
- a nitrogenous base
- a pentose (five-carbon) sugar
- a phosphate groups
In a nucleotide, every nitrogenous base is linked to a sugar molecule, which itself is linked to one or even more phosphate groups.
NITROGENOUS BASE
- The nitrogenous bases are organic compounds because they include both carbon and nitrogen.
- Purines are the amino acids adenine and guanine. Pyrimidines are the bases of cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
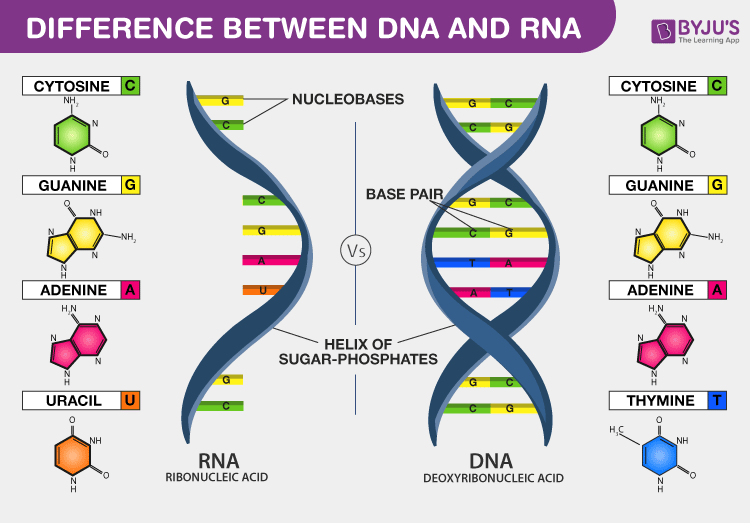
DNA:
- There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA- thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and adenine (A) that interlinked to form a ladder structure.
- The adenine is paired with thymine consisting of two hydrogen bonds while cytosine is paired with guanine consisting of three hydrogen bonds.
RNA:
- The nitrogenous bases in RNA don’t include thymine (T).
- Instead of thymine (T), it includes uracil (U) along with adenine (A), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
CONCLUSION:
- The nitrogenous bases present in DNA are thymine(T), guanine(G), cytosine(C), and adenine(A).
- Thymine is the nitrogenous base which not found in RNA.
- Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Uracil (U) are the bases present in RNA.
FAQs:
1. Which nitrogenous base is not present in RNA?
The thymine nitrogenous base is not present in RNA.
2. Name the bases present in RNA.
Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Uracil (U) are the bases present in RNA.
3. Which bases are present in DNA?
The nitrogenous bases present in DNA are thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and adenine (A). Thymine is the nitrogenous base which not found in RNA.
We hope you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about which base is found in DNA but not in RNA! Join our Discord community to get any questions you may have answered and to engage with other students just like you! Don’t forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms – we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
SOURCES:
- DNA and RNA. https://www.ck12.org/c/chemistry/dna-and-rna/lesson/DNA-and-RNA-CHEM/. Accessed 16 Feb, 2022.
- DNA and RNA. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introchem/chapter/dna-and-rna/. Accessed 16 Feb, 2022.